Cholesterol auxotrophy and intolerance to ezetimibe in mice with SREBP-2 deficiency in the intestine
- PMID: 28630260
- PMCID: PMC5625122
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M077610
Cholesterol auxotrophy and intolerance to ezetimibe in mice with SREBP-2 deficiency in the intestine
Abstract
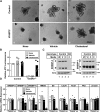
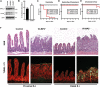
SREBP-2 activates transcription of all genes needed for cholesterol biosynthesis. To study SREBP-2 function in the intestine, we generated a mouse model (Vil-BP2-/- ) in which Cre recombinase ablates SREBP-2 in intestinal epithelia. Intestines of Vil-BP2-/- mice had reduced expression of genes required for sterol synthesis, in vivo sterol synthesis rates, and epithelial cholesterol contents. On a cholesterol-free diet, the mice displayed chronic enteropathy with histological abnormalities of both villi and crypts, growth restriction, and reduced survival that was prevented by supplementation of cholesterol in the diet. Likewise, SREBP-2-deficient enteroids required exogenous cholesterol for growth. Blockade of luminal cholesterol uptake into enterocytes with ezetimibe precipitated acutely lethal intestinal damage in Vil-BP2-/- mice, highlighting the critical interplay in the small intestine of sterol absorption via NPC1L1 and sterol synthesis via SREBP-2 in sustaining the intestinal mucosa. These data show that the small intestine requires SREBP-2 to drive cholesterol synthesis that sustains the intestinal epithelia when uptake of cholesterol from the gut lumen is not available, and provide a unique example of cholesterol auxotrophy expressed in an intact, adult mammal.
Keywords: Niemann-Pick C1-like 1; SREBP; Scap; cholesterol/biosynthesis; fatty acid/synthesis; organoid.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
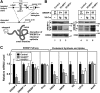
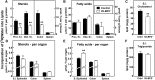
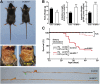
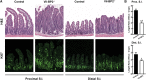
Comment in
-
The good side of cholesterol: a requirement for maintenance of intestinal integrity.J Lipid Res. 2017 Oct;58(10):1935-1936. doi: 10.1194/jlr.C079715. Epub 2017 Aug 2. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28768704 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Horton J. D., Shimomura I., Brown M. S., Hammer R. E., Goldstein J. L., and Shimano H.. 1998. Activation of cholesterol synthesis in preference to fatty acid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of transgenic mice overproducing sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2. J. Clin. Invest. 101: 2331–2339. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang T., Espenshade P. J., Wright M. E., Yabe D., Gong Y., Aebersold R., Goldstein J. L., and Brown M. S.. 2002. Crucial step in cholesterol homeostasis: sterols promote binding of SCAP to INSIG-1, a membrane protein that facilitates retention of SREBPs in ER. Cell. 110: 489–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

