Toll-like receptor pathway evolution in deuterostomes
- PMID: 28630328
- PMCID: PMC5502590
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1617722114
Toll-like receptor pathway evolution in deuterostomes
Abstract
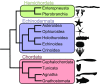
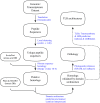
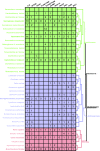
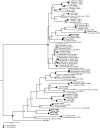
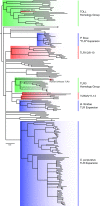
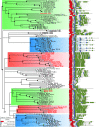
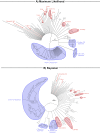
Animals have evolved an array of pattern-recognition receptor families essential for recognizing conserved molecular motifs characteristic of pathogenic microbes. One such family is the Toll-like receptors (TLRs). On pathogen binding, TLRs initiate specialized cytokine signaling catered to the class of invading pathogen. This signaling is pivotal for activating adaptive immunity in vertebrates, suggesting a close evolutionary relationship between innate and adaptive immune systems. Despite significant advances toward understanding TLR-facilitated immunity in vertebrates, knowledge of TLR pathway evolution in other deuterostomes is limited. By analyzing genomes and transcriptomes across 37 deuterostome taxa, we shed light on the evolution and diversity of TLR pathway signaling elements. Here, we show that the deuterostome ancestor possessed a molecular toolkit homologous to that which drives canonical MYD88-dependent TLR signaling in contemporary mammalian lineages. We also provide evidence that TLR3-facilitated antiviral signaling predates the origin of its TCAM1 dependence recognized in the vertebrates. SARM1, a negative regulator of TCAM1-dependent pathways in vertebrates, was also found to be present across all major deuterostome lineages despite the apparent absence of TCAM1 in invertebrate deuterostomes. Whether the presence of SARM1 is the result of its role in immunity regulation, neuron physiology, or a function of both is unclear. Additionally, Bayesian phylogenetic analyses corroborate several lineage-specific TLR gene expansions in urchins and cephalochordates. Importantly, our results underscore the need to sample across taxonomic groups to understand evolutionary patterns of the innate immunity foundation on which complex immunological novelties arose.
Keywords: Deuterostomia; Toll-like receptors; immunity evolution; innate immunity; molecular evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Beutler B. Innate immunity: An overview. Mol Immunol. 2004;40:845–859. - PubMed
-
- Rast JP, Litman GW. Towards understanding the evolutionary origins and early diversification of rearranging antigen receptors. Immunol Rev. 1998;166:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Pancer Z, et al. Somatic diversification of variable lymphocyte receptors in the agnathan sea lamprey. Nature. 2004;430:174–180. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Dzik JM. The ancestry and cumulative evolution of immune reactions. Acta Biochim Pol. 2010;57:443–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

