Association between HMGB1 and asthma: a literature review
- PMID: 28630596
- PMCID: PMC5471678
- DOI: 10.1186/s12948-017-0068-1
Association between HMGB1 and asthma: a literature review
Abstract
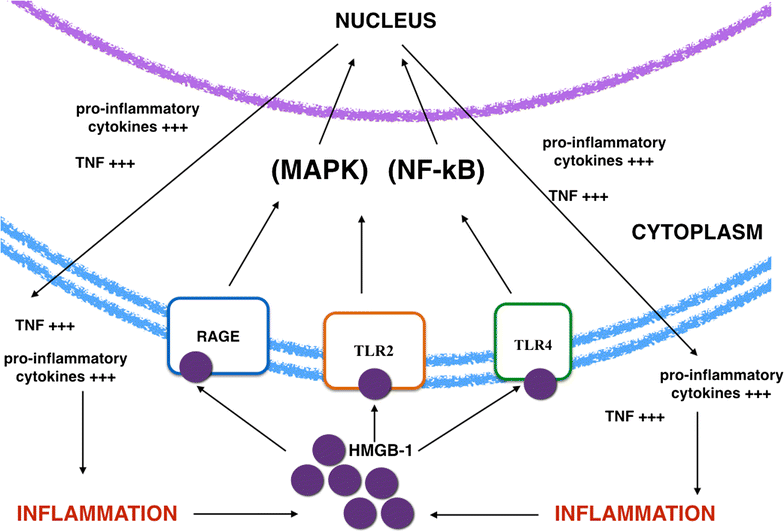
Background: Recently, some studies demonstrated that HMGB1, as proinflammatory mediator belonging to the alarmin family, has a key role in different acute and chronic immune disorders. Asthma is a complex disease characterised by recurrent and reversible airflow obstruction associated to airway hyper-responsiveness and airway inflammation.
Objective: This literature review aims to analyse advances on HMGB1 role, employment and potential diagnostic application in asthma.
Methods: We reviewed experimental studies that investigated the pathogenetic role of HMGB in bronchial airway hyper-responsiveness, inflammation and the correlation between HMGB1 level and asthma.
Results: A total of 19 studies assessing the association between HMGB1 and asthma were identified.
Conclusions: What emerged from this literature review was the confirmation of HMGB-1 involvement in diseases characterised by chronic inflammation, especially in pulmonary pathologies. Findings reported suggest a potential role of the alarmin in being a stadiation method and a marker of therapeutic efficacy; finally, inhibiting HMGB1 in humans in order to contrast inflammation should be the aim for future further studies.
Keywords: Alarmin; Allergy; Asthma; COPD; Cytokines; HMGB-1; Inflammation; RAGE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High mobility group box 1: a novel mediator of Th2-type response-induced airway inflammation of acute allergic asthma.J Thorac Dis. 2015 Oct;7(10):1732-41. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.10.18. J Thorac Dis. 2015. PMID: 26623095 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1-induced asthmatic airway inflammation through GRP75-mediated enhancement of ER-mitochondrial Ca2+ transfer and ROS increased.J Cell Biochem. 2018 May;119(5):4205-4215. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26653. Epub 2018 Jan 25. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29292841
-
Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in PM2.5-exposed asthmatic rats.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Jun 11;513(4):898-903. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.165. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31003767
-
Eosinophilic airway disorders.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Apr;27(2):128-33. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-939515. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16612763 Review.
-
HMGB1, an innate alarmin, plays a critical role in chronic inflammation of adipose tissue in obesity.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Oct 15;454:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.06.012. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28619625 Review.
Cited by
-
Progressive Lung Injury, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Rats Following Inhalation of Sulfur Mustard.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Dec 1;178(2):358-374. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa150. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33002157 Free PMC article.
-
Questioning Cause and Effect: Children with Severe Asthma Exhibit High Levels of Inflammatory Biomarkers Including Beta-Hexosaminidase, but Low Levels of Vitamin A and Immunoglobulins.Biomedicines. 2020 Oct 6;8(10):393. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100393. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33036262 Free PMC article.
-
Allergen-specific immunotherapy with Alutard SQ improves allergic inflammation in house-dust mites-induced allergic asthma rats through inactivation of the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Jan 31;15(1):77-89. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-715. Epub 2023 Jan 10. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 36794148 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin Protects Against Airway Remodeling Through the Modulation of Autophagy via HMGB1 Suppression in House Dust Mite-Induced Chronic Asthma.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Aug 12;14:3891-3904. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S322724. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34408470 Free PMC article.
-
Yanghepingchuan granule improves airway inflammation by inhibiting autophagy via miRNA328-3p/high mobility group box 1/Toll-like receptor 4 targeting of the pathway of signaling in rat models of asthma.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):6251-6264. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1262. Epub 2023 Nov 17. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 38090296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romani M, Rodman TC, Vidali G, Bustin M. Serological analysis of species specificity in the high mobility group chromosomal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:2918–2922. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources