The adult cavus foot
- PMID: 28630759
- PMCID: PMC5467681
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.160077
The adult cavus foot
Abstract
Cavovarus deformity can be classified by the severity of malalignment ranging from a subtle and flexible to a severe and fixed cavovarus deformity of the foot.In the mild cavovarus foot, careful clinical assessment is required to identify the deformity.Weight-bearing radiographs are necessary to indicate the apex of the deformity and quantify the correction required.Surgery is performed when conservative measures fail and various surgical procedures have been described, including a combination of soft-tissue releases, tendon transfers and osteotomies, all with the aim of achieving a plantigrade and balanced foot.Joint-sparing surgery is the best option in flexible cavovarus foot even in Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease (peroneal muscular atrophy).Arthrodesis is indicated in severe rigid cavus foot or in degenerative cases. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2017;2. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.160077. Originally published online at www.efortopenreviews.org.
Keywords: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; arthrodesis; cavus foot; osteotomy; tendon transfers.
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of Interest Statement: None.
Figures
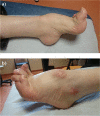




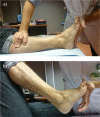



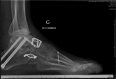
References
-
- Aminian A, Sangeorzan BJ. The anatomy of cavus foot deformity. Foot Ankle Clin 2008;13:191-198, v. - PubMed
-
- Nogueira MP, Farcetta F, Zuccon A. Cavus foot. Foot Ankle Clin 2015;20:645-656. - PubMed
-
- Di Fabio R, Lispi L, Santorelli FM, et al. Idiopathic pes cavus in adults is not associated with neurophysiological impairment in the lower limbs. Neurol Sci 2015;36:2287-2290. - PubMed
-
- Mestdagh H, Maynou C, Butin E, Durieu I. Pes cavus in adult. In: Bouysset M, ed. Bone and joint disorders of the foot and ankle. Berlin: Springer, 1998:173-182.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

