Development of a Branched Radio-Frequency Ion Trap for Electron Based Dissociation and Related Applications
- PMID: 28630811
- PMCID: PMC5469727
- DOI: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0058
Development of a Branched Radio-Frequency Ion Trap for Electron Based Dissociation and Related Applications
Abstract
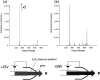
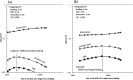
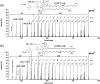
Collision-induced dissociation (CID) is the most common tool for molecular analysis in mass spectrometry to date. However, there are difficulties associated with many applications because CID does not provide sufficient information to permit details of the molecular structures to be elucidated, including post-translational-modifications in proteomics, as well as isomer differentiation in metabolomics and lipidomics. To face these challenges, we are developing fast electron-based dissociation devices using a novel radio-frequency ion trap (i.e., a branched ion trap). These devices have the ability to perform electron capture dissociation (ECD) on multiply protonated peptide/proteins; in addition, the electron impact excitation of ions from organics (EIEIO) can be also performed on singly charged molecules using such a device. In this article, we review the development of this technology, in particular on how reaction speed for EIEIO analyses on singly charged ions can be improved. We also overview some unique, recently reported applications in both lipidomics and glycoproteomics.
Keywords: ECD; EIEIO; lipidomics; proteomics.
Figures






References
-
- 1) J. M. Wells, S. A. McLuckey. Collision-induced dissociation (CID) of peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 402: 148–185, 2005. - PubMed
-
- 2) D. P. Little, J. P. Speir, M. W. Senko, P. B. O’Connor, F. W. McLafferty. Infrared multiphoton dissociation of large multiply charged ions for biomolecule sequencing. Anal. Chem. 66: 2809–2815, 1994. - PubMed
-
- 3) L. Sleno, D. A. Volmer. Ion activation methods for tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 39: 1091–1112, 2004. - PubMed
-
- 4) R. B. Cody, B. S. Freiser. Electron impact excitation of ions from organics: An alternative to collision induced dissociation. Anal. Chem. 51: 547–551, 1979.
-
- 5) R. A. Zubarev, N. L. Kelleher, F. W. McLafferty. Electron capture dissociation of multiply charged protein cations. A nonergodic process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120: 3265–3266, 1998.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

