Disruption of the Axonal Trafficking of Tyrosine Hydroxylase mRNA Impairs Catecholamine Biosynthesis in the Axons of Sympathetic Neurons
- PMID: 28630892
- PMCID: PMC5473686
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0385-16.2017
Disruption of the Axonal Trafficking of Tyrosine Hydroxylase mRNA Impairs Catecholamine Biosynthesis in the Axons of Sympathetic Neurons
Abstract
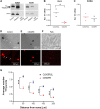
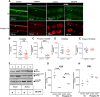
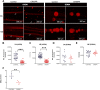
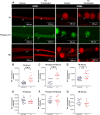
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is the enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of the catecholamine neurotransmitters. In a previous communication, evidence was provided that TH mRNA is trafficked to the axon, where it is locally translated. In addition, a 50-bp sequence element in the 3'untranslated region (3'UTR) of TH mRNA was identified that directs TH mRNA to distal axons (i.e., zip-code). In the present study, the hypothesis was tested that local translation of TH plays an important role in the biosynthesis of the catecholamine neurotransmitters in the axon and/or presynaptic nerve terminal. Toward this end, a targeted deletion of the axonal transport sequence element was developed, using the lentiviral delivery of the CRISPR/Cas9 system, and two guide RNA (gRNA) sequences flanking the 50-bp cis-acting regulatory element in rat superior cervical ganglion (SCG) neurons. Deletion of the axonal transport element reduced TH mRNA levels in the distal axons and reduced the axonal protein levels of TH and TH activity as measured by phosphorylation of SER40 in SCG neurons. Moreover, deletion of the zip-code diminished the axonal levels of dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE). Conversely, the local translation of exogenous TH mRNA in the distal axon enhanced TH levels and activity, and elevated axonal NE levels. Taken together, these results provide direct evidence to support the hypothesis that TH mRNA trafficking and local synthesis of TH play an important role in the synthesis of catecholamines in the axon and presynaptic terminal.
Keywords: 3’untranslated region; CRISPR Cas9; dopamine; local translation; mRNA trafficking; superior cervical ganglion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II mediates the axonal trafficking of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase mRNAs and enhances norepinephrine synthesis in primary sympathetic neurons.J Neurochem. 2019 Sep;150(6):666-677. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14821. Epub 2019 Jul 31. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 31306490 Free PMC article.
-
The local expression and trafficking of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA in the axons of sympathetic neurons.RNA. 2016 Jun;22(6):883-95. doi: 10.1261/rna.053272.115. Epub 2016 Apr 19. RNA. 2016. PMID: 27095027 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of axonal trafficking of cytochrome c oxidase IV mRNA.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010 Apr;43(4):422-30. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20144716 Free PMC article.
-
Genes for human catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes.Neurosci Res. 1991 Oct;12(2):315-45. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(91)90001-f. Neurosci Res. 1991. PMID: 1684650 Review.
-
Axonal mRNAs: functional significance in vertebrates and invertebrates.J Neurocytol. 2000 Nov-Dec;29(11-12):783-91. doi: 10.1023/a:1010987206526. J Neurocytol. 2000. PMID: 11466470 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Yiqi Huoxue Decoction on the Relationship between Remodeling of Cardiac Nerves and Macrophages after Myocardial Infarction in Rats.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Apr 7;2022:4441603. doi: 10.1155/2022/4441603. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 May 24;2023:9789870. doi: 10.1155/2023/9789870. PMID: 35432831 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
mRNP assembly, axonal transport, and local translation in neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res. 2018 Aug 15;1693(Pt A):75-91. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.018. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29462608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PM2.5 exposure contributes to anxiety and depression-like behaviors via phenyl-containing compounds interfering with dopamine receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 May 21;121(21):e2319595121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2319595121. Epub 2024 May 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38739786 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine release and dopamine-related gene expression in the amygdala are modulated by the gastrin-releasing peptide in opposite directions during stress-enhanced fear learning and extinction.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jun;30(6):2381-2394. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02843-8. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39580604 Free PMC article.
-
The Gastric Ganglion of Octopus vulgaris: Preliminary Characterization of Gene- and Putative Neurochemical-Complexity, and the Effect of Aggregata octopiana Digestive Tract Infection on Gene Expression.Front Physiol. 2017 Dec 15;8:1001. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01001. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29326594 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
