Ribosome rearrangements at the onset of translational bypassing
- PMID: 28630923
- PMCID: PMC5462505
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1700147
Ribosome rearrangements at the onset of translational bypassing
Abstract
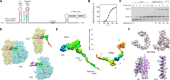
Bypassing is a recoding event that leads to the translation of two distal open reading frames into a single polypeptide chain. We present the structure of a translating ribosome stalled at the bypassing take-off site of gene 60 of bacteriophage T4. The nascent peptide in the exit tunnel anchors the P-site peptidyl-tRNAGly to the ribosome and locks an inactive conformation of the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). The mRNA forms a short dynamic hairpin in the decoding site. The ribosomal subunits adopt a rolling conformation in which the rotation of the small subunit around its long axis causes the opening of the A-site region. Together, PTC conformation and mRNA structure safeguard against premature termination and read-through of the stop codon and reconfigure the ribosome to a state poised for take-off and sliding along the noncoding mRNA gap.
Keywords: bypassing; recoding; ribosome; structure; translation.
Figures


References
-
- Baranov P. V., Atkins J. F., Yordanova M. M., Augmented genetic decoding: Global, local and temporal alterations of decoding processes and codon meaning. Nat. Rev. Genet. 16, 517–529 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Huang W. M., Ao S. Z., Casjens S., Orlandi R., Zeikus R., Weiss R., Winge D., Fang M., A persistent untranslated sequence within bacteriophage T4 DNA topoisomerase gene 60. Science 239, 1005–1012 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

