The Bacteroides fragilis pathogenicity island links virulence and strain competition
- PMID: 28632016
- PMCID: PMC5570422
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1290758
The Bacteroides fragilis pathogenicity island links virulence and strain competition
Abstract
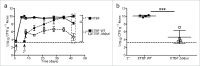
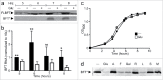
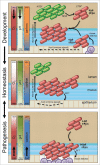
The mature microbiome is a stable ecosystem that resists perturbation despite constant host exposure to exogenous microbes. However, the microbial mechanisms determining microbiome development and composition are poorly understood. We recently demonstrated that a non-toxigenic B. fragilis (NTBF) strain restricts enteric colonization by an enterotoxigenic (ETBF) strain dependent on a type VI secretion system (T6SS). We show here that a second enterotoxigenic strain is competent to colonize, dependent on the Bacteroides fragilis pathogenicity island (BFPAI). Additional data showing complex environmental regulation of the Bacteroides fragilis toxin (BFT) suggest that virulence factors may be adapted to modify the colonic niche to provide a strain-specific colonization advantage. We conclude that more complex models of host-microbe-microbiome interactions are needed to investigate this hypothesis.
Keywords: bacteroides; competition; pathogenesis; secretion; toxin.
Figures

References
-
- Schaedler RW, Dubos R, Costello R. The development of the bacterial flora in the gastrointestinal tract of mice. J Exp Med 1965; 122:59-66; PMID:14325473; http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.122.1.59 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lax S, Smith DP, Hampton-Marcell J, Owens SM, Handley KM, Scott NM, Gibbons SM, Larsen P, Shogan BD, Weiss S, et al.. Longitudinal analysis of microbial interaction between humans and the indoor environment. Science 2014; 345:1048-52; PMID:25170151; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1254529 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gibbons SM, Schwartz T, Fouquier J, Mitchell M, Sangwan N, Gilbert JA, Kelley ST. Ecological succession and viability of human-associated microbiota on restroom surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 2015; 81:765-73; PMID:25398865; http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03117-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102:11070-5; PMID:16033867; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504978102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA, Affourtit JP, et al.. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009; 457:480-4; PMID:19043404; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature07540 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
