MiR-646 inhibited cell proliferation and EMT-induced metastasis by targeting FOXK1 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 28632723
- PMCID: PMC5558677
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.181
MiR-646 inhibited cell proliferation and EMT-induced metastasis by targeting FOXK1 in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: MiR-646 has been reported to be aberrantly expressed in human cancers. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of action of miR-646 in gastric cancer (GC) have not yet been investigated.
Methods: In vitro function of miR-646 in GC was evaluated using EdU assay, plate colony formation assay, and matrigel invasion assay. Real-time PCR or western blotting was performed to detect miR-646 and FOXK1 expressions. In vivo tumour growth and metastasis were conducted in nude mice.
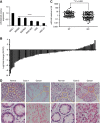
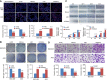
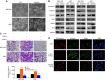
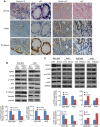
Results: MiR-646 expression was downregulated in GC tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. Low miR-646 expression is associated with malignant progression. Transient transfection of GC cells with miR-646 inhibited their growth and migration. Moreover, miR-646 influenced the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated proteins. TGF-β1 treatment significantly suppressed the expression of miR-646 and overexpression of this microRNA counteracted the influence of the TGF-β1-induced EMT phenotype. In terms of the underlying mechanism, miR-646 directly targeted FOXK1. In vivo, it inhibited the FOXK1-mediated proliferation and EMT-induced metastasis. Consistently, inverse correlations were also observed between the expression of miR-646 and FOXK1 in human GC tissue samples. Furthermore, miR-646 regulated Akt/mTOR signalling after FOXK1.
Conclusions: miR-646 inhibited GC cell proliferation and the EMT progression in GC cells by targeting FOXK1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA-cancer connection: the beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res 66: 7390–7394. - PubMed
-
- Dong P, Ihira K, Xiong Y, Watari H, Hanley SJ, Yamada T, Hosaka M, Kudo M, Yue J, Sakuragi N (2016) Reactivation of epigenetically silenced miR-124 reverses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inhibits invasion in endometrial cancer cells via the direct repression of IQGAP1 expression. Oncotarget 7: 20260–20270. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fu W, Tao T, Qi M, Wang L, Hu J, Li X, Xing N, Du R, Han B (2016) MicroRNA-132/212 upregulation inhibits TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting SOX4. Prostate 76: 1560–1570. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

