Androgen receptor mutations in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with apalutamide
- PMID: 28633425
- PMCID: PMC5834046
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdx283
Androgen receptor mutations in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with apalutamide
Abstract
Background: Mutations in the androgen receptor (AR) ligand-binding domain (LBD), such as F877L and T878A, have been associated with resistance to next-generation AR-directed therapies. ARN-509-001 was a phase I/II study that evaluated apalutamide activity in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Here, we evaluated the type and frequency of 11 relevant AR-LBD mutations in apalutamide-treated CRPC patients.
Patients and methods: Blood samples from men with nonmetastatic CRPC (nmCRPC) and metastatic CRPC (mCRPC) pre- or post-abiraterone acetate and prednisone (AAP) treatment (≥6 months' exposure) were evaluated at baseline and disease progression in trial ARN-509-001. Mutations were detected in circulating tumor DNA using a digital polymerase chain reaction-based method known as BEAMing (beads, emulsification, amplification and magnetics) (Sysmex Inostics' GmbH).
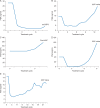
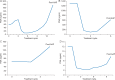
Results: Of the 97 total patients, 51 had nmCRPC, 25 had AAP-naïve mCRPC, and 21 had post-AAP mCRPC. Ninety-three were assessable for the mutation analysis at baseline and 82 of the 93 at progression. The overall frequency of detected AR mutations at baseline was 7/93 (7.5%) and at progression was 6/82 (7.3%). Three of the 82 (3.7%) mCRPC patients (2 AAP-naïve and 1 post-AAP) acquired AR F877L during apalutamide treatment. At baseline, 3 of the 93 (3.2%) post-AAP patients had detectable AR T878A, which was lost after apalutamide treatment in 1 patient who continued apalutamide treatment for 12 months.
Conclusions: The overall frequency of detected mutations at baseline (7.5%) and progression (7.3%) using the sensitive BEAMing assay was low, suggesting that, based on this assay, AR-LBD mutations such as F877L and T878A are not common contributors to de novo or acquired resistance to apalutamide.
Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT01171898.
Keywords: ARN-509; androgen receptor; apalutamide; castration-resistant prostate cancer; mutations.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

