Microsphere-Based Scaffolds in Regenerative Engineering
- PMID: 28633566
- PMCID: PMC11610505
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044712
Microsphere-Based Scaffolds in Regenerative Engineering
Abstract
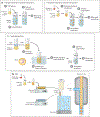
Microspheres have long been used in drug delivery applications because of their controlled release capabilities. They have increasingly served as the fundamental building block for fabricating scaffolds for regenerative engineering because of their ability to provide a porous network, offer high-resolution control over spatial organization, and deliver growth factors/drugs and/or nanophase materials. Because they provide physicochemical gradients via spatiotemporal release of bioactive factors and nanophase ceramics, microspheres are a desirable tool for engineering complex tissues and biological interfaces. In this review we describe various methods for microsphere fabrication and sintering, and elucidate how these methods influence both micro- and macroscopic scaffold properties, with a special focus on the nature of sintering. Furthermore, we review key applications of microsphere-based scaffolds in regenerating various tissues. We hope to inspire researchers to join a growing community of investigators using microspheres as tissue engineering scaffolds so that their full potential in regenerative engineering may be realized.
Keywords: microsphere fabrication; microsphere incorporating scaffolds; microsphere sintering; microsphere-based scaffolds; microspheres.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
C.J.B. is a shareholder and cofounder of Orbis Biosciences. The other authors are not aware of any affiliations, memberships, funding, or financial holdings that might be perceived as affecting the objectivity of this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microsphere-based seamless scaffolds containing macroscopic gradients of encapsulated factors for tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008 Dec;14(4):299-309. doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2008.0167. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008. PMID: 18795865 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional macroscopic scaffolds with a gradient in stiffness for functional regeneration of interfacial tissues.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010 Sep 1;94(3):870-6. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.32765. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010. PMID: 20336753 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive glass-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2012;126:195-226. doi: 10.1007/10_2011_106. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22085919 Review.
-
Progress in microsphere-based scaffolds in bone/cartilage tissue engineering.Biomed Mater. 2023 Oct 6;18(6). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/acfd78. Biomed Mater. 2023. PMID: 37751762 Review.
-
Polymer-coated microparticle scaffolds engineered for potential use in musculoskeletal tissue regeneration.Biomed Mater. 2021 May 24;16(4):10.1088/1748-605X/abfdfd. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/abfdfd. Biomed Mater. 2021. PMID: 33946056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanical Cues Affect Migration and Invasion of Cells From Three Different Directions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 17;8:583226. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.583226. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33043017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scalable preparation of osteogenic micro-tissues derived from hESC-derived immunity-and-matrix-regulatory cells within porous microcarriers in suspension culture.Cell Prolif. 2023 May;56(5):e13466. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13466. Epub 2023 May 17. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 37199065 Free PMC article.
-
From the microspheres to scaffolds: advances in polymer microsphere scaffolds for bone regeneration applications.Biomater Transl. 2024 Sep 28;5(3):274-299. doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2024.03.005. eCollection 2024. Biomater Transl. 2024. PMID: 39734699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regenerative engineering: a review of recent advances and future directions.Regen Med. 2021 May;16(5):495-512. doi: 10.2217/rme-2021-0016. Epub 2021 May 25. Regen Med. 2021. PMID: 34030463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Micro-/Nanoparticle Hybrid Hydrogel Platform on the Treatment of Articular Cartilage-Related Diseases.Gels. 2021 Sep 27;7(4):155. doi: 10.3390/gels7040155. Gels. 2021. PMID: 34698122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ravichandran R, Sundarrajan S, Venugopal JR, Mukherjee S, Ramakrishna S. 2012. Advances in polymeric systems for tissue engineering and biomedical applications. Macromol. Biosci. 12:286–311 - PubMed
-
- Subia B, Kundu J, Kundu S. 2010. Biomaterial Scaffold Fabrication Techniques for Potential Tissue Engineering Applications. www.intechopen.com: INTECH
-
- Shi X, Su K, Varshney RR, Wang Y, Wang D-A. 2011. Sintered microsphere scaffolds for controlled release and tissue engineering. Pharm. Res. 28:1224–28 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

