Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Human Diseases
- PMID: 28634583
- PMCID: PMC5459888
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00038
Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Human Diseases
Abstract
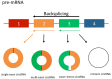
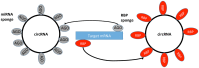
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are currently classed as non-coding RNA (ncRNA) that, unlike linear RNAs, form covalently closed continuous loops and act as gene regulators in mammals. They were originally thought to represent errors in splicing and considered to be of low abundance, however, there is now an increased appreciation of their important function in gene regulation. circRNAs are differentially generated by backsplicing of exons or from lariat introns. Unlike linear RNA, the 3' and 5' ends normally present in an RNA molecule have been joined together by covalent bonds leading to circularization. Interestingly, they have been found to be abundant, evolutionally conserved and relatively stable in the cytoplasm. These features confer numerous potential functions to circRNAs, such as acting as miRNA sponges, or binding to RNA-associated proteins to form RNA-protein complexes that regulate gene transcription. It has been proposed that circRNA regulate gene expression at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level by interacting with miRNAs and that circRNAs may have a role in regulating miRNA function in cancer initiation and progression. circRNAs appear to be more often downregulated in tumor tissue compared to normal tissue and this may be due to (i) errors in the back-splice machinery in malignant tissues, (ii) degradation of circRNAs by deregulated miRNAs in tumor tissue, or (iii) increasing cell proliferation leading to a reduction of circRNAs. circRNAs have been identified in exosomes and more recently, chromosomal translocations in cancer have been shown to generate aberrant fusion-circRNAs associated with resistance to drug treatments. In addition, though originally thought to be non-coding, there is now increasing evidence to suggest that select circRNAs can be translated into functional proteins. Although much remains to be elucidated about circRNA biology and mechanisms of gene regulation, these ncRNAs are quickly emerging as potential disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets in cancer.
Keywords: cancer; circRNAs; diseases; miRNA; non-coding RNA.
Figures
References
-
- Bachmayr-Heyda A., Reiner A. T., Auer K., Sukhbaatar N., Aust S., Bachleitner-Hofmann T., et al. (2015). Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation - exemplified with colorectal and ovarian cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Sci. Rep. 5:8057. 10.1038/srep08057 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

