Quantifiable predictive features define epitope-specific T cell receptor repertoires
- PMID: 28636592
- PMCID: PMC5616171
- DOI: 10.1038/nature22383
Quantifiable predictive features define epitope-specific T cell receptor repertoires
Abstract
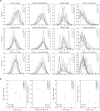
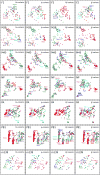
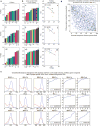
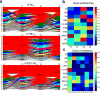
T cells are defined by a heterodimeric surface receptor, the T cell receptor (TCR), that mediates recognition of pathogen-associated epitopes through interactions with peptide and major histocompatibility complexes (pMHCs). TCRs are generated by genomic rearrangement of the germline TCR locus, a process termed V(D)J recombination, that has the potential to generate marked diversity of TCRs (estimated to range from 1015 (ref. 1) to as high as 1061 (ref. 2) possible receptors). Despite this potential diversity, TCRs from T cells that recognize the same pMHC epitope often share conserved sequence features, suggesting that it may be possible to predictively model epitope specificity. Here we report the in-depth characterization of ten epitope-specific TCR repertoires of CD8+ T cells from mice and humans, representing over 4,600 in-frame single-cell-derived TCRαβ sequence pairs from 110 subjects. We developed analytical tools to characterize these epitope-specific repertoires: a distance measure on the space of TCRs that permits clustering and visualization, a robust repertoire diversity metric that accommodates the low number of paired public receptors observed when compared to single-chain analyses, and a distance-based classifier that can assign previously unobserved TCRs to characterized repertoires with robust sensitivity and specificity. Our analyses demonstrate that each epitope-specific repertoire contains a clustered group of receptors that share core sequence similarities, together with a dispersed set of diverse 'outlier' sequences. By identifying shared motifs in core sequences, we were able to highlight key conserved residues driving essential elements of TCR recognition. These analyses provide insights into the generalizable, underlying features of epitope-specific repertoires and adaptive immune recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of this article at
Figures






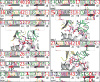

Comment in
-
Immunology: The patterns of T-cell target recognition.Nature. 2017 Jul 6;547(7661):36-38. doi: 10.1038/nature23091. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28636588 No abstract available.
-
Interpreting the T-cell receptor repertoire.Nat Biotechnol. 2017 Sep 11;35(9):829-830. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3957. Nat Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28898208 No abstract available.
References
-
- Davis MM, Bjorkman PJ. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988;334:395–402. - PubMed
-
- Mora T, Walczak AM. Quantifying lymphocyte receptor diversity. bioRxiv. 2016;046870 doi: 10.1101/046870. - DOI
-
- Alamyar E, Giudicelli V, Li S, Duroux P. IMGT/HighV-QUEST the IMGT® web portal for immunoglobulin (IG) or antibody and T cell receptor (TR) analysis from NGS high throughput and deep sequencing. Immunomethods. 2012
-
- Bolotin DA, et al. MiTCR: software for T-cell receptor sequencing data analysis. Nat Methods. 2013;10:813–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

