Practice- vs Physician-Level Variation in Use of Active Surveillance for Men With Low-Risk Prostate Cancer: Implications for Collaborative Quality Improvement
- PMID: 28636713
- PMCID: PMC5831460
- DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1586
Practice- vs Physician-Level Variation in Use of Active Surveillance for Men With Low-Risk Prostate Cancer: Implications for Collaborative Quality Improvement
Abstract
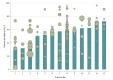
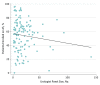
This study examines the proportion of men treated primarily with active surveillance across practices and among urologists in the Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cooperberg MR, Carroll PR. Trends in management for patients with localized prostate cancer, 1990-2013. JAMA. 2015;314(1):80-82. - PubMed
-
- Womble PR, Montie JE, Ye Z, Linsell SM, Lane BR, Miller DC; Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative . Contemporary use of initial active surveillance among men in Michigan with low-risk prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2015;67(1):44-50. - PubMed
-
- Cher ML, Dhir A, Auffenberg GB, et al. ; Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative . Appropriateness criteria for active surveillance of prostate cancer. J Urol. 2017;197(1):67-74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

