Incidence of thyroid dysfunction in an Iranian adult population: the predictor role of thyroid autoantibodies: results from a prospective population-based cohort study
- PMID: 28637498
- PMCID: PMC5480126
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-017-0260-2
Incidence of thyroid dysfunction in an Iranian adult population: the predictor role of thyroid autoantibodies: results from a prospective population-based cohort study
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of thyroid dysfunction is high in Isfahan, an area of iodine sufficient in Iran. The aim of this study is to investigate the incidence of thyroid dysfunctions in adults of metropolitan Isfahan and to determine the role of thyroid autoantibodies.
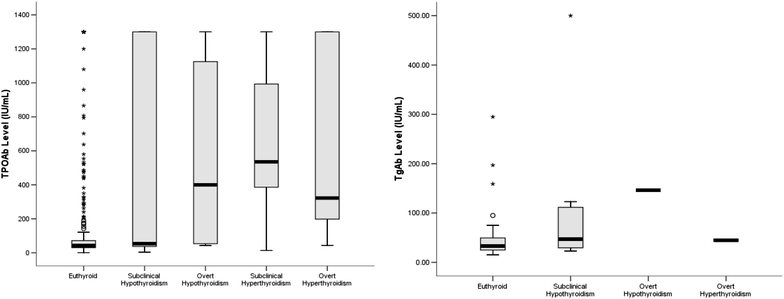
Methods: In a population-based cohort study in 2006-2011, we measured TSH, T4, T3, thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb), and thyroglobulin antibody (TgAb) in 618 out of 2254 people who were euthyroid in 2006. The incidence rates per 1000 person-year (pr) were calculated. The odds ratio (OR), relative risk (RR), and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were calculated based on logistic regression to quantify the potential predictors of thyroid dysfunction. The receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) analysis along with area under the curve (AUC) was used to determine the optimal cutoff values for baseline TPOAb and TgAb as predictors of thyroid dysfunction.
Results: Within a 6-year follow-up, the incidence rate of hypothyroidism was 3.3 in women and 2.1 in men while the incidence rate of hyperthyroidism was 3.8 in women and none in men per 1000 (person-year). A cutoff value of TPOAb at 38 IU/mL was obtained to differentiate the patients with hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, with specificity of 0.75 and sensitivity of 0.76, and AUC (CI 95%) of 0.882 (0.743-1.02), P = 0.01 and 0.817 (0.600-1.035) P = 0.033, respectively. There is a statistically significant association of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism with positive TPOAb [RR (CI 95%): 1.99 (1.27-3.13) and 2.20 (1.23-3.95), respectively].
Conclusions: The incidence rate of thyroid dysfunction is high in Isfahan, and higher TPOAb concentration is its strong predictor.
Keywords: Hyperthyroidism; Hypothyroidism; Incidence; Iran; TPO antibodies; Thyroid autoantibodies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Term Variations of Antithyroperoxidase Antibodies and its Clinical Significance.Horm Metab Res. 2019 Jun;51(6):347-352. doi: 10.1055/a-0887-6213. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Horm Metab Res. 2019. PMID: 31207655
-
The TSH levels and risk of hypothyroidism: Results from a population based prospective cohort study in an Iranian adult's population.Eur J Intern Med. 2017 Jun;41:55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2016.12.019. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Eur J Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28111157
-
Thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin auto-antibodies in patients with newly diagnosed overt hypothyroidism.Autoimmunity. 2006 Sep;39(6):497-503. doi: 10.1080/08916930600907913. Autoimmunity. 2006. PMID: 17060029
-
[Antibodies against thyroid gland peroxidase and thyroglobulin in various thyroid diseases].Orv Hetil. 1994 Jul 17;135(29):1579-84. Orv Hetil. 1994. PMID: 8058301 Review. Hungarian.
-
Why measure thyroglobulin autoantibodies rather than thyroid peroxidase autoantibodies?Thyroid. 2004 Jul;14(7):510-20. doi: 10.1089/1050725041517057. Thyroid. 2004. PMID: 15307940 Review.
Cited by
-
Unexpected high frequency of anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies in Golestan province, Iran.Caspian J Intern Med. 2023 Spring;14(2):371-375. doi: 10.22088/cjim.14.2.371. Caspian J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37223294 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Association between Gastric Cancer Mortality and Goiter in Sardinia.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Jan 1;22(1):105-110. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.1.105. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33507686 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between Mitochondrial Metabolism and Nasal Mucociliary Function as a Surrogate Method to Diagnose Thyroid Dysfunction: Insights from a Population-Based Study.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 20;12(8):1897. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081897. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200361 Free PMC article.
-
Association of miR-499 Polymorphism and Its Regulatory Networks with Hashimoto Thyroiditis Susceptibility: A Population-Based Case-Control Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 18;22(18):10094. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810094. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576267 Free PMC article.
-
A Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Reference Range: Iranian Thyroid Cohort study.Acta Biomed. 2021 Nov 3;92(5):e2021283. doi: 10.23750/abm.v92i5.9643. Acta Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34738602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aminorroaya A, et al. The prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in an iodine-sufficient area in Iran. Arch Iran Med. 2009;12(3):262–270. - PubMed
-
- Leese GP, et al. Increasing prevalence and incidence of thyroid disease in Tayside, Scotland: the thyroid epidemiology audit and research study (TEARS) Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2008;68(2):311–316. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials