Determination of Crucial Immunogenic Epitopes in Major Peanut Allergy Protein, Ara h2, via Novel Nanoallergen Platform
- PMID: 28638052
- PMCID: PMC5479826
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04268-6
Determination of Crucial Immunogenic Epitopes in Major Peanut Allergy Protein, Ara h2, via Novel Nanoallergen Platform
Abstract
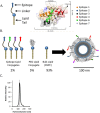
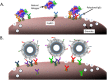
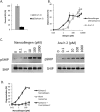
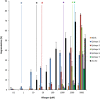
Current methods for detection and diagnosis of allergies do not provide epitope specific immunogenic information and hence lack critical information that could aid in the prediction of clinical responses. To address this issue, we developed a nanoparticle based platform, called nanoallergens that enable multivalent display of potential allergy epitopes for determining the immunogenicity of each IgE binding epitope. By synthesizing nanoallergens that present various epitopes from the major peanut allergen, Ara h2, we directly determined the immunogenicity of each epitope, alone and in combination with other epitopes, using patient sera. This information provided insights on which epitopes are most critical for physiological responses to Ara h2 and revealed the importance of both high and low affinity epitopes for allergic responses. We anticipate the nanoallergen platform to be used to provide information regarding allergic reactions and therefore potentially aid in more accurate diagnosis and design of personalized treatment options.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
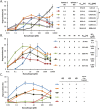
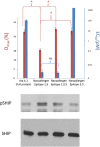
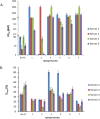
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

