Neurologically Potent Molecules from Crataegus oxyacantha; Isolation, Anticholinesterase Inhibition, and Molecular Docking
- PMID: 28638340
- PMCID: PMC5461367
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00327
Neurologically Potent Molecules from Crataegus oxyacantha; Isolation, Anticholinesterase Inhibition, and Molecular Docking
Abstract
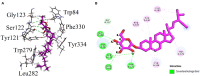
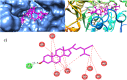
Crataegus oxyacantha is an important herbal supplement and famous for its antioxidant potential. The antioxidant in combination with anticholinesterase activity can be considered as an important target in the management of Alzheimer's disease. The compounds isolated from C. oxyacantha were evaluated for cholinesterases inhibitory activity using Ellman's assay with Galantamine as standard drug. Total of nine (1-9) compounds were isolated. Compounds 1 and 2 were isolated for the first time from natural source. Important natural products like β-Sitosterol-3-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside (3), lupeol (4), β-sitosterol (5), betulin (6), betulinic acid (7), oleanolic acid (8), and chrysin (9) have also been isolated from C. oxyacantha. Overall, all the compounds exhibited an overwhelming acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition potential in the range 5.22-44.47 μM. The compound 3 was prominent AChE inhibitor with IC50 value of 5.22 μM. Likewise, all the compounds were also potent in butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitions with IC50s of up to 0.55-15.36 μM. All the compounds, except 3, were selective toward BChE. Mechanism of the inhibition of both the enzymes were further studied by docking procedures using Genetic Optimization for Ligand Docking suit v5.4.1. Furthermore, computational blood brain barrier prediction of the isolated compounds suggest that these are BBB+.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Crataegus oxyacantha; acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition; butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibition; molecular docking; pharmacokinetic properties.
Figures



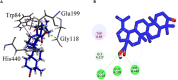
References
-
- Ayaz M., Junaid M., Ahmed J., Ullah F., Sadiq A., Ahmad S., et al. (2014). Phenolic contents, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of crude extract, subsequent fractions and crude saponins from Polygonum hydropiper L. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 14:145 10.1186/1472-6882-14-145 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayaz M., Junaid M., Ullah F., Sadiq A., Khan M. A., Ahmad W., et al. (2015). Comparative chemical profiling, cholinesterase inhibitions and anti-radicals properties of essential oils from Polygonum hydropiper L: a PRELIMINARY anti-Alzheimer’s study. Lipids Health Dis. 14 141 10.1186/s12944-015-0145-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

