Cost-effectiveness of Eplerenone in treatment of cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review
- PMID: 28638811
- PMCID: PMC5473015
- DOI: 10.18869/mjiri.31.4
Cost-effectiveness of Eplerenone in treatment of cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review
Abstract
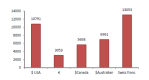
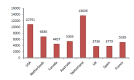
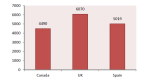
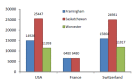
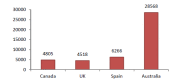
Background: No clear evidence is available on the cost-effectiveness of eplerenone in treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Thus, the present study aimed at systematically reviewing studies that have investigated this issue. Methods: This systematic review study was conducted in 2016. The required information were collected using key Mesh words from the following databases: Google scholar, PubMed, Science Direct, MagIran, SID, Scopus, and handsearching journals and the references of the selected articles. The quality of the selected articles was assessed by the Drummond's checklist. Results: Nine articles were included from 296 articles found in the literature review. The selected studies have been conducted in 8 countries (The United States, Britain, Australia, Switzerland, France, Spain, the Netherlands, and Canada). In general, the costeffectiveness of eplerenone was investigated in 31 757 patients with cardiovascular diseases. The average of quality-adjusted life years (QALY) in studies with nonmodeling approach was equal to 0.0908 in Framingham approach, 0.0595 in Saskatchewan approach, and 0.1309 in Worcester approach. The overall average cost of treating cardiovascular diseases with eplerenone was equal to US$6694 in 1 year. Cost per additional (QALY) was estimated to be US$9478. Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was high in the United States compared to European countries. The Average quality of articles was estimated to be 7.4 from 10. Conclusions: Based on the results of the studies reviewed in the present study, it seems that eplerenone has acceptable costeffectiveness compared with current treatments, placebo, and similar drugs.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Disease; Cost-effectiveness; Eplerenone; Systematic Review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost effectiveness of eplerenone in patients with heart failure after acute myocardial infarction who were taking both ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers: subanalysis of the EPHESUS.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10(1):55-63. doi: 10.2165/11319940-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20104935
-
Cost-effectiveness of eplerenone compared with placebo in patients with myocardial infarction complicated by left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure.Circulation. 2005 Mar 8;111(9):1106-13. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000157146.86758.BC. Epub 2005 Feb 21. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15723981 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness of eplerenone in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction--an analysis of the EPHESUS study from a Swiss perspective.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2006 Jun;20(3):193-204. doi: 10.1007/s10557-006-8282-y. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2006. PMID: 16775667 Clinical Trial.
-
The Cost-Effectiveness and Cost-Utility of Statin Drug for the Treatment of Patients with Cardiovascular Disease, A Systematic Review.Int J Prev Med. 2021 May 15;12:39. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_125_20. eCollection 2021. Int J Prev Med. 2021. PMID: 34249288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality Assessment of Published Articles in Iranian Journals Related to Economic Evaluation in Health Care Programs Based on Drummond's Checklist: A Narrative Review.Iran J Med Sci. 2017 Sep;42(5):427-436. Iran J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29234174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chung M, Asher R, Yamada D, Eagle K, Podrid P, Kowey P. Arrhythmias after cardiac and non-cardiac surgery In Cardiac arrhythmia 2nded Philadelphia. Lippincott Williams Wilkins. 2001:631–8.
-
- Yan JH, Pan L, Zhang XM, Sun CX, Cui GH. Lack of efficacy of Tai Chi in improving quality of life in breast cancer survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(8):3715–20. - PubMed
-
- Reinhardt UE, Cheng T-m. The world health report 2000-Health systems: improving performance. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2000;78(8):1064.
-
- Nagavi M. The pattern of mortality within 23 provinces of Iran in 2003, Tehran - IRAN: Health Deputy, Iranian Ministry of Health, 2005.
-
- Azami S, Tabrizi J, Abdollahi L, Yari Fard Kh, Daemi A, Sadati M. et al. Knowledge and Attitude of Top Managers toward Accreditation; in Tabriz and Ardabil Teaching Hospitals. Health. 2012;3(2):7–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources