Validation of a Novel Immunoline Assay for Patient Stratification according to Virulence of the Infecting Helicobacter pylori Strain and Eradication Status
- PMID: 28638837
- PMCID: PMC5468576
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8394593
Validation of a Novel Immunoline Assay for Patient Stratification according to Virulence of the Infecting Helicobacter pylori Strain and Eradication Status
Abstract
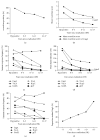
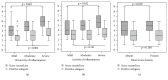
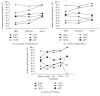
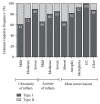
Helicobacter pylori infection shows a worldwide prevalence of around 50%. However, only a minority of infected individuals develop clinical symptoms or diseases. The presence of H. pylori virulence factors, such as CagA and VacA, has been associated with disease development, but assessment of virulence factor presence requires gastric biopsies. Here, we evaluate the H. pylori recomLine test for risk stratification of infected patients by comparing the test score and immune recognition of type I or type II strains defined by the virulence factors CagA, VacA, GroEL, UreA, HcpC, and gGT with patient's disease status according to histology. Moreover, the immune responses of eradicated individuals from two different populations were analysed. Their immune response frequencies and intensities against all antigens except CagA declined below the detection limit. CagA was particularly long lasting in both independent populations. An isolated CagA band often represents past eradication with a likelihood of 88.7%. In addition, a high recomLine score was significantly associated with high-grade gastritis, atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, and gastric cancer. Thus, the recomLine is a sensitive and specific noninvasive test for detecting serum responses against H. pylori in actively infected and eradicated individuals. Moreover, it allows stratifying patients according to their disease state.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Genotyping of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors vacA and cagA in individuals from two regions in Colombia with opposing risk for gastric cancer].Biomedica. 2014 Oct-Dec;34(4):567-73. doi: 10.1590/S0120-41572014000400009. Biomedica. 2014. PMID: 25504245 Spanish.
-
A novel line immunoassay based on recombinant virulence factors enables highly specific and sensitive serologic diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013 Nov;20(11):1703-10. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00433-13. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24006137 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of CagA-specific antibodies related to CagA status of Helicobacter pylori isolates using immunofluorescence test and PCR.Infection. 2001 May-Jun;29(3):154-8. doi: 10.1007/s15010-001-1102-1. Infection. 2001. PMID: 11440386
-
Epidemiology and role of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors in gastric cancer carcinogenesis.APMIS. 2020 Feb;128(2):150-161. doi: 10.1111/apm.13034. APMIS. 2020. PMID: 32352605 Review.
-
The Role of Helicobacter Pylori Infection in the Development of Gastric Cancer - Review of the Literature.Chirurgia (Bucur). 2024 Apr;119(eCollection):1-10. doi: 10.21614/chirurgia.119.eC.2971. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2024. PMID: 38657111 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of Helicobacter Pylori infection by invasive and non-invasive techniques in patients with gastrointestinal diseases from Iraq: A validation study.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 23;16(8):e0256393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256393. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34424925 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori serology is associated with worse overall survival in patients with melanoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Oncoimmunology. 2022 Jul 7;11(1):2096535. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2096535. eCollection 2022. Oncoimmunology. 2022. PMID: 35832043 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of multiplex serology in discriminating active vs past Helicobacter pylori infection in a primarily African American population in the southeastern United States.Helicobacter. 2020 Feb;25(1):e12671. doi: 10.1111/hel.12671. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Helicobacter. 2020. PMID: 31746104 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori Infection, Its Laboratory Diagnosis, and Antimicrobial Resistance: a Perspective of Clinical Relevance.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022 Sep 21;35(3):e0025821. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00258-21. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35404105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyses of the association between Helicobacter pylori antibody titre and pathogenicity before and after eradication: results of the Kyushu and Okinawa population study, a retrospective observational cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Aug 7;14(8):e083157. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-083157. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39117418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bures J., Kopácová M., Skodová Fendrichová M., Rejchrt S. Epidemiologie Helicobacter pylori. Vnitřní Lékařství. 2011;57(12):993–999. - PubMed
-
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984;1(8390):1311–1315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

