Subthalamic beta dynamics mirror Parkinsonian bradykinesia months after neurostimulator implantation
- PMID: 28639263
- PMCID: PMC5575541
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.27068
Subthalamic beta dynamics mirror Parkinsonian bradykinesia months after neurostimulator implantation
Abstract
Background: Exaggerated oscillatory activity in the beta frequency band in the subthalamic nucleus has been suggested to be related to bradykinesia in Parkinson's disease (PD). However, studies seeking correlations between such activity in the local field potential and motor performance have been limited to the immediate postoperative period, which may be confounded by a stun effect that leads to the temporary alleviation of PD deficits.
Methods: Local field potentials were recorded simultaneously with motor performance in PD patients several months after neurostimulator implantation. This was enabled by the chronic implantation of a pulse generator with the capacity to record and transmit local field potentials from deep brain stimulation electrodes. Specifically, we investigated oscillatory beta power dynamics and objective measures of bradykinesia during an upper limb alternating pronation and supination task in 9 patients.
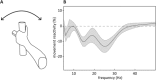
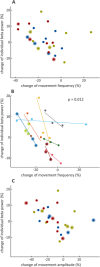
Results: Although beta power was suppressed during continuously repeated movements, this suppression progressively diminished over time in tandem with a progressive decrement in the frequency and amplitude of movements. The relationship between changes within local field potentials and movement parameters was significant across patients, and not present for theta/alpha frequencies (5-12 Hz). Change in movement frequency furthermore related to beta power dynamics within patients.
Conclusions: Changes in beta power are linked to changes in movement performance and the sequence effect of bradykinesia months after neurostimulator implantation. These findings provide further evidence that beta power may serve as a biomarker for bradykinesia and provide a suitable substrate for feedback control in chronic adaptive deep brain stimulation. © 2017 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; bradykinesia; deep brain stimulation; local field potential.
© 2017 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures


References
-
- Gibb WR, Lees AJ. A comparison of clinical and pathological features of young‐ and old‐onset Parkinson's disease. Neurology 1988;38(9):1402‐1406. - PubMed
-
- Agostino R, Berardelli A, Curra A, Accornero N, Manfredi M. Clinical impairment of sequential finger movements in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 1998;13(3):418‐421. - PubMed
-
- Agostino R, Berardelli A, Formica A, Stocchi F, Accornero N, Manfredi M. Analysis of repetitive and nonrepetitive sequential arm movements in patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 1994;9(3):311‐314. - PubMed
-
- Chen CC, Hsu YT, Chan HL, et al. Complexity of subthalamic 13‐35 Hz oscillatory activity directly correlates with clinical impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol 2010;224(1):234‐240. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

