Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese adolescents aged 12 to 17 years
- PMID: 28639320
- PMCID: PMC6481371
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012691
Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese adolescents aged 12 to 17 years
Abstract
Background: Adolescent overweight and obesity has increased globally, and can be associated with short- and long-term health consequences. Modifying known dietary and behavioural risk factors through behaviour changing interventions (BCI) may help to reduce childhood overweight and obesity. This is an update of a review published in 2009.
Objectives: To assess the effects of diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese adolescents aged 12 to 17 years.
Search methods: We performed a systematic literature search in: CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, CINAHL, LILACS, and the trial registers ClinicalTrials.gov and ICTRP Search Portal. We checked references of identified studies and systematic reviews. There were no language restrictions. The date of the last search was July 2016 for all databases.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for treating overweight or obesity in adolescents aged 12 to 17 years.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed risk of bias, evaluated the overall quality of the evidence using the GRADE instrument and extracted data following the guidelines of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We contacted trial authors for additional information.
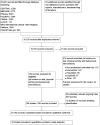
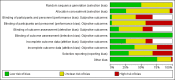
Main results: We included 44 completed RCTs (4781 participants) and 50 ongoing studies. The number of participants in each trial varied (10 to 521) as did the length of follow-up (6 to 24 months). Participants ages ranged from 12 to 17.5 years in all trials that reported mean age at baseline. Most of the trials used a multidisciplinary intervention with a combination of diet, physical activity and behavioural components. The content and duration of the intervention, its delivery and the comparators varied across trials. The studies contributing most information to outcomes of weight and body mass index (BMI) were from studies at a low risk of bias, but studies with a high risk of bias provided data on adverse events and quality of life.The mean difference (MD) of the change in BMI at the longest follow-up period in favour of BCI was -1.18 kg/m2 (95% confidence interval (CI) -1.67 to -0.69); 2774 participants; 28 trials; low quality evidence. BCI lowered the change in BMI z score by -0.13 units (95% CI -0.21 to -0.05); 2399 participants; 20 trials; low quality evidence. BCI lowered body weight by -3.67 kg (95% CI -5.21 to -2.13); 1993 participants; 20 trials; moderate quality evidence. The effect on weight measures persisted in trials with 18 to 24 months' follow-up for both BMI (MD -1.49 kg/m2 (95% CI -2.56 to -0.41); 760 participants; 6 trials and BMI z score MD -0.34 (95% CI -0.66 to -0.02); 602 participants; 5 trials).There were subgroup differences showing larger effects for both BMI and BMI z score in studies comparing interventions with no intervention/wait list control or usual care, compared with those testing concomitant interventions delivered to both the intervention and control group. There were no subgroup differences between interventions with and without parental involvement or by intervention type or setting (health care, community, school) or mode of delivery (individual versus group).The rate of adverse events in intervention and control groups was unclear with only five trials reporting harms, and of these, details were provided in only one (low quality evidence). None of the included studies reported on all-cause mortality, morbidity or socioeconomic effects.BCIs at the longest follow-up moderately improved adolescent's health-related quality of life (standardised mean difference 0.44 ((95% CI 0.09 to 0.79); P = 0.01; 972 participants; 7 trials; 8 comparisons; low quality of evidence) but not self-esteem.Trials were inconsistent in how they measured dietary intake, dietary behaviours, physical activity and behaviour.
Authors' conclusions: We found low quality evidence that multidisciplinary interventions involving a combination of diet, physical activity and behavioural components reduce measures of BMI and moderate quality evidence that they reduce weight in overweight or obese adolescents, mainly when compared with no treatment or waiting list controls. Inconsistent results, risk of bias or indirectness of outcome measures used mean that the evidence should be interpreted with caution. We have identified a large number of ongoing trials (50) which we will include in future updates of this review.
Conflict of interest statement
LA‐K: none known.
EL: none known.
JC: none known.
EM: none known.
RJ: none known.
HF: none known.
JO: none known.
MM: none known.
RV: none known.
CO: none known.
LA: none known.
LE: Louisa Ells is seconded to Public Health England two days per week but undertook this review within her role as Reader in Public Health and Obesity at Teesside University.
MIM: none known.
KR: none known.
Figures



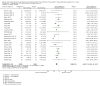
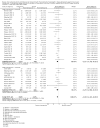




















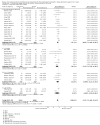

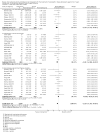
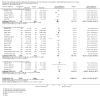




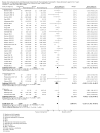


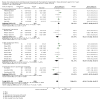
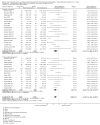
References
References to studies included in this review
Bean 2014 {published data only}
-
- NCT00167830. Barriers to treatment in obese adolescents. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00167830 Date first received: 9 September 2005.
Boodai 2014 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN37457227. National adolescent treatment trial for obesity in Kuwait. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN37457227 Date first assigned: 1 December 2009.
Brennan 2013 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12610000111077. The efficacy of a cognitive behavioural lifestyle intervention in improving body composition and cardiovascular fitness in overweight and obese adolescents. A wait‐listed randomised controlled trial. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12610000111077 Date first registered 3 February 2010.
-
- Brennan L, Walkley J, Fraser S, Greenway K, Wilks R. Motivational interviewing and cognitive behaviour therapy in the treatment of adolescent overweight and obesity: study design and methodology. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2008;29(3):359‐75. - PubMed
-
- Brennan L, Walkley J, Wilks R, Fraser S, Greenway K. Physiological and behavioural outcomes of a randomised controlled trial of a cognitive behavioural lifestyle intervention for overweight and obese adolescents. Obesity Research & Clinical Practice 2013;7(1):e23‐e41. - PubMed
-
- Brennan L, Wilks R, Walkley J, Fraser S, Greenway K. Treatment acceptability and psychosocial outcomes of a randomised controlled trial of a cognitive behavioural lifestyle intervention for overweight and obese adolescents. Behaviour Change 2012;29(01):36‐62. - PubMed
Brownell 1983 {published data only}
-
- Brownell K, Kelman J, Stunkard A. Treatment of obese children with and without their mothers: changes in weight and blood pressure. Pediatrics 1983;71(4):515‐23. - PubMed
Carraway 2014 {published data only}
-
- Carraway M. Project MENTOR+: Mentor‐led Exercise with Cognitive‐behavioral Therapy to Improve Perceived Competence, Reduce Social Anxiety, and Increase Physical Activity in Overweight Adolescents [Doctorate of Philosophy in Clinical Psychology Thesis]. Greenville (NC): East Carolina University, 2014.
Carrel 2005 {published data only}
-
- Carrel A, Clark R, Peterson S, Nemeth B, Sullivan J, Allen D. Improvement of fitness, body composition, and insulin sensitivity in overweight children in a school‐based exercise program: a randomized, controlled study. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2005;159(10):963‐8. - PubMed
Chandra 1968 {published data only}
-
- Chandra R. Obesity in childhood ‐ a clinical trial of low‐calorie "limical". Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1968;35(24):23‐6. - PubMed
Christie 2011 {published data only}
-
- Christie D, Hudson L, Costa S, Mathiot A, Holt R Kinra S, Kessel A, Wong I, et al. Effects of a motivational lifestyle intervention (the Healthy Eating and Lifestyle Programme (HELP)) on metabolic outcomes in obese adolescents: findings from a randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Diabetes 2015;16:45.
-
- Christie D, Hudson L, Costa S, Mathiot A, Holt R, Kinra S, et al. RCT of a motivational lifestyle intervention (the Healthy Eating and Lifestyle Programme (HELP)) for obese young people. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2015;100:A2‐A2.
-
- Christie D, Hudson L, Kinra S, Nazareth I, Holt R, Kessel A, et al. Does a motivational lifestyle intervention (the Healthy Eating and Lifestyle Programme (HELP) work for obese young people?. Journal of Adolescent Health 2015;2:S19.
-
- Christie D, Hudson L, Mathiot A, Cole T, Karlsen S, Kessel A, et al. Assessing the efficacy of the Healthy Eating and Lifestyle Programme (HELP) compared with enhanced standard care of the obese adolescent in the community: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2011;12:242. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Costa S, Hudson L, Christie D, Kinra S, Mathiot A, Wong I, et al. Fitness may be more important for cardiovascular health than adiposity in adolescent girls. Obesity Reviews 2014;15:108.
Daley 2005 {published data only}
-
- Daley A, Copeland R, Wright N, Roalfe A, Wales J. Exercise therapy as a treatment for psychopathologic conditions in obese and morbidly obese adolescents: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2006;118(5):2126‐34. - PubMed
-
- ISRCNT83888112. The psychological effects of exercise therapy in clinically obese children. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN83888112 Date first assigned: 17 August 2005.
Debar 2012 {published data only}
-
- NCT01068236. Primary care treatment for overweight adolescent females (SHINE). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01068236 Date first received: 11 February 2010.
Ebbeling 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ebbeling C, Leidig M, Sinclair K, Hangen J, Ludwig D. A reduced‐glycemic load diet in the treatment of adolescent obesity. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(8):773‐9. - PubMed
Ebbeling 2012 {published data only}
-
- NCT00381160. Reducing sugar‐sweetened beverage consumption in overweight adolescents (BASH). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00381160 Date first received: 25 September 2006.
Ford 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ford A, Bergh C, Södersten P, Sabin M, Hollinghurst S, Hunt L, et al. Treatment of childhood obesity by retraining eating behaviour: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2010;340:b5388. - PubMed
-
- Galhardo J, Hunt L, Lightman S, Sabin M, Bergh C, Sodersten P, et al. Normalizing eating behavior reduces body weight and improves gastrointestinal hormonal secretion in obese adolescents. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2011;97(2):E193‐201. - PubMed
-
- NCT00407420. Can a novel treatment using "Mandometer®" technology improve weight loss in a childhood obesity clinic?. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00407420 Date first received: 1 December 2006.
Gourlan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gourlan M, Sarrazin P, Trouilloud D. Motivational interviewing as a way to promote physical activity in obese adolescents: a randomised‐controlled trial using self‐determination theory as an explanatory framework. Psychology & Health 2013;28(11):1265‐86. - PubMed
Grey 2009 {published data only}
-
- Grey M, Berry D, Davidson M, Galasso P, Gustafson E, Melkus G. Preliminary testing of a program to prevent type 2 diabetes among high‐risk youth. Journal of School Health 2004;74(1):10‐5. - PubMed
Hofsteenge 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hofsteenge G, Chinapaw M, Delemarre‐van de Waal H, Weijs P. Long‐term effect of the Go4it group treatment for obese adolescents: a randomised controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition 2014;33(3):385‐91. - PubMed
-
- NTR691. GO4IT ‐ the effectiveness of a group intervention programme on the lifestyle of adolescents with obesity. www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=691 Date first registered: 19 July 2006.
-
- Weijs P, Hofsteenge A, Chinapaw M, Delemarre‐van de Waal H. Long‐term effect of the Go4it group treatment for obese adolescents: a randomised controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition, Supplement 2012;7:130. - PubMed
Jelalian 2016 {published data only}
-
- Jelalian E, Jandasek B, Wolff J, Seaboyer L, Jones R, Spirito A. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy plus healthy lifestyle enhancement for depressed, overweight/obese adolescents: results of a pilot trial. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology 2016 Jun 16 [Epub ahead of print]:1‐10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCT01128764. Integrated treatment for comorbid depression and obesity in adolescents. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01128764 Date first received: 21 May 2010.
Jiang 2005 {published data only}
Kong 2013 {published data only}
Kong 2014 {published data only}
-
- NCT01278563. A trial to investigate the impact of a low glycemic index (GI) diet on body mass index and obesity related cardiovascular and hormonal factors in Chinese adolescents. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01278563 Date first received: 18 January 2011.
Love‐Osborne 2014 {published data only}
-
- Love‐Osborne K, Fortune R, Sheeder J, Federico S, Haemer M. School‐based health center‐based treatment for obese adolescents: feasibility and body mass index effects. Childhood Obesity 2014;10:424‐31. - PubMed
Luna‐Pech 2014 {published data only}
-
- Luna‐Pech J, Torres‐Mendoza B, Luna‐Pech J, Garcia‐Cobas C, Navarrete‐Navarro S, Elizalde‐Lozano A. Normocaloric diet improves asthma‐related quality of life in obese pubertal adolescents. International Archives of Allergy & Immunology 2014;163:252‐8. - PubMed
NCT00132132 {published data only}
-
- NCT00132132. Study of impact of behavioral intervention ‐ exercise, nutrition, education ‐ on body mass index (BMI). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00132132 Date first received: 17 August 2005.
NCT00807560 {published data only}
-
- NCT00807560. Parent‐based treatment for pediatric overweight (PO). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00807560 Date first received: 11 December 2008.
Nguyen 2012 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12606000175572. Community‐based weight management of overweight and obese adolescents: a randomised controlled trial of extended therapeutic contact vs recommended care with primary outcomes body mass index standard deviation score and waist circumference standard deviation score. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12606000175572 Date first registered: 15 May 2006.
-
- Kornman K, Shrewsbury V, Chou A, Nguyen B, Lee A, O'Connor J, et al. Electronic therapeutic contact for adolescent weight management: the Loozit study. Telemedicine Journal & E‐Health 2010;16:678‐85. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen B, Shrewsbury V, Lau C, O'Connor J, Steinbeck K, Hill A, et al. Adolescent and parent views of an adolescent weight management program: lessons from the Loozit randomised controlled trial. Obesity Research and Clinical Practice 2012;6:56.
-
- Nguyen B, Shrewsbury V, O'Connor J, Lau C, Steinbeck K, Hill A, Baur L. A process evaluation of an adolescent weight management intervention: findings and recommendations. Health Promotion International 2015;30(2):201‐12. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen B, Shrewsbury V, O'Connor J, Steinbeck K, Hill A, Shah S, et al. Two‐year outcomes of an adjunctive telephone coaching and electronic contact intervention for adolescent weight‐loss maintenance: the Loozit randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Obesity 2013;37(3):468‐72. - PubMed
Norman 2016 {published data only}
Pakpour 2015 {published data only}
-
- NCT02180802. Parental involvement improves the effect of motivational interviewing on weight loss in obese adolescents: a randomized controlled trial study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02180802 Date first received: 1 July 2014.
-
- Pakpour A, Gellert P, Dombrowski S, Fridlund B. Motivational interviewing with parents for obesity: an RCT. Pediatrics 2015;135(3):e644‐52. - PubMed
Patrick 2013 {published data only}
-
- NCT00412165. PACE‐iDP: an intervention for youth at risk for diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00412165 Date first received: 13 December 2006.
Patsopoulou 2017 {published data only}
-
- NCT02653508. Evaluating the efficacy of the Feeding Exercise Trial in Adolescents (FETA Project) in Central Greece (FETA). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02653508 Date first received: 17 December 2015.
-
- Patsopoulou A, Tsimtsiou Z, Katsioulis A, Malissiova E, Rachiotis G, Hadjichristodoulou C. Evaluating the efficacy of the Feeding Exercise Randomized Trial in overweight and obese adolescents. Childhood Obesity 2017;13(2):128‐37. - PubMed
-
- Patsopoulou A, Tsimtsiou Z, Katsioulis A, Rachiotis G, Malissiova E, Hadjichristodoulou C. Prevalence and risk factors of overweight and obesity among adolescents and their parents in Central Greece (FETA Project). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2015;13(1):83. - PMC - PubMed
Pbert 2013 {published data only}
Pitetti 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pitetti K, Rendoff A, Grover T, Beets M. The efficacy of a 9‐month treadmill walking program on the exercise capacity and weight reduction for adolescents with severe autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2007;37(6):997‐1006. - PubMed
Resnicow 2005 {published data only}
-
- Resnicow K, Taylor R, Baskin M, McCarty F. Results of Go Girls: a weight control program for overweight African‐American adolescent females. Obesity Research 2005;13(10):1739‐48. - PubMed
Saelens 2002 {published data only}
-
- Saelens B, Sallis J, Wilfley D, Patrick K, Cella J, Buchta R. Behavioral weight control for overweight adolescents initiated in primary care. Obesity Research 2002;10(1):22‐32. - PubMed
Savoye 2007 {published data only}
-
- NCT00409422. Effects of a comprehensive weight management program on obese adolescents and children. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00409422 Date first received: 6 December 2006.
-
- Savoye M, Shaw M, Dziura J, Tamborlane W, Rose P, Guandalini C, et al. Effects of a weight management program on body composition and metabolic parameters in overweight children: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007;297(24):2697‐704. - PubMed
Schranz 2014 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12609001078246. Can resistance training change the strength, body composition and self‐concept of overweight and obese adolescent males? A randomised controlled trial. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12609001078246 Date first registered: 16 December 2009. - PubMed
-
- Schranz N, Olds T, Tomkinson G. Can resistance training change the strength, body composition and self‐concept of overweight and obese adolescent males? A randomised controlled trial. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2012;15:S358. - PubMed
-
- Schranz N, Tomkinson G, Parletta N, Petkov J, Olds T. Can resistance training change the strength, body composition and self‐concept of overweight and obese adolescent males? A randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2014;48:1482‐8. - PubMed
Sigal 2014 {published data only}
-
- Alberga A, Goldfield G, Kenny G, Hadjiyannakis S, Phillips P, Prud'homme D, et al. Healthy Eating, Aerobic and Resistance Training in Youth (HEARTY): study rationale, design and methods. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2012;33:839‐47. - PubMed
-
- Goldfield G, Kenny G, Alberga A, Prud'homme D, Hadjiyannakis S, Gougeon R, et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on psychological health in adolescents with obesity: the HEARTY Rrandomized controlled trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2015;83(6):1123. - PubMed
-
- NCT00195858. Healthy Eating Aerobic and Resistance Training in Youth (HEARTY) trial. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00195858 Date first received: 12 September 2005.
-
- Sigal R, Alberga A, Goldfield G, Prud'homme D, Hadjiyannakis S, Gougeon R, et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on percentage body fat and cardiometabolic risk markers in obese adolescents: the Healthy Eating Aerobic and Resistance Training in Youth randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatrics 2014;168:1006‐14. - PubMed
Toulabi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Toulabi T, Nikoo M, Amini F, Nazari H, Mardani M. The influence of a behavior modification interventional program on body mass index in obese adolescents. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association / Taiwan Yi Zhi 2012;111(3):153‐9. - PubMed
van Egmond‐Frohlich 2006 {published data only}
-
- Egmond‐Frohlich A, Brauer W, Goldschmidt H, Hoff‐Emden H, Oepen J, Zimmermann E. Effects of a programme for structured outpatient follow‐up care after inpatient rehabilitation of obese children and adolescents ‐ a multicentre, randomized study. Rehabilitation 2006;45(1):40‐51. - PubMed
Vissers 2008 {published data only}
-
- Vissers D, Meulenaere A, Vanroy C, Vanherle K, Sompel A, Truijen S, et al. Effect of a multidisciplinary school‐based lifestyle intervention on body weight and metabolic variables in overweight and obese youth. E‐SPEN, the European E‐journal of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism 2008;3(5):e196‐202.
Visuthranukul 2015 {published data only}
-
- NCT02049788. Effects of a low glycemic index in obese children. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02049788 Date first received: 28 January 2014.
-
- Visuthranukul C, Sirimongkol P, Prachansuwan A, Pruksananonda C, Chomtho S. Low‐glycemic index diet may improve insulin sensitivity in obese children. Pediatric Research 2015;78(5):567‐73. - PubMed
Vos 2011 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN36146436. The effect of lifestyle treatment on childhood obesity. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN36146436 Date first assigned: 13 July 2010.
-
- Vos R, Huisman S, Houdijk E, Pijl H, Wit J. The effect of family‐based multidisciplinary cognitive behavioral treatment on health‐related quality of life in childhood obesity. Quality of Life Research 2012;21(9):1587‐94. - PubMed
Walpole 2013 {published data only}
-
- NCT01246349. Motivational interviewing for weight loss. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01246349 Date first received: 11 November 2010.
-
- Walpole B, Dettmer E, Morrongiello B, McCrindle B, Hamilton J. Motivational interviewing to enhance self‐efficacy and promote weight loss in overweight and obese adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2013;39(9):944‐53. - PubMed
Wengle 2011 {published data only}
Wong 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wong J, Ebbeling C, Robinson L, Feldman H, Ludwig D. Does the recommendation to drink 8 cups of water per day promote weight loss?. FASEB Journal 2015;29:747‐18.
References to studies excluded from this review
Balagopal 2005 {published data only}
-
- Balagopal P, George D, Patton N, Yarandi H, Roberts W, Bayne E, et al. Lifestyle‐only intervention attenuates the inflammatory state associated with obesity: a randomized controlled study in adolescents. Journal of Pediatrics 2005;146(3):342‐8. - PubMed
Belenchia 2013 {published data only}
-
- Belenchia A, Tosh A, Hillman L, Peterson C. Correcting vitamin D insufficiency improves insulin sensitivity in obese adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2013;97(4):774‐81. - PubMed
Braet 2004 {published data only}
-
- Braet C, Tanghe A, Decaluwé V, Moens E, Rosseel Y. Inpatient treatment for children with obesity: weight loss, psychological well‐being, and eating behavior. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2004;29(7):519‐29. - PubMed
Carrel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Carrel A, Clark R, Peterson S, Eickhoff J, Allen D. School‐based fitness changes are lost during the summer vacation. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2007;161(6):561‐4. - PubMed
Crandall 2006 {published data only}
-
- Crandall M. The effectiveness of a program of comprehensive behavior modification therapy and sibutramine for obese adolescents. Thesis 2006; Vol. 69:3841.
Daly 2013 {published data only}
-
- Daly P. Obese Adolescent Females and Actual Behavioral Responses to a Mindful Eating Intervention [Doctoral dissertation]. Tucson (AZ): University of Arizona, 2013.
Dancy 2006 {published data only}
-
- Dancy B, Crittenden K, Talashek M. Effectiveness of the mother/daughter health promotion intervention in enhancing daughters' healthy eating behavior. APHA 134th Annual Meeting and Exposition; 2006 Nov 4‐8; Boston (MA). 2006.
De Jesus 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jesus S, Prapavessis H. The effects of a peer modeling intervention on cardiorespiratory fitness parameters and self‐efficacy in obese adolescents. Behavioral Medicine 2013;39(4):129‐37. - PubMed
DeVore 2013 {published data only}
Doyle 2008 {published data only}
Dreyer‐Gillette 2014 {published data only}
-
- Dreyer‐Gillette M, Odar Stough C, Best C, Beck A, Hampl S. Comparison of a condensed 12‐week version and a 24‐week version of a family‐based pediatric weight management program. Childhood Obesity 2014;10(5):375‐82. - PubMed
Faulkner 2013 {published data only}
Fonseca 2016 {published data only}
-
- NCT01904474. E‐therapeutic program for obese adolescents. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01904474 Date first received: 9 July 2013.
Freire 2013 {published data only}
-
- Freire S, Fisberg M, Cozzolino S. Dietary intervention causes redistribution of zinc in obese adolescents. Biological Trace Element Research 2013;154(2):168‐77. - PubMed
Garnett 2014 {published data only}
Giel 2013 {published data only}
-
- Giel K, Zipfel S, Schweizer R, Braun R, Ranke M, Binder G, et al. Eating disorder pathology in adolescents participating in a lifestyle intervention for obesity: associations with weight change, general psychopathology and health‐related quality of life. Obesity Facts 2013;6(4):307‐16. - PMC - PubMed
Hay 2016 {published data only}
-
- Hay J, Wittmeier K, MacIntosh A, Wicklow B, Duhamel T, Sellers E, et al. Physical activity intensity and type 2 diabetes risk in overweight youth: a randomized trial. International Journal of Obesity 2016;40:607‐14. - PubMed
Jelalian 1999 {published data only}
-
- Jelalian E, Saelens B. Empirically supported treatments in pediatric psychology: pediatric obesity. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1999;24(3):223‐48. - PubMed
Jelalian 2010 {published data only}
Jones 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jones M, Luce K, Osborne M, Taylor K, Cunning D, Doyle A, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of an internet‐facilitated intervention for reducing binge eating and overweight in adolescents. Pediatrics 2008;121(3):453‐62. - PubMed
Jones 2009 {published data only}
-
- Jones M. Reducing Binge Eating and Overweight in Adolescents via the Internet [Doctoral thesis]. Palo Alto (CA): Palo Alto University, 2009.
Lee 2013a {published data only}
Lee 2013b {published data only}
-
- Lee S, Deldin A, White D, Kim Y, Libman I, Rivera‐Vega M, et al. Aerobic exercise but not resistance exercise reduces intrahepatic lipid content and visceral fat and improves insulin sensitivity in obese adolescent girls: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism 2013;305(10):E1222‐9. - PMC - PubMed
Lee 2013c {published data only}
Lovely 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lovely R, Hossain J, Ramsey J, Komakula V, George D, Farrell D, et al. Obesity‐related increased γ' fibrinogen concentration in children and its reduction by a physical activity‐based lifestyle intervention: a randomized controlled study. Journal of Pediatrics 2013;163(2):333‐8. - PubMed
Lubans 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lubans D, Morgan P. Evaluation of an extra‐curricular school sport programme promoting lifestyle and lifetime activity for adolescents. Journal of Sports Sciences 2008;26(5):519‐29. - PubMed
NCT00863083 {published data only}
-
- NCT00863083. Reducing barriers to behavior change among youth with pediatric overweight and obesity. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00863083 Date first received: 16 March 2009.
NCT01044134 {published data only}
-
- NCT01044134. Think AHEAD (a healthy eating and drinking) study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01044134 Date first received: 5 January 2010.
NCT02011646 {published data only}
-
- NCT02011646. Healthy body study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02011646 Date first received: 10 December 2013.
NCT02295761 {published data only}
-
- NCT02295761. Promoting overweight adolescents physical activity. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02295761 Date first received: 18 February 2014.
Nunes 2016 {published data only}
-
- Nunes JE, Cunha HS, Freitas ZR, Nogueira AM, Dâmaso AR, Espindola FS, et al. Interdisciplinary therapy changes superoxide dismutase activity and adiponectin in obese adolescents: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Sports Sciences 2016;34(10):945‐50. - PubMed
Parks 2014 {published data only}
Racil 2013 {published data only}
-
- Racil G, Ounis O, Hammouda O, Kallel A, Zouhal H, Chamari K, et al. Effects of high vs. moderate exercise intensity during interval training on lipids and adiponectin levels in obese young females. European Journal of Applied Physiology 2013;113(10):2531‐40. - PubMed
Sabzghabaee 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sabzghabaee AM, Khayam I, Kelishadi R, Ghannadi A, Soltani R, Badri S, et al. Effect of Zizyphus jujuba fruits on dyslipidemia in obese adolescents: a triple‐masked randomized controlled clinical trial. Medical Archives 2013;67(3):156. - PubMed
Sarvestani 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sarvestani R, Jamalfard M, Kargar M, Kaveh M, Tabatabaee H. Effect of dietary behaviour modification on anthropometric indices and eating behaviour in obese adolescent girls. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2009;65(8):1670‐5. - PubMed
Shrewsbury 2011 {published data only}
Sussman 2013 {published data only}
Van 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vann L, Stanford F, Durkin M, Hanna A, Knight L, Stallworth J. "Moving and losing": a pilot study incorporating physical activity to decrease obesity in the pediatric population. Journal of the South Carolina Medical Association (1975) 2013;109(4):116‐20. - PubMed
Ventura 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ventura E, Davis J, Byrd‐Williams C, Toledo‐Corral C, Spruijt‐Metz D, Weigensberg M, et al. The effects of a randomized, controlled, modified‐carbohydrate nutrition intervention on the metabolic syndrome in overweight Latino adolescents. Obesity 2009;17:S183‐4.
Wadden 1990 {published data only}
-
- Wadden T, Stunkard A, Rich L, Rubin C, Sweidel G, McKinney S. Obesity in black adolescent girls: a controlled clinical trial of treatment by diet, behavior modification, and parental support. Pediatrics 1990;85(3):345‐52. - PubMed
Wiegand 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wiegand S, Bau A, Ernert A, Krude H. MAINTAIN: an intervention study of weight regain after weight loss in adolescents and children reveals an only minor role of leptin in weight regain. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 2014;82:1‐507.
Wilson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wilson A, Jung M, Cramp A, Simatovic J, Prapavessis H, Clarson C. Effects of a group‐based exercise and self‐regulatory intervention on obese adolescents' physical activity, social cognitions, body composition and strength: a randomized feasibility study. Journal of Health Psychology 2012;17:1223‐37. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Angerer 2015 {published data only}
-
- Angerer P, Niedermeier H, Graf T, Manthey A, Marten‐Mittag B, Schmidt H, et al. Fit4You ‐ a programme for prevention and reduction of overweight in apprentices in the workplace setting. Gesundheitswesen (Bundesverband der Arzte des Offentlichen Gesundheitsdienstes (Germany) 2015;77:S95‐6. [PUBMED: 23970389] - PubMed
Barbeau 2003 {published data only}
-
- Barbeau P, Gutin B, Litaker M, Ramsey L, Cannady W, Allison J, et al. Influence of physical training on plasma leptin in obese youths. Canadian Journal of Applied Physiology 2003;28(3):382‐96. - PubMed
Bohlin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bohlin A, Klaesson S, Kowalski J. Can telephone consultations substitute visits in treatment of childhood obesity? Results from a randomized trial. Obesity Facts 2012;5(Suppl 1):237.
Campos 2017 {published data only}
-
- Campos R, Masquio D, Corgosinho F, Lima S, Piano A, Carnier J, et al. Homeostasis Model Assessment‐Adiponectin: the role of different types of physical exercise in obese adolescents. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 2017; Vol. 57, issue 6:831‐8. - PubMed
Cocca 2016 {published data only}
-
- Cocca A, Lomas R, Enríquez M, Cocca M, Ceballos O. Effects of a school‐based intervention program on metabolic syndrome parameters in school‐aged youth. Obesity Reviews 2016;17:131‐2.
Garrett 1979 {published data only}
-
- Garrett L. Group behavioral therapy versus family behavioral therapy in treatment of obese adolescent females [Doctor of Philosophy thesis]. University of Pennsylvania, 1979:1364‐5.
Gracianette 1982 {published data only}
-
- Gracianette C. The application of behavioral techniques to change eating habits and/or exercise habits to effect weight reduction and maintenance in adolescents: a year‐long study [Doctor of Philosophy thesis]. Baton Rouge (LA): Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College, 1982.
Li 2006 {published data only}
-
- Li M. Anti‐obesity effect of comprehensive diet and sports in girl students with simple obesity or overweight. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;10(32):44‐6.
Makkes 2015 {unpublished data only}
-
- Makkes S. Intensive inpatient treatment for severely obese children and adolescents: costs and effects [Doctoral Thesis]. Amsterdam (Netherlands): VU University Amsterdam, 2015.
-
- Makkes S, Halberstadt J, Renders C, Bosmans J, Baan‐Slootweg O, Seidell C. Health Effects of Lifestyle Interventions in Obese children and adolescents Study (HELIOS) ‐ a randomised controlled trial. Obesity Reviews 2011;12:58.
-
- NTR1678. Het HELIOS onderzoek naar behandeling van kinderen en adolescenten met ernstige obesitas. www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=1678 Date first registered: 20 February 2009.
NCT00462267 {published data only}
-
- NCT00462267. Examining the feasibility of collaborative care treatment for overweight adolescents (SHINE‐Garfield). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00462267 Date first received: 17 April 2007.
NCT00475163 {published data only}
-
- NCT00475163. Mentors in motion: a physical activity intervention for obese adolescents (MIM). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00475163 Date first received: 17 May 2007.
Shapiro 1976 {published data only}
-
- Shapiro J. A comparison of various reward and monitoring procedures in the behavioral treatment of overweight children. Dissertation 1976; Vol. 36, issue 11‐B:5816‐7.
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12607000632493 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12607000632493. Active video games to improve body composition and physical activity in children. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12607000632493 Date first registered: 12 December 2007.
-
- Maddison R, Foley L, Mhurchu CN, Jull A, Jiang Y, Prapavessis H, et al. Feasibility, design and conduct of a pragmatic randomized controlled trial to reduce overweight and obesity in children: the electronic games to aid motivation to exercise (eGAME) study. BMC Public Health 2009;9:146. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-146] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
ACTRN12611000139976 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12611000139976. Staying fit adolescent weight management study. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12611000139976 Date first registered: 7 February 2011.
ACTRN12611000862943 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12611000862943. Whanau Pakari: a multidisciplinary intervention for child and adolescent obesity. anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=343300 Date first registered: 15 August 2011.
ACTRN12613001037796 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12613001037796. Effect of exercise intensity on cardiac and vascular function, and intra‐abdominal fat in obese children and adolescents. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12613001037796 Date first registered: 18 September 2013.
ACTRN12615000558527 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12615000558527. The effectiveness of a community weight management program with a behavioural incentive scheme compared to participation in a standard community weight management program in overweight children on relative weight loss and behaviour change. anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=368491 Date first registered: 29 May 2015.
Chew 2016 {published data only}
ChiCTR‐TRC‐13003501 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR‐TRC‐13003501. Lifestyle intervention in obese Chinese adolescents with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled study. www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=6059 Date first registered: 21 August 2013.
DRKS00004583 {published data only}
-
- DRKS00004583. Feasibility and efficacy of a weight maintenance treatment approach for adolescent obesity via telephone counseling following an obesity treatment program: a randomized controlled trial. drks‐neu.uniklinik‐freiburg.de/drks_web/navigate.do?navigationId=trial.HTML&TRIAL_ID=DR... Date first registered: 30 November 2012.
-
- Marked J, Herget S, Marschke S, Vogel M, Hilbert A, Bluher S. Weight maintenance treatment approach for adolescent obesity via telephone counseling following an inpatient obesity treatment program ‐ study concept. Obesity Facts Vol. 5:30.
-
- Markert J, Herget S, Vogel M, Gausche R, Hilbert A, Bluher S. After care treatment approach for adolescent obesity via telephone counseling following an obesity treatment program‐study concept. Hormone Research in Paediatrics Vol. 78:279.
DRKS00005299 {published data only}
-
- DRKS00005299. Impact of resistance versus endurance exercise on anthropometric and metabolic parameters within a standardized one year obesity treatment program for obese children and adolescents. drks‐neu.uniklinik‐freiburg.de/drks_web/navigate.do?navigationId=trial.HTML&TRIAL_ID=DR... Date first registered: 13 September 2013.
DRKS00006781 {published data only}
-
- DRKS00006781. Feasibility of a media‐supported high‐intensity interval training program for overweight and obese adolescents. drks‐neu.uniklinik‐freiburg.de/drks_web/navigate.do?navigationId=trial.HTML&TRIAL_ID=DR... Date first registered: 17 September 2014.
DRKS00007879 {published data only}
-
- DRKS00007879. Development and evaluation of a computer‐based self‐regulation training for obese children and adolescents. drks‐neu.uniklinik‐freiburg.de/drks_web/navigate.do?navigationId=trial.HTML&TRIAL_ID=DR... Date first registered: 13 July 2015.
EUCTR2009‐016921‐32‐ES {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2009‐016921‐32‐ES. A phase II, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, in parallel groups clinical trial to assess the safety and efficacy of dietary supplementation with tryptophan to achieve weight loss, and its neuropsychological effects in adolescents with obesity. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=eudract_number:200... Date first registered: not available.
IRCT201012235440N1 {published data only}
-
- IRCT201012235440N1. Effectiveness of a theory‐based intervention on obesity‐related behaviors, laboratory indices, body composition, body mass index and health‐related quality of life in overweight adolescents. www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?id=5440&number=1 Date first registered: 18 February 2011.
IRCT2013103115211N1 {published data only}
-
- IRCT2013103115211N1. Study on the effect of nutrition education and physical activity intervention using social cognitive theory for overweight and obese student girls of middle school of Shahinshahr. www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?id=15211&number=1 Date first registered: 27 November 2013.
ISRCTN04152711 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN04152711. Preventing obesity in young people attending primary dental care settings: an exploratory randomised controlled trial. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN04152711 Date first assigned: 24 May 2012.
-
- Murphy M, Porter J, Yusuf H, Ntouva A, Newton T, Kolliakou A, et al. Considerations and lessons learned from designing a motivational interviewing obesity intervention for young people attending dental practices: a study protocol paper. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2013;36(1):126‐34. - PubMed
NCT00562263 {published data only}
-
- NCT00562263. Barriers to effective weight loss in overweight adolescents (TEENS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00562263 Date first received: 20 November 2007.
NCT00850629 {published data only}
-
- NCT00850629. Hormonal regulation of body weight maintenance. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00850629 Date first received: 17 February 2009.
NCT00881478 {published data only}
-
- NCT00881478. Family intervention for obese children using portion control strategy for weight control (FOCUS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00881478 Date first received: 13 April 2009.
NCT00940966 {published data only}
-
- NCT00940966. A pilot study to determine the efficacy of a low carbohydrate diet in treatment of adolescents with metabolic syndrome. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00940966 Date first received: 15 July 2009.
NCT00998413 {published data only}
-
- NCT00998413. Weight‐reduction intervention in asthmatic children with overweight/obesity. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00998413 Date first received: 19 October 2009.
NCT01023139 {published data only}
-
- NCT01023139. Efficacy in adolescents of continued behavior modification following a six month sibutramine‐based weight management intervention (AOS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01023139 Date first received: 1 December 2009.
NCT01221220 {published data only}
-
- NCT01221220. Environmental strategies & behavior change to reduce overeating in obese children. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01221220 Date first received: 13 October 2010.
NCT01350531 {published data only}
-
- NCT01350531. Interventionist procedures for adherence to weight loss recommendations in black adolescents. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01350531 Date first received: 21 April 2011.
NCT01374386 {published data only}
-
- NCT01374386. Impact of Exergaming on adolescent youth. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01374386 Date first received: 14 June 2011.
NCT01448551 {published data only}
-
- NCT01448551. MPOWERed messages: tailored mobile messages to enhance weight loss for teens. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01448551 Date first received: 5 October 2011.
NCT01456221 {published data only}
-
- NCT01456221. Intervention study with omega‐3 fatty acids for weight loss and insulin resistance in adolescents (O3WLIRADOL). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01456221 Date first received: 12 October 2011.
NCT01514279 {published data only}
-
- NCT01514279. Ideas moving parents and adolescents to change together (IMPACT). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01514279 Date first received: 20 December 2011.
NCT01677923 {published data only}
-
- NCT01677923. Obesity in children and adolescents: associated risks and early intervention (OCA). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01677923 Date first received: 30 July 2012.
NCT01688453 {published data only}
-
- NCT01688453. Overweight management and social inequalities (PRALIMAP‐INES). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01688453 Date first received: 7 September 2012.
NCT01764113 {published data only}
-
- NCT01764113. Effect of mindful eating on body mass index in obese adolescents. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01764113 Date first received: 7 January 2013.
NCT01794546 {published data only}
-
- NCT01794546. Integrated care for pediatric obesity using telehealth. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01794546 Date first received: 15 February 2013.
NCT01796067 {published data only}
-
- NCT01796067. Families improving together (FIT) for weight loss. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01796067 Date first received: 22 January 2013.
NCT01804855 {published data only}
-
- NCT01804855. Effectiveness of a smartphone app for adolescent obesity management. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01804855 Date first received: 4 March 2013.
NCT01840631 {published data only}
-
- NCT01840631. A trial to study the effects of group versus individual dietary counseling in pediatric obesity. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01840631 Date first received: 8 March 2013.
NCT02034994 {published data only}
-
- NCT02034994. Combining primary and secondary prevention for reduction of excessive weight gain in school. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02034994 Date first received: 10 January 2014.
NCT02086851 {published data only}
-
- NCT02086851. Study of a structured parent intervention on adolescent weight loss modification program. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02086851 Date first received: 7 February 2014.
NCT02228278 {published data only}
-
- NCT02228278. Healthcare text messaging to improve diet, physical activity and weight loss in a pediatric lipid clinic (Text4Fit). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02228278 Date first received: 25 August 2014.
NCT02280772 {published data only}
-
- NCT02280772. Effect of glucomannan supplementation on body weight in overweight and obese children. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02280772 Date first received: 29 October 2014.
NCT02353637 {published data only}
-
- NCT02353637. The Peds Obesity study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02353637 Date first received: 21 January 2015.
NCT02444689 {published data only}
-
- NCT02444689. EMPower: electronic media powering positive health changes in youth. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02444689 Date first received: 12 May 2015.
NCT02615353 {published data only}
-
- NCT02615353. Preventing diabetes in Latino youth. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02615353 Date first received: 4 November 2015.
NCT02687516 {published data only}
-
- NCT02687516. Treatment of severely obese children and adolescents employing "Family‐based Behavioral Social Facilitation Treatment". clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02687516 Date first received: 21 February 2014.
NCT02711488 {published data only}
-
- NCT02711488. Managing adolescent obesity at local level by combining primary and secondary intervention (PAAPAS‐DC). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02711488 Date first received: 15 February 2016.
NCT02745795 {published data only}
-
- NCT02745795. Efficacy of motivational interview in the treatment of obesity and overweight in adolescents (IMAGINE). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02745795 Date first received: 5 April 2016.
NCT02794090 {published data only}
-
- NCT02794090. Childhood obesity treatment ‐ telephone coaching vc usual care. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02794090 Date first received: 31 May 2016.
NTR5676 {published data only}
-
- NTR5676. The focus on strength programme: an innovative strength‐based physical activity intervention to improve body composition and to stimulate physical activity in adolescents (12‐18years) with overweight or obesity. www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=5676 Date first registered: 8 February 2016.
Ramalho 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ramalho SM, Conceiçao E, Saint Maurice P, Machado P. Taking the route back: new technologies for overweight and obesity treatment in childhood and adolescence ‐ study protocol. Obesity Facts 2016;9:368‐108.
RBR‐38p23s {published data only}
-
- RBR‐38p23s. Multifocal intervention in obese adolescents: social competence, behavior problems, academic performance and weight reduction. www.ensaiosclinicos.gov.br/rg/RBR‐38p23s/ Date first registered: 23 April 2013.
Spieker 2015 {published data only}
TCTR20130515001 {published data only}
-
- TCTR20130515001. Effectiveness of weight reduction program on intrinsic motivation and health related outcomes in overweight secondary school students. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=TCTR20130515001 Date first registered: 15 May 2013.
Additional references
Bandura 1997
-
- Bandura, A. Self‐efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: Freeman & Co, 1997.
Beller 2013
Bocca 2013
-
- Bocca G, Ongering EC, Stolk RP, Sauer PJ. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in 3‐ to 5‐year old overweight or obese children. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 2013;80(3):201‐6. - PubMed
CDC 2000
-
- Centers for Disease Control Growth Charts. Centers for Disease Control Growth Charts. www.cdc.gov/growthcharts 2000.
CMO 2015
-
- Chief Medical Officer. Annual report of the Chief Medical Officer: surveillance volume, 2012: on the state of the public's health. www.gov.uk/government/publications/chief‐medical‐officer‐annualreport‐su... (accessed 30 March 2015).
Cole 2000
Cole 2012
-
- Cole TJ, Lobstein T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut‐offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatric Obesity 2012;7(4):284‐94. - PubMed
Collins 2006
-
- Collins C, Warren J, Neve M, McCoy P, Stokes B. Measuring effectiveness of dietetic interventions in child obesity: a systematic review of randomized trials. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2006;160(9):906‐22. - PubMed
Daniels 2009
-
- Daniels SR. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity 2009;33(Suppl 1):S60‐5. - PubMed
de Onis 2010
-
- Onis M, Blössner M, Borghi E. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92(5):1257‐64. - PubMed
Dewar 2013
-
- Dewar D, Morgan P, Plotnikoff R, Okely A, Collins C, Batterham M, et al. The nutrition and enjoyable activity for teen girls study: a cluster randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2013;45(3):313‐7. - PubMed
Doak 2006
-
- Doak C, Visscher T, Renders C, Seidell J. The prevention of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: a review of interventions and programmes. Obesity Reviews 2006;7(1):111‐36. - PubMed
Eady 2008
Egan 2013
Egbewale 2014
Ells 2015
-
- Ells LJ, Hancock C, Copley VR, Mead E, Dinsdale H, Kinra S, et al. Prevalence of severe childhood obesity in England: 2006‐2013. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2015;100(7):631‐6. - PubMed
Follmann 1992
-
- Follmann D, Elliot P, Suh I, Cutler J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1992;45(7):769‐73. - PubMed
Freedman 2006
-
- Freedman DS, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Ogden CL, Dietz WH. Racial and ethnic differences in secular trends for childhood BMI, weight, and height. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 2006;14(2):301‐8. - PubMed
Glenny 1997
-
- Glenny AM, O'Meara S, Melville A, Sheldon TA, Wilson C. The treatment and prevention of obesity: a systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 1997;21(9):715‐37. - PubMed
Griffiths 2010
-
- Griffiths LJ, Parsons TJ, Hill AJ. Self‐esteem and quality of life in obese children and adolescents: a systematic review. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2010;5(4):282‐304. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2009
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011b
Ho 2012
-
- Ho M, Garnett S, Baur L, Burrows T, Stewart L, Neve M, et al. Effectiveness of lifestyle interventions in child obesity: systematic review with meta‐analysis. Pediatrics 2012;130:e1647‐71. - PubMed
Hróbjartsson 2013
-
- Hróbjartsson A, Thomsen AS, Emanuelsson F, Tendal B, Hilden J, Boutron I, et al. Observer bias in randomized clinical trials with measurement scale outcomes: a systematic review of trials with both blinded and nonblinded assessors. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2013;185(4):E201‐11. - PMC - PubMed
HSCIC 2015
-
- Health and Social Care Information Centre. National Child Measurement Programme ‐ England, 2012‐13 school year. http://content.digital.nhs.uk/catalogue/PUB13115 (accessed 30 March 2015).
Kelly 2008
-
- Kelly S, Melnyk B. Systematic review of multicomponent interventions with overweight middle adolescents: implications for clinical practice and research. Worldviews on Evidence‐Based Nursing 2008;5(2):113‐35. - PubMed
Kelly 2013
-
- Kelly AS, Barlow SE, Rao G, Inge TH, Hayman LL, Steinberger J, et al. Severe obesity in children and adolescents: identification, associated health risks, and treatment approaches: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013;128(15):1689‐712. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
Knai 2012
Kothandan 2014
Leclercq 2013
-
- Leclercq E, Leeflang MM, Dalen EC, Kremer LC. Validation of search filters for identifying pediatric studies in PubMed. Journal of Pediatrics 2013;162(3):629‐34. - PubMed
Liberati 2009
Lobstein 2004
-
- Lobstein T, Baur L, Uauy R. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obesity Reviews 2004;5(Suppl 1):4‐104. - PubMed
MacDonell 2010
-
- MacDonell K, Ellis D, Naar‐King S, Cunningham P. Predictors of home‐based obesity treatment efficacy for African American youth. Children's Health Care 2010;39(1):1‐4.
McGovern 2008
-
- McGovern L, Johnson J, Paulo R, Hettinger A, Singhal V, Kamath C, et al. Treatment of pediatric obesity: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized trials. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2008;93(12):4600‐5. - PubMed
Meader 2014
Narang 2012
Ng 2014
NICE 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Weight management: lifestyle services for overweight or obese children and young people. NICE Guidelines PH47, 2013. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ph47 (accessed 24 May 2017).
NOO NHS 2011
-
- National Obesity Observatory on behalf of the Public Health Observatories in England. A simple guide to classifying body mass index in children, 2011. www.noo.org.uk/uploads/doc/vid_11601_A_simple_guide_to_classifying_BMI_i... (accessed 3 November 2015).
Olds 2011
-
- Olds T, Maher C, Zumin S, Péneau S, Lioret S, Castetbon K, et al. Evidence that the prevalence of childhood overweight is plateauing: data from nine countries. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2011;6(5‐6):342‐60. - PubMed
Orsi 2011
-
- Orsi C, Hale D, Lynch, J. Pediatric obesity epidemiology. Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity 2011;18(1):14‐22. - PubMed
Parsons 1999
-
- Parsons TJ, Power C, Logan S, Summerbell CD. Childhood predictors of adult obesity: a systematic review. International Journal of Obesity 1999;23(Suppl 8):S1‐S107. - PubMed
Paulis 2014
-
- Paulis WD, Silva S, Koes BW, Middelkoop M. Overweight and obesity are associated with musculoskeletal complaints as early as childhood: a systematic review. Obesity Reviews 2014;15(1):52‐67. - PubMed
Peirson 2015
Penedo 2005
-
- Penedo F, Dahn J. Exercise and well‐being: a review of mental and physical health benefits associated with physical activity. Current Opinion in Psychiatry 2005;18(2):189‐93. - PubMed
Puhl 2007
-
- Puhl RM, Latner JD. Stigma, obesity, and the health of the nation's children. Psychology Bulletin 2007;133(4):557‐80. - PubMed
Rajput 2014
-
- Rajput N, Tuohy P, Mishra S, Smith A, Taylor B. Overweight and obesity in 4‐5‐year‐old children in New Zealand: results from the first 4 years (2009‐2012) of the B4School Check programme. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2014;51(3):334‐43. - PubMed
Reilly 2003
Riley 2011
-
- Riley RD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ. Interpretation of random effects meta‐analyses. BMJ 2011;342:d549. - PubMed
Rokholm 2010
-
- Rokholm B, Baker JL, Sørenson TI. The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999 ‐ a review of evidence and perspectives. Obesity Reviews 2010;11(12):835‐46. - PubMed
Ruotsalainen 2015
-
- Ruotsalainen H, Kyngäs H, Tammelin T, Kääriäinen M. Systematic review of physical activity and exercise interventions on body mass indices, subsequent physical activity and psychological symptoms in overweight and obese adolescents. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2015;1(11):2461‐77. - PubMed
Shrewsbury 2008
-
- Shrewsbury V, Wardle J. Socioeconomic status and adiposity in childhood: a systematic review of cross‐sectional studies 1990‐2005. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 2008;16(2):275‐84. - PubMed
Singh 2008
-
- Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JW, Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJ. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obesity Reviews 2008;9(5):474‐88. - PubMed
Skinner 2014
-
- Skinner AC, Skelton JA. Prevalence and trends in obesity and severe obesity among children in the United States, 1999‐2012. JAMA Pediatrics 2014;168(6):561‐6. - PubMed
Spear 2007
-
- Spear B, Barlow S, Ervin C, Ludwig D, Saelens B, Schetzina K, et al. Recommendations for treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity. Pediatrics 2007;120(4):S254‐88. - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. - PubMed
Stuart and Stevenson 1959
-
- Stuart HC, Stevenson SS, Nelson WE. Textbook of pediatrics. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1959.
Tang‐Peronard 2008
-
- Tang‐Peronard JL, Heitmann BL. Stigmatization of obese children and adolescents, the importance of gender. Obesity Reviews 2008;9(6):522‐34. - PubMed
Wang 2012
Whitaker 1997
-
- Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(13):869‐73. - PubMed
White 2004
-
- White M, Martin P, Newton R, Walden H, York‐Crowe E, Gordon S, et al. Mediators of weight loss in a family‐based intervention presented over the Internet. Obesity Research 2004;12(7):1050‐9. - PubMed
Whitlock 2010
-
- Whitlock E, O'Connor E, Williams S, Beil T, Lutz K. Effectiveness of weight management interventions in children: a targeted systematic review for the USPSTF. Pediatrics 2010;125:396‐418. - PubMed
WHO 2002
-
- World Health Organization. Report of a Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation. Diet nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/publications/trs916/en/. Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
WHO 2009
-
- WHO. WHO AnthroPlus for personal computers manual: software for assessing growth of the world’s children and adolescents. http://www.who.int/growthref/tools/who_anthroplus_manual.pdf 2009.
WHO 2015a
-
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet on overweight and obesity. www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en (accessed 30 March 2015).
WHO 2015b
-
- World Health Organization. The WHO child growth standards. www.who.int/childgrowth/publications/technical˙report˙pub/en/ (accessed 30 March 2015).
WHO 2015c
-
- World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/end‐childhood‐obesity/interim‐report‐for‐comment/en/. (accessed 5 June 2017).
Wilfley 2007
Wong 2006a
Wong 2006b
-
- Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Optimal CINAHL search strategies for identifying therapy studies and review articles. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2006;38(2):194‐9. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Oude Luttikhuis 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

