Dressings and topical agents for treating pressure ulcers
- PMID: 28639707
- PMCID: PMC6481609
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011947.pub2
Dressings and topical agents for treating pressure ulcers
Abstract
Background: Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, decubitus ulcers and pressure injuries, are localised areas of injury to the skin or the underlying tissue, or both. Dressings are widely used to treat pressure ulcers and promote healing, and there are many options to choose from including alginate, hydrocolloid and protease-modulating dressings. Topical agents have also been used as alternatives to dressings in order to promote healing.A clear and current overview of all the evidence is required to facilitate decision-making regarding the use of dressings or topical agents for the treatment of pressure ulcers. Such a review would ideally help people with pressure ulcers and health professionals assess the best treatment options. This review is a network meta-analysis (NMA) which assesses the probability of complete ulcer healing associated with alternative dressings and topical agents.
Objectives: To assess the effects of dressings and topical agents for healing pressure ulcers in any care setting. We aimed to examine this evidence base as a whole, determining probabilities that each treatment is the best, with full assessment of uncertainty and evidence quality.
Search methods: In July 2016 we searched the Cochrane Wounds Specialised Register; the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); Ovid MEDLINE; Ovid MEDLINE (In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations); Ovid Embase and EBSCO CINAHL Plus. We also searched clinical trials registries for ongoing and unpublished studies, and scanned reference lists of relevant included studies as well as reviews, meta-analyses, guidelines and health technology reports to identify additional studies. There were no restrictions with respect to language, date of publication or study setting.
Selection criteria: Published or unpublished randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the effects of at least one of the following interventions with any other intervention in the treatment of pressure ulcers (Stage 2 or above): any dressing, or any topical agent applied directly to an open pressure ulcer and left in situ. We excluded from this review dressings attached to external devices such as negative pressure wound therapies, skin grafts, growth factor treatments, platelet gels and larval therapy.
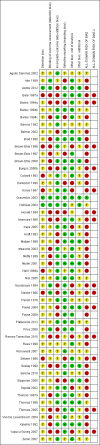
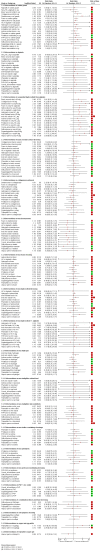
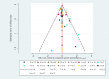
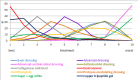
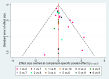
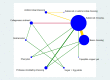
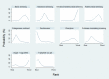
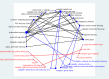
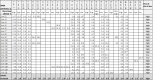
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently performed study selection, risk of bias assessment and data extraction. We conducted network meta-analysis using frequentist mega-regression methods for the efficacy outcome, probability of complete healing. We modelled the relative effectiveness of any two treatments as a function of each treatment relative to the reference treatment (saline gauze). We assumed that treatment effects were similar within dressings classes (e.g. hydrocolloid, foam). We present estimates of effect with their 95% confidence intervals for individual treatments compared with every other, and we report ranking probabilities for each intervention (probability of being the best, second best, etc treatment). We assessed the certainty (quality) of the body of evidence using GRADE for each network comparison and for the network as whole.
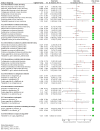
Main results: We included 51 studies (2947 participants) in this review and carried out NMA in a network of linked interventions for the sole outcome of probability of complete healing. The network included 21 different interventions (13 dressings, 6 topical agents and 2 supplementary linking interventions) and was informed by 39 studies in 2127 participants, of whom 783 had completely healed wounds.We judged the network to be sparse: overall, there were relatively few participants, with few events, both for the number of interventions and the number of mixed treatment contrasts; most studies were small or very small. The consequence of this sparseness is high imprecision in the evidence, and this, coupled with the (mainly) high risk of bias in the studies informing the network, means that we judged the vast majority of the evidence to be of low or very low certainty. We have no confidence in the findings regarding the rank order of interventions in this review (very low-certainty evidence), but we report here a summary of results for some comparisons of interventions compared with saline gauze. We present here only the findings from evidence which we did not consider to be very low certainty, but these reported results should still be interpreted in the context of the very low certainty of the network as a whole.It is not clear whether regimens involving protease-modulating dressings increase the probability of pressure ulcer healing compared with saline gauze (risk ratio (RR) 1.65, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.92 to 2.94) (moderate-certainty evidence: low risk of bias, downgraded for imprecision). This risk ratio of 1.65 corresponds to an absolute difference of 102 more people healed with protease modulating dressings per 1000 people treated than with saline gauze alone (95% CI 13 fewer to 302 more). It is unclear whether the following interventions increase the probability of healing compared with saline gauze (low-certainty evidence): collagenase ointment (RR 2.12, 95% CI 1.06 to 4.22); foam dressings (RR 1.52, 95% CI 1.03 to 2.26); basic wound contact dressings (RR 1.30, 95% CI 0.65 to 2.58) and polyvinylpyrrolidone plus zinc oxide (RR 1.31, 95% CI 0.37 to 4.62); the latter two interventions both had confidence intervals consistent with both a clinically important benefit and a clinically important harm, and the former two interventions each had high risk of bias as well as imprecision.
Authors' conclusions: A network meta-analysis (NMA) of data from 39 studies (evaluating 21 dressings and topical agents for pressure ulcers) is sparse and the evidence is of low or very low certainty (due mainly to risk of bias and imprecision). Consequently we are unable to determine which dressings or topical agents are the most likely to heal pressure ulcers, and it is generally unclear whether the treatments examined are more effective than saline gauze.More research is needed to determine whether particular dressings or topical agents improve the probability of healing of pressure ulcers. The NMA is uninformative regarding which interventions might best be included in a large trial, and it may be that research is directed towards prevention, leaving clinicians to decide which treatment to use on the basis of wound symptoms, clinical experience, patient preference and cost.
Conflict of interest statement
Maggie Westby: my employment at the University of Manchester is funded by National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) and focuses on high priority Cochrane Reviews in the prevention and treatment of wounds.
Jo Dumville: I receive research funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) for the production of systematic reviews focusing on high priority Cochrane Reviews in the prevention and treatment of wounds. This work was also partly funded by the National Institute for Health Research Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care (NIHR CLAHRC) Greater Manchester.
Marta Soares: none known.
Nikki Stubbs: funding from pharmaceutical companies has supported training and educational events, and payments have been received by the author for non‐product‐related educational sessions. These have been unrelated to the subject matter of the review and have never been in support or in pursuit of the promotion of products.
Gill Norman: my employment at the University of Manchester is funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) and focuses on high priority Cochrane Reviews in the prevention and treatment of wounds.
Figures


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Aguilo Sanchez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Aguilo Sanchez S, Figueiras Mareque L, Quintilla Gatnau A, Veiga Bogo L. Assessment of the efficacy of a hidropolomeric [sic] dressing in three dimensions and a hydrocolloid with calcium alginate in the treatment of pressure ulcers. 12th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2002 May 23‐25; Granada, Spain. 2002:113.
Alm 1989 {published data only}
-
- Alm A, Hornmark AM, Fall PA, Linder L, Bergstrand B, Ehrnebo M, et al. Care of pressure sores: a controlled study of the use of a hydrocolloid dressing compared with wet saline gauze compresses. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1989;149(Suppl):1‐10. - PubMed
Ashby 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ashby R, Dumville J, Soares M, McGinnis E, Stubbs N, Adderley U, et al. A pilot trial of topical negative pressure therapy (TNP) for the treatment of grade III/IV pressure ulcers. EWMA Journal 2010;10(2):202.
-
- Ashby R, Dumville J, Soares MO, Adderley U, McGinnis E, Stubbs N, et al. A pilot study of negative pressure wound therapy for the treatment of grade III/IV pressure ulcers. International Nursing Research Conference; 2011 May 16‐18; Harrogate, UK. 2011:95.
-
- Ashby RL, Dumville JC, Soares MO, McGinnis E, Stubbs N, Torgerson DJ, et al. A pilot randomised controlled trial of negative pressure wound therapy to treat grade III/IV pressure ulcers. Trials 2012;13(119):available from trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1745‐6215‐13‐119. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-13-119] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Bale 1997a {published data only}
-
- Bale S, Squires D, Varnon T, Walker A, Benbow M, Harding KG. A comparison of two dressings in pressure sore management. Journal of Wound Care 1997;6(10):463‐6. - PubMed
-
- Benbow M. A multicentre pilot study to investigate the physical performance of a novel Allevyn Adhesive dressing. In: Suggett A, Cherry G, Mani R, Eagelstein W editor(s). Evidence‐based Wound Care. International Congress and Symposium Series Number 227. Royal Society of Medicine Press Limited, 1998:49‐53.
-
- Shutler S, Stock J, Bale S, Harding KG, Squires D, Wilson I, et al. A multi‐centre comparison of a hydrocellular adhesive dressing (Allevyn Adhesive) and a hydrocolloid dressing (Granuflex) in the management of stage 2 and 3 pressure sores. Fifth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995, November 21‐24, Harrogate, UK. 1996:poster.
Banks 1994a {published data only}
-
- Banks V, Bale SE. Comparing two dressings for exuding pressure sores in community patients. Journal of Wound Care 1994;3(4):175‐8. - PubMed
-
- Banks V, Riggs R, Bale S, Harding KG. Comparison of an absorbent semi‐permeable polyurethane dressing (Spyrosorb/Mitraflex) and a hydrocolloid dressing (Granuflex E) for the treatment of moderately exuding stage II and III pressure sores in community patients. Third European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1993 October 19‐22; Harrogate, UK. 1994:159.
Banks 1994b {published data only}
-
- Banks V, Bale S. Superficial pressure sores: comparing two regimes. Journal of Wound Care 1994;3(1):8‐10. - PubMed
-
- Banks V, Bale S, Harding K. A comparative study to evaluate the effectiveness of Lyofoam A in the treatment of superficial pressure sores. Third European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1993 October 19‐22; Harrogate, UK. 1994:21‐4.
Banks 1994c {published data only}
-
- Banks V, Bale S, Harding K. The use of two dressings for moderately exuding pressure sores. Journal of Wound Care 1994;3(3):132‐4. - PubMed
-
- Riggs R, Banks V, Bale S, Harding K. Comparison of an absorbent semi‐permeable polyurethane dressing (Spyrosorb/Mitraflex) and a hydrocolloid dressing (Granuflex E) for the treatment of moderately exuding pressure sores in hospitalised patients. Third European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1993 October 19‐22; Harrogate, UK. 1994:159.
Barrois 1992 {published data only}
-
- Barrois B. Comparison of Granuflex and medicated paraffin gauze in pressure sores. Second European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1992 October 20‐23; Harrogate, UK. 1993:209‐10.
-
- Huchon D. Comparison between Granuflex and paraffin‐impregnated medical gauze in the treatment of pressure sores. Euroservices Communication: Going into the '90s: the Pharmacist and Wound Care 1992:23‐6.
Belmin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Belmin J, Meaume S, Rabus MT, Bohbot S, Investigators of the Sequential Treatment of the Elderly with Pressure Sores (STEPS) Trial. Sequential treatment with calcium alginate dressings and hydrocolloid dressings accelerates pressure ulcer healing in older subjects: a multicenter randomized trial of sequential versus nonsequential treatment with hydrocolloid dressings alone. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2002;50(2):269‐74. - PubMed
-
- Meaume S. A randomized controlled study to compare a sequential treatment using alginate‐CMC and hydrocolloid dressing or hydrocolloid dressing alone in decubitus ulcer management. Ninth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1999 November 9‐11; Harrogate, UK. 1999:11.
-
- Meaume S, Faucher N, Henry O, Belmin J. A randomised controlled study to compare a sequential treatment using alginate‐CMC and hydrocolloid dressing to hydrocolloid dressing alone in decubitus ulcers management. 12th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2002 May 23‐25; Granada, Spain. 2002:123.
-
- Rabus MT, Dare F, Mouel LE, Meaume S. Sequential treatment using alginate‐CMC and hydrocolloid dressing in pressure ulcers: results of a controlled study (STEPS study). Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:159.
Brod 1990 {published data only}
-
- Brod M, McHenry E, Plasse TF, Fedorczyk D, Trout JR. A randomized comparison of poly‐hema and hydrocolloid dressings for treatment of pressure sores. Archives of Dermatology 1990;126(7):969‐70. - PubMed
Brown‐Etris 1996 {published data only}
-
- Brown‐Etris M, Fowler E, Papen J, Stanfield J, Harris A, Tintle T, et al. Comparison and evaluation of the performance characteristics, usability and effectiveness on wound healing of Transorbent versus Duoderm CGF. Fifth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995 November 21‐24; Harrogate, UK. 1996:151‐5.
Brown‐Etris 1997 {published data only}
-
- Brown‐Etris M, Bateman D, Sheilds D, Punchello M, Gokoo CF, Scott R, et al. Final report of a clinical study designed to evaluate and compare a collagen alginate dressing and a calcium‐sodium alginate dressing in pressure ulcers. European Wound Management Association Conference; 1997 April 27‐29; Milan, Italy. 1997:21.
Brown‐Etris 2008 {published data only}
-
- Brown‐Etris M, Milne C, Orsted H, Gates JL, Netsch D, Punchello M, et al. A prospective, randomized, multisite clinical evaluation of a transparent absorbent acrylic dressing and a hydrocolloid dressing in the management of Stage II and shallow Stage III pressure ulcers. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2008;21(4):169‐74. - PubMed
-
- Brown‐Etris M, Punchello M, O'Connor T, Milne C, Orsted H, Couture N, et al. A randomized comparative clinical evaluation of a transparent absorbent acrylic dressing and a hydrocolloid dressing on stage II and III pressure ulcers. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing 2006;33(Suppl 1):S53.
Burgos 2000b {published data only}
-
- Burgos A, Gimenez J, Moreno E, Lamberto E, Ultrera M, Urraca EM, et al. Cost, efficacy, efficiency and tolerability of collagenase ointment versus hydrocolloid occlusive dressing in the treatment of pressure ulcers. Clinical Drug Investigation 2000;19(5):357‐65.
Colwell 1993 {published data only}
-
- Colwell JC, Foreman MD, Trotter JP. A comparison of the efficacy and cost‐effectiveness of two methods of managing pressure ulcers. Decubitus 1993;6(4):28‐36. - PubMed
Darkovich 1990 {published data only}
-
- Darkovich SL, Brown‐Etris M, Spencer M. Biofilm hydrogel dressing: a clinical evaluation in the treatment of pressure sores. Ostomy/Wound Management 1990;29:47‐60. - PubMed
Gorse 1987 {published data only}
-
- Gorse GJ, Messner RL. Improved pressure sore healing with hydrocolloid dressings. Archives of Dermatology 1987;123(6):766‐71. - PubMed
Graumlich 2003 {published data only}
-
- Graumlich JF, Blough LS, McLaughlin RG, Milbrandt JC, Calderon CL, Agha SA, et al. Healing pressure ulcers with collagen or hydrocolloid: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(2):147‐54. - PubMed
Hollisaz 2004 {published data only}
Hondé 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hondé C, Derks C, Tudor D. Local treatment of pressure sores in the elderly: amino acid copolymer membrane versus hydrocolloid dressing. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1994;42(11):1180‐3. - PubMed
Imamura 1989 {published data only}
-
- Imamura Y. The clinical effect of KT‐136 (sugar and povidone‐iodine ointment) on decubitus ulcers: a comparative study with lysozyme ointment. Japanese Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1989;17(Suppl 1):255‐80.
Kaya 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kaya AZ, Turani N, Akyüz M. The effectiveness of a hydrogel dressing compared with standard management of pressure ulcers. Journal of Wound Care 2005;14(1):42‐4. - PubMed
Kraft 1993 {published data only}
-
- Kraft MR, Lawson L, Pohlmann B, Reid Lokos C, Barder L. A comparison of Epi‐Lock and saline dressings in the treatment of pressure ulcers. Decubitus 1993;6(6):42‐8. - PubMed
Matzen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Matzen S, Peschardt A, Alsbjørn B. A new amorphous hydrocolloid for the treatment of pressure sores: a randomised controlled study. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery 1999;33(1):13‐5. - PubMed
Meaume 2003 {published data only}
-
- Meaume S, Looverbosch D, Heyman H, Romanelli M, Ciangherotti A, Charpin S. A study to compare a new self‐adherent soft silicone dressing with a self‐adherent polymer dressing in stage II pressure ulcers. Ostomy/Wound Management 2003;49(9):44‐6, 48. - PubMed
-
- Meaume S, Looverbosch D, Heyman H, Romanelli M, Ciangherotti, Charoin S. Randomised open multicentric study comparing Mepilex Border with Tielle in patients with grade II pressure ulcers [Etude ouverte randomisée multicentrique comparant Mepilex Border à Tielle chez des patients porteurs d’escarres de stade II]. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:47.
Motta 1999 {published data only}
-
- Motta G, Dunham L, Dye T, Mentz J, O'Connell‐Gifford E, Smith E. Clinical efficacy and cost‐effectiveness of a new synthetic polymer sheet wound dressing. Ostomy/Wound Management 1999;45(10):41, 44‐6, 48. - PubMed
Muller 2001 {published data only}
-
- Muller E, Leen MW, Bergemann R. Economic evaluation of collagenase‐containing ointment and hydrocolloid dressing in the treatment of pressure ulcers. PharmacoEconomics 2001;19(12):1209‐16. - PubMed
-
- Leen MW. Collagenase treatment of chronic ulcers. Wound Repair and Regeneration 1998;6(5):483.
Neill 1989a {published data only}
-
- Neill KM, Conforti C, Kedas A, Burris JF. Pressure sore response to a new hydrocolloid dressing. Wounds 1989;1:173‐85.
Nisi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Nisi G, Brandi C, Grimaldi L, Calabrò M, D'Aniello C. Use of a protease‐modulating matrix in the treatment of pressure sores. Chirurgia Italiana 2005;57(4):465‐8. - PubMed
Nussbaum 1994 {published data only}
-
- Nussbaum EL, Biemann I, Mustard B, Michlovitz S, Buinewicz BR. Comparison of ultrasound/ultraviolet‐C and laser for treatment of pressure ulcers in patients with spinal cord injury. Physical Therapy 1994;74(9):812‐23; discussion 24. - PubMed
Oleske 1986 {published data only}
-
- Oleske DM, Smith XP, White P, Pottage J, Donovan MI. A randomized clinical trial of two dressing methods for the treatment of low‐grade pressure ulcers. Journal of Enterostomal Therapy 1986;13(3):90‐8. - PubMed
Parish 1979 {published data only}
-
- Parish LC, Collins E. Decubitus ulcers: a comparative study. Cutis 1979;23(1):106‐10. - PubMed
Payne 2004 {published data only}
-
- Payne WG, Wright TE, Ochs D, Mannari RJ, Robson MC, Edington H, et al. An exploratory study of dermal replacement therapy in the treatment of stage III pressure ulcers. Journal of Applied Research 2004;4(1):12‐23.
Payne 2009 {published data only}
-
- Payne WG, Posnett J, Alvarez O, Brown‐Etris M, Jameson G, Wolcott R, et al. A prospective, randomized clinical trial to assess the cost‐effectiveness of a modern foam dressing versus a traditional saline gauze dressing in the treatment of stage II pressure ulcers. Ostomy/Wound Management 2009;55(2):50‐5. - PubMed
Piatkowski 2012 {published data only}
-
- Piatkowski A, Ulrich D, Seidel D, Abel M, Pallua N, Andriessen A. RCT comparing collagen and foam dressings in pressure ulcers evaluating their influence on healing time angiogenesis and pro‐inflammatory cells. EWMA Journal 2011;11(2 Suppl):42.
-
- Piatkowski A, Ulrich D, Seidel D, Abel M, Pallua N, Andriessen A. Randomised, controlled pilot to compare collagen and foam in stagnating pressure ulcers. Journal of Wound Care 2012;21(10):505‐11. - PubMed
-
- Piatkowski A, Ulrich D, Seidel S, Abel M, Pallua N, Andriessen A. Randomized controlled pilot comparing collagen and foam dressings in pressure ulcer patients evaluating their influence on healing time, angiogenesis and proinflammatory cells. 15ème Conférence Nationale des Plaies et Cicatrisations ‐ prévention et traitement; 2011 January 16‐18; Paris, France. 2011:79.
Price 2000 {published data only}
-
- Price P, Bale S, Crook H, Harding KG. The effect of a radiant heat dressing in the management of patients with Stage III and IV pressure ulcers. 13th Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and 10th Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 2000 April 1‐4; Dallas (TX). 2000:D14.
-
- Price P, Bale S, Crook H, Harding KG. The effect of a radiant heat dressing on pressure ulcers. Journal of Wound Care 2000;9(4):201‐5. - PubMed
Ramos‐Torrecillas 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ramos‐Torrecillas J, Garcia‐Martinez O, Luna‐Bertos E, Ocana‐Peinado FM, Ruiz C. Effectiveness of platelet‐rich plasma and hyaluronic acid for the treatment and care of pressure ulcers. Biological Research for Nursing 2015;17(2):152‐8. - PubMed
Rees 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rees RS, Robson MC, Smiell JM, Perry BH. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of Becaplermin (recombinant human platelet‐derived growth factor‐BB) gel in the treatment of pressure ulcers. Wound Repair and Regeneration 1998;6(3):246. - PubMed
-
- Rees RS, Robson MC, Smiell JM, Perry BH. Becaplermin gel in the treatment of pressure ulcers: a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Wound Repair and Regeneration 1998;6(5):478. - PubMed
-
- Rees RS, Robson MC, Smiell JM, Perry BH, the Pressure Ulcer Study Group. Becaplermin gel in the treatment of pressure ulcers: a phase II randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Wound Repair and Regeneration 1999;7(3):141‐7. - PubMed
Romanelli 2001 {published data only}
-
- Romanelli M, Semeraro RM, Siani S. A pilot study on the use of a tripeptide‐copper gel on pressure ulcers: preliminary results. 11th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2001 May 17‐19; Dublin, Ireland. 2001:82.
Sebern 1986 {published data only}
-
- Sebern MD. Pressure ulcer management in home health care: efficacy and cost effectiveness of moisture vapor permeable dressing. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1986;67(10):726‐9. - PubMed
Seeley 1999 {published data only}
-
- Seeley J, Jensen JL, Hutcherson J. A randomized clinical study comparing a hydrocellular dressing to a hydrocolloid dressing in the management of pressure ulcers. Ostomy/Wound management 1999;45(6):39‐44, 46. - PubMed
Serena 2010 {published data only}
-
- Serena T, Wolcott R, DiSalvo M, Hurley D. Bilayered living cell‐based treatment for pressure ulcers: results of a prospective, randomized, multi‐center, open‐label clinical trial. Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and the Wound Healing Society; 2010 April 17‐20; Orlando (FL). 2010:S38. [Abstract CR‐070]
Sipponen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sipponen A, Jokinen JJ, Lohi J, Sipponen P. Efficiency of resin salve from Norway spruce in treatment of pressure ulcers and chronic surgical and traumatic wounds. 19th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2009 May 20‐22; Helsinki, Finland. 2009:41.
-
- Sipponen A, Jokinen JJ, Sipponen P, Papp A, Sarna S, Lohi J. Beneficial effect of resin salve in treatment of severe pressure ulcers: a prospective, randomized and controlled multicentre trial. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;158(5):1055‐62. - PubMed
Sopata 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sopata M, Luczak J, Ciupinska M. Effect of bacteriological status on pressure ulcer healing in patients with advanced cancer. Journal of Wound Care 2002;11(3):107‐10. - PubMed
Thomas 1997a {published data only}
-
- Banks V, Fear‐Price M, Orpin J, Hagelstein S, Colgate G, Humphreys J, et al. A comparative open multi‐centre trial of Tielle hydropolymer dressing and Granuflex improved formulation. Fifth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995 November 21‐24, Harrogate, UK. 1996:163‐7.
-
- Thomas S, Banks V, Fear‐Price M, Hagelstein S, Harding KG, Orpin J, et al. A comparison of two dressings in the management of chronic wounds. Journal of Wound Care 1997;6(8):383‐6. - PubMed
Thomas 1998 {published data only}
-
- Thomas DR, Goode PS. Acemannan hydrogel versus saline dressings for pressure ulcers: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Medicine 1998;46(7):283A. - PubMed
-
- Thomas DR, Goode PS, LaMaster K, Tennyson T. Acemannan hydrogel dressing versus saline dressing for pressure ulcers. A randomized, controlled trial. Advances in Wound Care 1998;11(6):273‐6. - PubMed
Thomas 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thomas DR, Diebold MR, Eggemeyer LM. A controlled, randomized, comparative study of a radiant heat bandage on the healing of stage 3‐4 pressure ulcers: a pilot study. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2005;6(1):46‐9. - PubMed
Van De Looverbosch 2004 {published data only}
-
- Looverbosch D, Heyman H, Dierick AM. Explorative, comparative study with enamel matrix protein in pressure ulcer stage II. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:X014.
Xakellis 1992 {published data only}
-
- Xakellis GC, Chrischilles EA. Hydrocolloid versus saline‐gauze dressings in treating pressure ulcers: a cost‐effectiveness analysis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1992;73(5):463‐9. - PubMed
Yapucu Güneş 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yapucu Güneş U, Eşer I. Effectiveness of a honey dressing for healing pressure ulcers. Journal of Wound Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2007;34(2):184‐90. - PubMed
Zeron 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zeron HM, Krotzsch Gomez FE, Hernandez Munoz RE. Pressure ulcers: a pilot study for treatment with collagen polyvinylpyrrolidone. International Journal of Dermatology 2007;46(3):314‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbott 1968 {published data only}
Agren 1985 {published data only}
-
- Agren MS, Stromberg HE. Topical treatment of pressure ulcers. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 1985;19(1):97‐100. - PubMed
Ahmad 2008 {published data only}
Alvarez 1999 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez OM, Fernandez‐Obregon A, Davis SC, Cazzaniga AL, Pacheco H. A prospective randomized clinical trial of papain‐urea for the debridement of pressure ulcers. 31st Annual Wound, Ostomy and Continence Conference; 1999 June 19‐23; Minneapolis (MN). 1999:488.
Alvarez 2000a {published data only}
-
- Alvarez OM, Fernandez‐Obregon A, Rogers RS, Bergamo L, Masso J, Black M. Chemical debridement of pressure ulcers: a prospective, randomized, comparative trial of collagenase and papain/urea formulations. Wounds 2000;12(2):15‐25.
Alvarez 2000b {published data only}
-
- Alvarez OM, Fernandez‐Obregon A, Hoboken NJ, Rogers RR, Masso J, Davis SC, et al. Enzymatic debridement of pressure ulcers: a prospective randomized comparative clinical trial. 13th Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and 10th Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 2000 April 1‐4; Dallas (TX). 2000:C69.
Alvarez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez OM, Fernandez‐Obregon A, Rogers RS, Bergamo L, Masso J, Black M. A prospective, randomized, comparative study of collagenase and papain‐urea for pressure ulcer debridement. Wounds 2002;14(8):293‐301.
Alvarez Vázquez 2014 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez Vázquez JC, Estany Gestal A, Álvarez Suárez T, Mosquera JB, Castro Prado J, Gutiérrez Moeda E, et al. Prevention of deterioration of the cutaneous integrity in the sacral area through the application of an atraumatic self‐adherent foam dressing [Prevención del deterioro de la integridad cutánea en el sacro mediante la aplicación de una espuma de adhesión atraumática]. Metas de Enfermería 2014;17(2):14‐20.
Aminian 1999 {published data only}
-
- Aminian R, Shams M, Karim‐Aghaee B, Soveyd M, Omrani GR. The role of the autologous platelet‐derived growth factor in the management of decubitus ulcer. Archives of Iranian medicine 1999;2(2):98‐101.
Amione 2005 {published data only}
-
- Amione P, Ricci E, Topo F, Izzo L, Pirovano R, Rega V, et al. Comparison of Allevyn Adhesive and Biatain Adhesive in the management of pressure ulcers. Journal of Wound Care 2005;14(8):365‐70. - PubMed
Anitua 2008 {published data only}
-
- Anitua E, Aguirre JJ, Algorta J, Ayerdi E, Cabezas AI, Orive G, et al. Effectiveness of autologous preparation rich in growth factors for the treatment of chronic cutaneous ulcers. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2008;84(2):415‐21. - PubMed
Anonymous 1982 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Does metronidazole help leg ulcers and pressure sores?. Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin 1982;20(3):9‐10. - PubMed
Anonymous 2000 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Vacuum‐assisted closure for chronic wound healing. Tecnologica 2000;MAP (Medical Advisory Panel) Supplement:19‐20. - PubMed
Anzai 1989 {published data only}
-
- Anzai T, Shiratori A, Otomo E, Honda S, Yamamoto T, Nishikawa T, et al. Evaluation of clinical utility of NI‐009 on various cutaneous ulcers: comparative study with base. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicine) 1989;5(12):2585‐612.
Avanzi 1998a {published data only}
-
- Avanzi A, Martinelli R, Accardi S, Giraudi C, Peroli P, Rowan S. An adhesive hydrocellular dressing versus a hydrocolloid dressing in the treatment of 2nd and 3rd degree pressure sores. Eighth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1998 April 26‐28; Madrid, Spain. 1998:116.
Avanzi 1998b {published data only}
-
- Avanzi R, Martinelli R, Accardi S, Giraudi C, Peroli P, Andriessen A, et al. Adhesive hydrocellular dressing versus hydrocolloid dressing in the treatment of stage II and III pressure sores. European Wound Management Association Conference; 1998 November; Harrogate, UK. 1998:11.
Avanzi 2000a {published data only}
-
- Avanzi A, Martinelli M, Accardi S, Giraudi C, Peroli P, Andriessen A. Adhesive hydrocellular dressing vs hydrocolloid dressing in the treatment of 2nd and 3rd degree pressure sores. 10th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2000 May 18‐20; Stockholm, Sweden. 2000:29.
Avanzi 2000b {published data only}
-
- Avanzi A, Martinelli R, Accardi S, Giraudi C, Peroli P, Rowan S, et al. Adhesive hydrocellular dressing vs hydrocolloid dressing in the treatment of pressure sores. First World Wound Healing Congress; 2000 September 10‐13; Melbourne, Australia. 2000:90.
Avanzi 2000c {published data only}
-
- Avanzi A, Martinelli M, Accardi S, Giraudi C, Peroli P, Andriessen A, et al. Adhesive hydrocellular dressing vs hydrocolloid dressing in the treatment of 2nd and 3rd degree pressure sores. A prospective, controlled randomised comparative multi‐centre clinical evaluation. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2000;8:A406.
Avanzi 2001 {published data only}
-
- Avanzi A, Martinelli M, Accardi S, Giraudi C, Peroli P, Andreissen A, et al. Adhesive hydrocellular dressing vs hydrocolloid dressing in the management of stage 2 and stage 3 pressure ulcers. 11th European Tissue Repair Society Annual Conference; 2001 September 5‐8; Cardiff, Wales. 2001:43.
Baade 1965 {published data only}
-
- Baade S. Local application of an anabolically active steroid to promote wound healing. Die Medizinische Welt 1965;32:1828‐30. - PubMed
Baatenburg de Jong 2004 {published data only}
-
- Baatenburg de Jong H, Admiraal H. Comparing cost per use of 3M Cavilon No Sting Barrier Film with zinc oxide oil in incontinent patients. Journal of Wound Care 2004;13(9):398‐400. - PubMed
Baker 1981 {published data only}
-
- Baker PG, Haig G. Metronidazole in the treatment of chronic pressure sores and ulcers. A comparison with standard treatment in general practice. Practitioner 1981;225(1354):569‐73. - PubMed
Bale 1997b {published data only}
-
- Bale S, Banks V, Hagelstein S, Harding KG. A randomized, controlled parallel‐group clinical trial to compare two amorphous hydrogels in the debridement of pressure sores. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1996 October 1‐4; Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1997:244‐8.
Bale 1997c {published data only}
-
- Bale S, Crook H. The preliminary results of a comparative study on the performance characteristics of a new hydrogel versus an existing hydrogel on necrotic pressure ulcers. European Wound Management Association Conference; 1997 April 27‐29; Milan, Italy. 1997:66‐8.
Bale 1998a {published data only}
-
- Bale S, Hagelstein S, Banks V, Harding KG. Costs of dressings in the community. Journal of Wound Care 1998;7(7):327‐30. - PubMed
-
- Harding KG, Bale S, Banks V, Orpin J. A cost effectiveness study using Allevyn hydrocellular dressings. Fourth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1994 September 6‐9; Copenhagen, Denmark. 1995:57‐9.
Bale 1998b {published data only}
-
- Bale S, Banks V, Haglestein S, Harding KG. A comparison of two amorphous hydrogels in the debridement of pressure sores. Journal of Wound Care 1998;7(2):65‐8. - PubMed
Bale 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bale S, Tebbie N, Price P. A topical metronidazole gel used to treat malodorous wounds. British Journal of Nursing 2004;13(11):S4‐11. - PubMed
Banks 1997a {published data only}
-
- Banks V, Bale S, Harding K, Harding EF. Evaluation of a new polyurethane foam dressing. Journal of Wound Care 1997;6(6):266‐9. - PubMed
-
- Banks V, Bale S, Harding KG, Harding EF. A randomized, stratified, controlled, parallel‐group clinical trial of a new polyurethane foam dressing (Lyofoam Extra) versus a hydrocellular dressing in the treatment of moderate to heavily exuding wounds. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1996 October 1‐4; Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1997:235‐3.
-
- Banks V, Bale S, Harding KG, Harding EF. An interim analysis of a randomized stratified controlled parallel‐group clinical trial of a new polyurethane foam dressing versus a hydrocellular dressing in the treatment of moderate to heavily exuding wounds. Fifth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995, November 21‐24; Harrogate, UK. 1996:177‐80.
-
- Banks V, Fear M, Orpin J, Hagelstein S, Thomas N, Colgate G, et al. A comparative open multi‐center trial of hydropolymer dressing and hydrocolloid. Ninth Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and Sixth Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 1996 April 20‐24; Atlanta (GA). 1996:113.
-
- Banks V, Hagelstein S, Bale S, Harding KG. A comparison of a new polyurethane dressing versus a hydrocellular dressing in the treatment of moderate to heavily exudating wounds. Ninth Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and Sixth Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 1996 April 20‐24; Atlanta (GA). 1996:113.
Banks 1997b {published data only}
-
- Banks, Fear M, Hagelstein S, Bale S, Thomas S, Harding KG. A randomized controlled community comparison of Duoderm Extra Thin with an adhesive film as a secondary dressing. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1996 October 1‐4; Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1997:238‐41.
Barnes 1992 {published data only}
-
- Barnes J, Burns K. Management of pressure sores: a comparison of Granuflex hydrocolloid dressing and Granuflex E hydrocolloid dressing. Euroservices Communication: Going into the '90s: the Pharmacist and Wound Care 1992:19‐21.
Bazzigaluppi 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bazzigaluppi F, Biraghi MG, Fano M, Moschin AM, Toscani P, Cervone C, et al. Cadexomer iodine in the treatment of cutaneous ulcers: open, multicentric trial. Gazetta Medica Italiana 1991;150(11):471‐80.
Becker 1984 {published data only}
-
- Becker L, Goodemote C. Treating pressure sores with or without antacid. American Journal of Nursing 1984;84(3):351‐2. - PubMed
Beele 2010 {published data only}
Berard 1986 {published data only}
-
- Berard P, Montandon S, Jedynak D, Saubier EC. Trial of a hydrocolloid in occlusive dressings in the treatment of skin wounds, "Duoderm". Revista de Enfermeria 1986;9(1):17‐20. - PubMed
Bigolari 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bigolari M, Mosca P, Astengo F, Biraghi M, Balestreri R. Randomized clinical trial with Cadexomer iodine in decubitus ulcers [Studio clinico randomizzato con cadexomero iodico nelle ulcere da decubito]. Gazzetta Medica Italiana 1991;150(5):177‐85.
Bito 2012 {published data only}
Blanco Blanco 2002 {published data only}
-
- Blanco Blanco J, Ballester Torralba J, Rueda Lopez J, Torra i Bou JE. Comparative study of the use of a heel protecting bandage and a special hydrocellular dressing in the prevention of pressure ulcers in elderly participants. 12th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2002 May 23‐25; Granada, Spain. 2002:114.
Blum 1973 {published data only}
-
- Blum G. Therapeutic results with Iruxol in ulcus cruris, decubitus ulcer and burns. Schweizerische Rundschau für Medizin Praxis 1973;62(26):820‐6. - PubMed
Boxer 1969 {published data only}
-
- Boxer AM, Gottesman N, Bernstein H, Mandl I. Debridement of dermal ulcers and decubiti with collagenase. Geriatrics 1969;24(7):75‐86. - PubMed
Boykin 1989 {published data only}
-
- Boykin A, Winland‐Brown J. Pressure sores: nursing management. National League for Nursing Publications 1989;15(2232):252‐6.
Brady 1987 {published data only}
-
- Brady SM. Management of pressure sores with occlusive dressings in a select population. Nursing Management 1987;18:47‐50. - PubMed
Brem 2000 {published data only}
-
- Brem H, Kirsner RS. Use of Graftskin (APLIGRAF) in the treatment of pressure ulcers and acute wounds. Wounds 2000;12(5 (Suppl)):72A‐77A.
Brett 2003 {published data only}
-
- Brett DW, Alvarez OM, Fernandez‐Obregon AC. March 2003 Letters to the Editor. Wounds 2003;15(3):available from: www.woundsresearch.com/article/1368.
Brown‐Etris 1999a {published data only}
-
- Brown‐Etris M, Punchello M, Shields D, Bateman D, Stanfield J, Edvalson J, et al. Final report: a comparison clinical study to evaluate the efficacy of 20% hypertonic wound gel vs collagenase ointment for the debridement of nonviable tissue in dermal wounds. 31st Annual Wound, Ostomy and Continence Conference; 1999 June 19‐23; Minneapolis (MN). 1999:245.
Brown‐Etris 1999b {published data only}
-
- Brown‐Etris M, Punchello M, Shields D, Barnes H, Galluzzi K, Whalen A, et al. Interim analysis of a randomized prospective multi‐centred 20‐week comparison of two wound management systems on pressure ulcers. 31st Annual Wound, Ostomy and Continence Conference; 1999 June 19‐23; Minneapolis (MN). 1999.
Burgos 2000 {published data only}
-
- Burgos A, Gimenez J, Moreno E, Campos J, Ardanaz J, Talaero C, et al. Collagenase ointment application at 24‐ versus 48‐hour intervals in the treatment of pressure ulcers. A randomised multicentre study. Clinical Drug Investigation 2000;19(6):399‐407.
Burke 1998 {published data only}
-
- Burke DT, Ho CH, Saucier MA. Hydrotherapy effects on pressure ulcer healing. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1997;78(9):1053. - PubMed
-
- Burke DT, Ho CH, Saucier MA, Stewart G. Effects of hydrotherapy on pressure ulcer healing. American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1998;77(5):394‐8. - PubMed
Capillas Pérez 2000 {published data only}
-
- Capillas Pérez R, Cabre Aguilar V, Gil Colome AM, Gaitano Garcia A, Torra i Bou JE. Comparison of the effectiveness and cost of treatment with humid environment as compared to traditional cure. Clinical trial on primary care patients with venous leg ulcers and pressure ulcers. Revista de Enfermería 2000;23(1):17‐24. - PubMed
Carusone 2001 {published data only}
-
- Carusone A, Carella GR, Coppini R, Lorenzo E, Mancuso M, Mazzon S, et al. Effectiveness evaluation of a specific topic treatment for pressure sores prevention in high risk patients using transcutaneous oxymetry. 11th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2001 May 17‐19; Dublin, Ireland. 2001:75.
Casali 1997 {published data only}
-
- Casali B, Bonati PA, DelGin G, Ascari C. The use of a blood platelet lysate in the treatment of pressure sores. Experimental observations. European Wound Management Association Conference; 1997 April 27‐29; Milan, Italy. 1997.
Chang 1998 {published data only}
-
- Chang KW, Alsagoff S, Ong KT, Sim PH. Pressure ulcers: randomised controlled trial comparing hydrocolloid and saline gauze dressings. Medical Journal of Malaysia 1998;53(4):428‐31. - PubMed
Chen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chen Q. Effect of egg albumen combined with infrared ray irradiation to treat patients with bedsore induced by fecal incontinence. Chinese Nursing Research 2004;18(9A):1550‐1.
Cheneworth 1994 {published data only}
-
- Cheneworth CC, Hagglund KH, Valmassoi B, Brannon C. Portrait of practice: healing heel ulcers. Advances in Wound Care 1994;7(2):44‐8. - PubMed
Chirwa 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chirwa Z, Bhengu T, Litiane K. The cost effectiveness of using calcium alginate silver matrix in the treatment of wounds. EWMA Journal 2010;10(2):257. [Abstract P299]
Chuangsuwanich 2011a {published data only}
Chuangsuwanich 2011b {published data only}
-
- Chuangsuwanich A, Charnsanti O, Lohsiriwat V, Kangwanpoom C, Thong‐In N. The efficacy of silver mesh dressing compared with silver sulfadiazine cream for the treatment of pressure ulcers. Chotmaihet Thangphaet (Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand) 2011;94(5):559‐65. - PubMed
Chuangsuwanich 2013 {published data only}
Colin 1996a {published data only}
-
- Colin D, Kurring PA, Yvon C. Managing sloughy pressure sores. Journal of Wound Care 1996;5(10):444‐6. - PubMed
Colin 1996b {published data only}
-
- Colin D, Kurring PA, Quinlan D, Yvon C. The clinical investigation of an amorphous hydrogel compared with a dextranomer paste dressing in the management of sloughy pressure sores. Fifth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995 November 21‐24; Harrogate, UK. 1996:155‐9.
Colonna 2004 {published data only}
-
- Colonna MR, Amadeo G, Giofre C, Strano A, Stagno D'Alcontres F. Are nanocristalline silver dressings effective in reducing both secretions and bacterial colonization in necrotic infected wounds?. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:91.
Cooper 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cooper P, Gray D, Russell F. Comparing Tena Wash Mousse with Clinisan Foam Cleanser: the results of a comparative study. Wounds UK 2008;4(3):12‐21.
Coutts 2000 {published data only}
-
- Coutts P, Sibbald RG, Inman K, Maltby‐Stephens N. The use of an adhesive hydrocellular foam compared to a hydrocolloid dressing for the treatment of Stage II and III pressure ulcers. 13th Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and 10th Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 2000 April 1‐4; Dallas, (TX). 2000:D7.
D'Aniello 1998 {published data only}
-
- D'Aniello C. Hydrocolloid dressing preparation to surgery for 3rd degree pressure sores. Eighth Annual Meeting of the European Tissue Repair Society; 1998 August 27‐30; Copenhagen, Denmark. 1998:A463.
Dat 2014 {published data only}
Day 1995 {published data only}
-
- Day A, Dombranski S, Farkas C, Foster C, Godin J, Moody M, et al. Managing sacral pressure ulcers with hydrocolloid dressings: results of a controlled, clinical study. Ostomy/Wound management 1995;41(2):52‐4, 56, 58 passim. - PubMed
Dealey 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dealey C, Keogh A, Dealey C, Keogh A. A randomized, controlled, parallel‐group clinical trial of a new polyurethane foam island dressing versus a hydrocolloid island dressing in the treatment of grade II and III pressure sores. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995 November 21‐24; Harrogate, UK. 1997:94‐5.
Dealey 1998 {published data only}
-
- Dealey C. Obtaining the evidence for clinically effective wound care. British Journal of Nursing 1998;7(20):1236, 1238, 1240 passim. - PubMed
Dealey 2008 {published data only}
-
- Dealey C. Review: evidence of the effectiveness of hydrocolloids for healing pressure ulcers is limited. Evidence‐Based Nursing 2008;11(4):115. - PubMed
De Laat 2005 {published data only}
-
- Laat EH, Scholte op Reimer WJ, Achterberg T. Pressure ulcers: diagnostics and interventions aimed at wound‐related complaints: a review of the literature. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2005;14(4):464‐72. - PubMed
De Laat 2011 {published data only}
-
- Laat EH, Boogaard MH, Spauwen PH, Kuppevelt DH, Goor H, Schoonhoven L. Faster wound healing with topical negative pressure therapy in difficult‐to‐heal wounds: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Annals of Plastic Surgery 2011;67(6):626‐31. - PubMed
Dierick 2004a {published data only}
-
- Dierick AM, Looverbosch D, Heyman H. Explorative, comparative study with enamel matrix protein in pressure ulcer stage II. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:15.
Dierick 2004b {published data only}
-
- Dierick AM, Looverbosh D, Heyman H, Looverbosh D. An open, randomised, explorative, phase II, investigation comparing enamel matrix derivative proteins (EMD) and control in patients with pressure ulcer stage II. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2004;12(2):A26.
Dobrzanski 1990 {published data only}
-
- Dobrzanski S, Kelly CM, Gray JI, Gregg AJ, Cosgrove CA. Granuflex dressings in treatment of full thickness pressure sores. Professional Nurse 1990;5(11):594‐9. - PubMed
Durović 2008 {published data only}
-
- Durović A, Maric D, Brdareski Z, Jevtic M, Durdevic S. The effects of polarized light therapy in pressure ulcer healing. Vojnosanitetski Pregled (Military‐Medical and Pharmaceutical Review) 2008;65(12):906‐12. - PubMed
Dwivedi 2016 {published data only}
-
- Dwivedi MK, Srivastava RN, Bhagat AK, Agarwal R, Baghel K, Jain A, et al. Pressure ulcer management in paraplegic patients with a novel negative pressure device: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Wound Care 2016;25(4):199‐207. - PubMed
Ellis 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ellis S, Leaper D. Observed effects of local radiant heat on the quality and quantity of bacteria in full thickness pressure ulcers. 12th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2002 May 23‐25; Granada, Spain. 2002:146.
Ellis 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ellis SL, Finn P, Noone M, Leaper DJ. Eradication of methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus from pressure sores using warming therapy. Surgical Infections 2003;4(1):53‐5. - PubMed
El Zayat 1989 {published data only}
-
- Zayat SG. Preliminary experience with topical phenytoin in wound healing in a war zone. Military Medicine 1989;154(4):178‐80. - PubMed
Engdahl 1980 {published data only}
-
- Engdahl E. Clinical evaluation of Debrisan® on pressure sores. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1980;28(3):377‐80.
Esch 1989 {published data only}
-
- Esch B, Raptis G. Treatment of decubitus ulcer with Crilanomer and Dextranomer. Zeitschrift fur Hautkrankheiten 1989;64(12):1135‐8. - PubMed
Farsaei 2014 {published data only}
-
- Farsaei S, Khalili H, Farboud ES, Karimzadeh I, Beigmohammadi MT. Efficacy of topical atorvastatin for the treatment of pressure ulcers: a randomized clinical trial. Pharmacotherapy 2014;34(1):19‐27. - PubMed
Fear 1992 {published data only}
-
- Fear M, Thomas S. Wound cleansing properties of Debrisan and Scherisorb gel: interim results of a clinical trial. First European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1991 September 4‐6; Cardiff, UK. 1992:162‐4.
Feldman 2005 {published data only}
-
- Feldman D, Jennings A, Andino R. Preliminary evaluation of an electrical stimulation bandage (POSiFECT dressing). Wound Repair and Regeneration 2006;14(1):A29. [Abstract 242]
Felzani 2011 {published data only}
-
- Felzani G, Spoletini I, Convento A, Lorenzo B, Rossi P, Miceli M. Effect of lysine hyaluronate on the healing of decubitus ulcers in rehabilitation patients. Advances in Therapy 2011;28(5):439‐45. - PubMed
Flanagan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Flanagan M. The efficacy of a hydrogel in the treatment of wounds with non‐viable tissue. Journal of Wound Care 1995;4(6):264‐7. - PubMed
Ford 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ford CN, Reinhard ER, Yeh D, Syrek D, Las Morenas A, Bergman SB, et al. Interim analysis of a prospective, randomized trial of vacuum‐assisted closure versus the healthpoint system in the management of pressure ulcers. Annals of Plastic Surgery 2002;49(1):55‐61. - PubMed
Fowler 1983 {published data only}
-
- Fowler EM. Clinical trial report: new, once‐daily pressure sore dressing speeds healing. Registered Nurse 1983;46(4):56‐7. - PubMed
Franek 2011 {published data only}
-
- Franek A, Kostur R, Taradaj J, Blaszczak E, Szlachta Z, Dolibog P, et al. Effect of high voltage monophasic stimulation on pressure ulcer healing: results from a randomized controlled trial. Wounds 2011;23(1):15‐23.
Franek 2012 {published data only}
-
- Franek A, Kostur R, Polak A, Taradaj J, Szlachta Z, Blaszczak E, et al. Using high‐voltage electrical stimulation in the treatment of recalcitrant pressure ulcers: results of a randomized, controlled clinical study. Ostomy/Wound Management 2012;58(3):30‐44. - PubMed
Franken 1999 {published data only}
-
- Franken K, Neuman HA, Andersen KE, Larsen AM. The preliminary results of a comparative study of performance characteristics and safety of a foam dressing Biatain Adhesive versus Tielle on pressure sores. Ninth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1999 November 9‐11; Harrogate, UK. 1999:8.
Fulco 2015 {published data only}
-
- Fulco I, Erba P, Valeri RC, Vournakis J, Schaefer DJ. Poly‐N‐acetyl glucosamine nanofibers for negative‐pressure wound therapies. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2015;23(2):197‐202. - PubMed
Fønnebø 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fønnebø V. Well‐established ointment from folk medicine heals pressure ulcers better than conventional treatment. Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies 2008;13(3):183‐4.
García González 2002 {published data only}
-
- García González RF, Verdu Soriano J, Gago Fornells M, Rueda Lopez J, Segovia Gomez T, Peters Gutierrez FS. The effect of non‐irritant film barriers on the control of maceration in the care of pressure ulcers using adhesive hydrocolloid dressings. 12th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2002 May 23‐25; Granada, Spain. 2002:224.
Garrett 1969 {published data only}
-
- Garrett TA. Bacillus subtilis protease: a new topical agent for debridement. Clinical Medicine 1969;76(May):11‐5.
Gerding 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gerding GA, Browning JS. Oxyquinoline‐containing ointment vs. standard therapy for Stage I and Stage II skin lesions. Dermatology Nursing 1992;4(5):389‐98. - PubMed
Gilligan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gilligan AM, Waycaster C. Cost‐effectiveness of becaplermin gel on wound closure in the treatment of pressure ulcers. Value in Health 2014;17(3):A249.
Goldmeier 1997 {published data only}
-
- Goldmeier S. The use of CTM with essential fatty acid in decubits ulcers of cardiac patients [sic] [Comparaçäo dos triglicerídeos cadeia média com ácidos graxos essenciais, com o polivinilpirrolidona‐iodo no tratamento das úlceras de decúbito em pacientes cardiopatas]. Revista Paulista de Enfermagem 1997;16(1/3):30‐4.
Gostishchev 1983 {published data only}
-
- Gostishchev VK, Vasilkova ZF, Khanin AG, Vavilova GS, Lebedskoj AG. Debrisan in the treatment of purulent wounds. Vestnik Khirurgii Imeni I. I. Grekova 1983;131(9):56‐9. - PubMed
Greer 1999 {published data only}
-
- Greer SE, Longaker MT, Margiotta M. Preliminary results from a multicenter, randomized, controlled study of the use of subatmospheric pressure dressing for pressure ulcer healing. Wound Repair and Regeneration 1999;7(4):A255.
Gregory 1997 {published data only}
-
- Gregory JE, Cox DA, Borchers V, Pfister C. A controlled trial of RH‐TGF‐B3 in decubitus ulcers. Seventh Annual Meeting of the European Tissue Repair Society; 1997 August 23‐26; Köln, Germany. 1997:3.
Guthrie 1989 {published data only}
-
- Guthrie M, Diakiw J, Zaydon AC, Clark M, Rinaldi E. A randomized double‐blind clinical study of dermagran dual therapeutic system in the treatment of decubitus ulcers. Wounds 1989;1(3):142‐54.
Hamilton Hislop 1962 {published data only}
-
- Hamilton Hislop HH, Pritchard JG. A clinical trial of creams for the prevention and treatment of pressure sores in geriatric patients. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1962;16(6):409‐12. - PubMed
Hampton 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hampton S. Treatment of macerated and excoriated peri‐wound areas. Seventh European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1997 November 18‐20; Harrogate, UK. 1998:46.
Harada 1996 {published data only}
-
- Harada S, Ohara K, Takemura T, Niimura M, Nishikawa T, Kukita A. Clinical evaluation of M‐1011G (lysozyme hydrochloride ointment‐gauze) in patients with decubitus ulcer: a multi‐centered comparative study with lysozyme hydrochloride ointment. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicine) 1996;12(2):321‐39.
Harding 1996 {published data only}
-
- Harding KG, Bale S, Stock J, Shutler S, Squires D, Wilson I, et al. A multi‐center comparison of a hydrocellular adhesive dressing and a hydrocolloid dressing in the management of stage II and III pressure ulcers. Ninth Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and 6th Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 1996 April 20‐24; Atlanta (GA). 1996:114.
Harding 2000 {published data only}
-
- Harding KG, Cutting K, Price P. The cost‐effectiveness of wound management protocols of care. British Journal of Nursing 2000;9(19):Tissue Viability Supplement: S6, S8, S10 passim. - PubMed
Helaly 1988 {published data only}
-
- Helaly P, Vogt E, Schneider G, Ballanzin D, Balmer A, Benninger R, et al. Wound healing impairment and topical enzymatic therapy: a multicentric double‐blind study. Schweizerische Rundschau für Medizin Praxis 1988;77(52):1428‐34. - PubMed
Heuckeroth 2013 {published data only}
-
- Heuckeroth L, Palm R. How effective are silver wound dressings? Wound healing of critically colonized and infected wounds. Pflege Zeitschrift 2013;66(6):362‐5. - PubMed
Heyer 2013 {published data only}
-
- Heyer K, Augustin M, Protz K, Herberger K, Spehr C, Rustenbach SJ. Effectiveness of advanced versus conventional wound dressings on healing of chronic wounds: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Dermatology 2013;226(2):172‐84. - PubMed
Hinz 1986 {published data only}
-
- Hinz J, Hautzinger H, Stahl KW. Rationale for and results from a randomised, double‐blind trial of tetrachlorodecaoxygen anion complex in wound healing. Lancet 1986;1(8485):825‐8. - PubMed
Hirshberg 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hirshberg J, Coleman J, Marchant B, Rees RS. TGF‐beta3 in the treatment of pressure ulcers: a preliminary report. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2001;14(2):91‐5. - PubMed
Hock 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hock S, Piaskowski P. A comparative randomized study on the performance of Comfeel SeaSorb dressing and Kaltostat on pressure sores. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1996 October 1‐4; Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1997:95.
Hofman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hofman D, Burgess B, Cherry GW, Robinson BJ, Ryan TJ. Management of pressure sores and leg ulcers with Duoderm hydroactive gel. Fourth Annual Meeting of the European Tissue Repair Society; 1994 August 25‐28; Oxford, UK. 1994:198.
Horch 2005 {published data only}
-
- Horch RE, Kopp J, Bach AD. The influence of Suprasorb P and Suprasorb C on proteases and their inhibitors in pressure sores. Zeitschrift für Wundheilung 2005;5:213.
Hsu 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hsu YC, Chang HH, Chen MF, Chen JC. Therapeutic effect of sheng‐ji‐san on pressure ulcers. American Journal of Chinese Medicine 2000;28(3‐4):391‐9. - PubMed
Hu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hu KX, Zhang HW, Zhou F, Yao G, Shi JP, Wang LF, et al. Observation on the therapeutic effects of negative‐pressure wound therapy on the treatment of complicated and refractory wounds. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi (Chinese Journal of Burns) 2009;25(4):249‐52. - PubMed
Ishibashi 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ishibashi Y, Niimura M, Nishikawa T, Imamura S, Ogawa H, Ikeda S, et al. Clinical results of multicenter comparative study with lyophilized porcine dermis (KT‐104) and solcoseryl ointment (SS‐094) on intractable skin ulcers: a prospective randomized trial. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicine) 1991;7(12):2811‐28.
Ishibashi 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ishibashi Y, Soeda S, Oura T, Nishikawa T, Niimura M, Nakajima H, et al. Clinical effects of KCB‐1, a solution of recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor, on skin ulcers: A phase III study comparing with sugar and povidone iodine ointment. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicine) 1996;12(10):2159‐87.
Janssen 1989 {published data only}
-
- Janssen PA, Janssen H, Cauwenbergh G, Doncker P, Beule K, Lewi P, et al. Use of topical ketanserin in the treatment of skin ulcers: a double‐blind study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1989;21(1):85‐90. - PubMed
Jercinovic 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jercinovic A, Karba R, Vodovnic L, Stefanovska A, Kroselj P, Turk R, et al. Low frequency pulsed current and pressure ulcer healing. IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering 1994;2(4):225‐33.
Johnson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Johnson A. Dressings for deep wounds. Nursing Times 1992;88(4):55‐6, 58. - PubMed
Kallianinen 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kallianinen LK, Hirshberg J, Marchant B, Rees RS. Role of platelet‐derived growth factor as an adjunct to surgery in the management of pressure ulcers. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2000;106(6):1243‐8. - PubMed
Karap 2008 {published data only}
-
- Karap Z. Significant difference in pain levels of delayed‐healing wounds during applying an ionic silver hydrofibre dressing. EWMA Journal 2008;8(2 (Suppl) ):244. [Abstract P281]
Kerihuel 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kerihuel JC. Effect of activated charcoal dressings on healing outcomes of chronic wounds. Journal of Wound Care 2010;19(5):208, 210‐2, 214‐5. - PubMed
Kerstein 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kerstein MD. Unexpected economics of ulcer care protocols. Southern Medical Journal 2004;97(2):135‐6. - PubMed
Kim 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kim YC, Shin JC, Park CI, Oh SH, Choi SM, Kim YS. Efficacy of hydrocolloid occlusive dressing technique in decubitus ulcer treatment: a comparative study. Yonsei Medical Journal 1996;37(3):181‐5. - PubMed
Kloth 2000a {published data only}
-
- Kloth LC, Berman JE, Nett MJ, Dumit‐Minkel S, Warzel J. A randomized controlled trial using a heated dressing on full‐thickness pressure ulcers. 13th Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and 10th Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 2000 April 1‐4; Dallas (TX). 2000:10.
Kloth 2000b {published data only}
-
- Kloth LC, Berman JE, Dumit‐Minkel S, Sutton CH, Papanek PE, Wurzel J. Effects of a normothermic dressing on pressure ulcer healing. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2000;13(2):69‐74. - PubMed
Kloth 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kloth LC, Berman JE, Nett MJ, Papanek PE. Twelve week randomized trial to evaluate noncontact normothermic wound therapy on full‐thickness pressure ulcers. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2001;9(5):399. - PubMed
Kloth 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kloth LC, Berman JE, Nett M, Papanek PE, Dumit‐Minkel S. A randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate the effects of noncontact normothermic wound therapy on chronic full‐thickness pressure ulcers. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2002;15(6):270‐6. - PubMed
Knudsen 1982 {published data only}
-
- Knudsen L, Solvhoj L, Christensen B. The use of a haemodialysate in the treatment of decubital ulcer: a double‐blind randomized clinical study. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1982;32(3):498‐504.
Kohr 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kohr R, Whittle H, MacLean B, Garrett M. A qualitative comparison of three sacral pressure ulcer dressings. 13th Annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and 10th Annual Medical Research Forum on Wound Repair; 2000 April 1‐4 ; Dallas (TX). 2000:D10‐11.
Kordestani 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kordestani S, Shahrezaee M, Tahmasebi MN, Hajimahmodi H, Haji Ghasemali D, Abyaneh MS. A randomised controlled trial on the effectiveness of an advanced wound dressing used in Iran. Journal of Wound Care 2008;17(7):323‐7. - PubMed
Kucan 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kucan JO, Robson MC, Heggers JP, Ko F. Comparison of silver sulfadiazine, povidone‐iodine and physiologic saline in the treatment of chronic pressure ulcers. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1981;29(5):232‐5. - PubMed
Kuflik 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kuflik A, Stillo JV, Sanders D, Roland K, Sweeney T, Lemke PM. Petrolatum versus RESURFIX ointment in the treatment of pressure ulcers. Ostomy/Wound Management 2001;47(2):52‐3, 55‐6. - PubMed
Kuisma 1987 {published data only}
-
- Kuisma I, Tamelander G. Mucopolysaccharide polysulphate cream in the prevention of pressure sores: a double blind study. Annals of Clinical Research 1987;19(6):374‐7. - PubMed
Kukita 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kukita A, Oura T, Aoki T, Harada S, Takeda K, Tashiro M, et al. Clinical evaluation of NI‐009 on various cutaneous ulcers: comparative study with Elase‐C ointment. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicine) 1990;6(4):817‐48.
Kurring 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kurring PA, Roberts CD, Quinlan D. Evaluation of a hydrocellular dressing in the management of exuding wounds in the community. British Journal of Nursing 1994;3(20):1049‐53. - PubMed
Kurzuk‐Howard 1985 {published data only}
-
- Kurzuk‐Howard G, Simpson L, Palmieri A. Decubitus ulcer care: a comparative study. Western Journal of Nursing Research 1985;7(1):58‐79. - PubMed
Landi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Landi F, Aloe L, Russo A, Cesari M, Onder G, Bonini S, et al. Topical treatment of pressure ulcers with nerve growth factor: a randomized clinical trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;139(8):635‐41. - PubMed
Langer 1996 {published data only}
-
- Langer SW. Testing the efficacy of a material for the relief of pressure in the prevention and treatment of decubitus ulcers. Krankenpflege Journal 1996;34(6):263‐5. - PubMed
Lazareth 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lazareth I, Meaume S, Sigal‐Grinberg ML, Combemale P, Guyadec T, Zagnoli A. Efficacy of a silver lipidocolloid dressing on heavily colonised wounds: a republished RCT. Journal of Wound Care 2012;21(2):96‐102. - PubMed
Lechner 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lechner JL, Ksiazekl S, Chang J, Rozek SL, Smith JM. Carrington dermal wound gel versus current treatments for the healing of decubitus ulcers and other dermal wounds. 26th Annual ASHP Midyear Clinical Meeting; 1991 December 8‐12; New Orleans (LA). 1992:294.
Lee 1975 {published data only}
-
- Lee LK, Ambrus JL. Collagenase therapy for decubitus ulcers. Geriatrics 1975;30(5):91‐8. - PubMed
Lee 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lee RL, Leung PH, Wong TK. A randomized controlled trial of topical tea tree preparation for MRSA colonized wounds. International Journal of Nursing Sciences 2014;1(1):7‐14.
LeVasseur 1991 {published data only}
-
- LeVasseur SA, Helme RD. A double‐blind clinical trial to compare the efficacy of an active based cream F14001 against a placebo non‐active based cream for the treatment of pressure ulcers in a population of elderly subjects. Journal of Advanced Nursing 1991;16(8):952‐6. - PubMed
Li 2016 {published data only}
Lin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Lin JY, Wu XH. The effect of bactroban cream for treating bedsores. Contemporary Nurse 1997;2:38.
Lindsay 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lindsay S, Clark R, Cullen B. Silver dressings: do they work?. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence nursing 2011;38(3 Suppl):S88.
Lingner 1984 {published data only}
-
- Lingner C, Rolstad BS, Wetherill K, Danielson S. Clinical trial of a moisture vapor‐permeable dressing on superficial pressure sores. Journal of Enterostomal Therapy 1984;11(4):147‐9. - PubMed
Liu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Liu H‐H, Liu S. Comparison of the effectiveness of different dressings on grade 2 pressure ulcers. Fourth Congress of the World Union of Wound Healing Societies; 2012 September 2‐6; Yokohama, Japan. 2012.
Liu 2013 {published data only}
Ljungberg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ljungberg S. Comparison of dextranomer paste and saline dressings for management of decubital ulcers. Clinical Therapeutics 1998;20(4):737‐43. - PubMed
Llewellyn 1996 {published data only}
-
- Llewellyn M, Baggott JE, Thomas N, Bale S. Comparison of a new alginate containing hydrocolloid vs traditional granuflex dressing on exuding pressure sores. Second Joint Meeting of the Wound Healing Society and the European Tissue Repair Society; 1996 May 15‐17; Boston (MA). 1996:130.
Lopez‐Jimenez 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lopez‐Jimenez E, Romero S, Hahn TW. A crossover study evaluating an adhesive foam dressing for heel ulcers. 13th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2003 May 22‐24; Pisa, Italy. 2003:211. [Poster 80]
Lum 1996 {published data only}
-
- Lum C, Cheung W, Chow PM, Woo J, Hui E, Or KH. Use of a hydrogel in pressure sore management: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Fifth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995 November 21‐24; Harrogate, UK. 1996:283.
Macario 2002 {published data only}
-
- Macario A, Dexter F. Is noncontact normothermic wound therapy cost effective for the treatment of stages 3 and 4 pressure ulcers?. Wounds 2002;14(3):93‐106.
Manzanero‐Lopez 2004 {published data only}
-
- Manzanero‐Lopez E, Perez‐Luis B. Evaluation of a new dressing in the management of pressure sores. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:170.
Martin 1996 {published data only}
-
- Martin SJ, Corrado OJ, Kay EA. Enzymatic debridement for necrotic wounds. Journal of Wound Care 1996;5(7):310‐1. - PubMed
Meaume 1996a {published data only}
-
- Meaume S, Bonnefoy M, Guihur B, Montalembert C, Remy F, Bohbot S. Decubitus ulcers in the aged. Local care and results of a randomized multicenter study. Soins 1996;October(609):40‐5. - PubMed
Meaume 1996b {published data only}
-
- Meaume S, Sayag J, Bonnefoy M, Brasseur C, Drunat O, Sebbane G, et al. Calcium alginate dressing (Algosteril) in the management of full‐thickness pressure sores: a controlled, randomized study on elderly patients. Fifth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995 November 21‐24; Harrogate, UK. 1996:19.
Meaume 2005 {published data only}
-
- Meaume S, Vallet D, Morere MN, Taot L. Evaluation of a silver‐releasing hydroalginate dressing in chronic wounds with signs of local infection. Journal of Wound Care 2005;14(9):411‐9. - PubMed
-
- Meaume S, Vallet D, Morere MN, Teot L. Evaluation of a silver‐releasing hydroalginate dressing in chronic wounds with signs of local infection. Zeitschrift für Wundheilung 2006;11(5):236‐45. - PubMed
Mian 1992 {published data only}
-
- Mian E, Martini P, Beconcini D, Mian M. Healing of open skin surfaces with collagen foils. International Journal of Tissue Reactions 1992;14(Suppl):27‐34. - PubMed
Milne 2012 {published data only}
-
- Milne CT, Ciccarelli A, Lassy M. A comparison of collagenase to hydrogel dressings in maintenance debridement and wound closure. Wounds 2012;24(11):317‐22. - PubMed
-
- Milne CT, Ciccarelli AO. A comparison of collagenase to hydrogel dressing in wound debridement, maintenance, debridement and wound healing. Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and the Wound Healing Society; 2010 April 17‐20; Orlando, Florida. 2010:S70. [Abstract CS‐077]
-
- Waycaster C, Milne CT. Clinical and economic benefit of enzymatic debridement of pressure ulcers compared to autolytic debridement with a hydrogel dressing. Journal of Medical Economics 2013;16(7):976‐86. - PubMed
Mizuhara 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mizuhara A, Bito S, Ohnishi S, Takeuchi K, Kobayashi K, Akiyama K. The therapeutic effectiveness of wrap therapy: a study comparing wrap therapy to standard therapy per current guidelines. Fourth Congress of the World Union of Wound Healing Societies; 2012 September 2‐6; Yokohama, Japan. 2012.
Mo 2015 {published data only}
-
- Mo X, Cen J, Gibson E, Wang R, Percival SL. An open multicenter comparative randomized clinical study on chitosan. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2015;23(4):518‐24. - PubMed
Moberg 1983 {published data only}
-
- Moberg S, Hoffman L, Grennert ML, Holst A. A randomized trial of cadexomer iodine in decubitus ulcers. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1983;31(8):462‐5. - PubMed
Mody 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mody GN, Nirmal IA, Duraisamy S, Perakath B. A blinded, prospective, randomized controlled trial of topical negative pressure wound closure in India. Ostomy/Wound Management 2008;54(12):36‐46. - PubMed
Moody 1991 {published data only}
-
- Moody M. Tissue viability: calcium alginate: a dressing trial. Nursing Standard 1991;13(Suppl):3‐6. - PubMed
Moody 2002 {published data only}
-
- Moody M. Relieve the pressure. Elderly care 2002;11(4):12‐14. - PubMed
Moore 2011 {published data only}
-
- Moore C, Young J. Effectiveness of silver in wound care treatment. Physical Therapy Reviews 2011;16(3):201‐9.
Morimoto 2015 {published data only}
Motta 1991 {published data only}
-
- Motta GJ. The effectiveness of Dermagran topical therapy for treating chronic wounds in nursing facility residents. Ostomy/Wound Management 1991;36:35‐8. - PubMed
Motta 2004 {published data only}
-
- Motta GJ, Milne CT, Corbett LQ. Impact of antimicrobial gauze on bacterial colonies in wounds that require packing. Ostomy/Wound Management 2004;50(8):48‐62. - PubMed
Mouës 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mouës CM, Bemd GJ, Heule F, Hovius SE. A prospective randomized trial comparing vacuum therapy to conventional moist gauze therapy. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:6. [Abstract A001]
-
- Mouës CM, Bemd GJ, Meerding WJ, Hovius SE. Cost analysis comparing vacuum‐assisted closure wound therapy to conventional moist gauze therapy. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:87. [Abstract A008]
-
- Mouës CM, Bemd GC, Meerding WJ, Hovius SE. An economic evaluation of the use of TNP on full‐thickness wounds. Journal of Wound Care 2005;14(5):224‐7. - PubMed
-
- Mouës CM, Vos MC, Bemd GJ, Stijnen T, Hovius SE. Bacterial load in relation to vacuum‐assisted closure wound therapy: a prospective randomized trial. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2004;12(1):11‐7. - PubMed
-
- Mouës CM, Vos MC, Bemd GJCM, Stijnen T, Hovius SE. Bacterial load in relation to vacuum‐assisted closure wound therapy. 13th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2003 May 22‐24; Pisa, Italy. 2003:69.
Mouës 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mouës CM, Bemd GJ, Heule F, Hovius SE. Comparing conventional gauze therapy to vacuum‐assisted closure wound therapy: a prospective randomised trial. Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Aesthetic Surgery 2007;60(6):672‐81. - PubMed
Mulder 1989a {published data only}
-
- Mulder G, Kissil M, Mahr JJ. Bacterial growth under occlusive and non‐occlusive wound dressings. Wounds 1989;1(1):63‐9.
Mulder 1989b {published data only}
Mulder 1993a {published data only}
-
- Mulder GD, Altman M, Seeley JE, Tintle T. Prospective randomized study of the efficacy of hydrogel, hydrocolloid, and saline solution‐moistened dressings on the management of pressure ulcers. Wound Repair and Regeneration 1993;1(4):213‐8. - PubMed
Mulder 1993b {published data only}
-
- Mulder GD. A prospective controlled randomized study of the efficacy of Clearsite, DuoDERM, and wet‐to‐dry gauze dressing in the management of pressure ulcers. Second European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1992 October 20‐23; Harrogate, UK. 1993:45.
Münter 2006 {published data only}
-
- Münter KC, Beele H, Russell L, Basse PB, Groechenig E, Crespi A, et al. The CONTOP study: improved healing of delayed healing ulcers with sustained silver‐releasing foam dressing versus other silver dressings. 16th Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 2006 May 18‐20; Prague, Czech Republic. 2006:210. [Abstract P068]
-
- Münter KC, Beele H, Russell L, Crespi A, Grochenig E, Basse P, et al. The CONTOP study: a large‐scale, comparative, randomised study in patients treated with a sustained silver‐releasing foam dressing. European Wound Management Association Conference; 2005 September 15‐17; Stuttgart, Germany. 2005:292. [Poster 193]
-
- Münter KC, Beele H, Russell L, Crespi A, Gruchenig E, Basse P, et al. Effect of a sustained silver‐releasing dressing on ulcers with delayed healing: the CONTOP study. Journal of Wound Care 2006;15(5):199‐206. - PubMed
-
- Russell L, Nebbioso G, Münter KC, Beele H, Basse PB, Dienst H. The CONTOP Study: a hydro‐activated silver containing foam dressing versus standard care. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting, 2004 July 8‐13, Paris, France. 2004:89.
-
- Scalise A, Forma O, Happe M, Hahn TW. The CONTOP study: real life experiences from an international study comparing a silver containing hydro‐activated foam dressing with standard wound care. 13th Conference of the European Wound Management Association. 2003:212. [Poster 81]
Mustoe 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mustoe TA, Cutler NR, Allman RM, Goode PS, Deuel TF, Prause JA, et al. A phase II study to evaluate recombinant platelet‐derived growth factor‐BB in the treatment of stage 3 and 4 pressure ulcers. Archives of Surgery 1994;129(2):213‐9. - PubMed
Myers 1990 {published data only}
-
- Myers SA, Takiguch S, Slavish S, Rose CL. Consistent wound care and nutritional support in treatment. Decubitus 1990;3(3):16‐28. - PubMed
Nasar 1982 {published data only}
-
- Nasar MA, Morley R. Cost‐effectiveness in treating deep pressure sores and ulcers. Practitioner 1982;226:307‐10. - PubMed
NCT02299557 {published data only}
-
- NCT02299557. A double blind study to examine the effect of oxymetazoline gel on anal pressure and incontinence in spinal cord injury patients. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02299557 (first received 17 November 2014).
Neill 1989b {published data only}
-
- Neill K. Clarification of research: comparative evaluation of a hydrocolloid dressing formulation and wet‐to‐damp gauze dressings in the management of pressure sores. Decubitus 1989;2(2):7. - PubMed
Niezgoda 2004 {published data only}
-
- Niezgoda JA. A comparison of vacuum assisted closure therapy to moist wound care in the treatment of pressure ulcers: preliminary results of a multicenter trial. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:53.
Niimura 1990 {published data only}
-
- Niimura M, Nishikawa T, Yamamoto K, Ogawa H, Ohara K, Ogawa N. Dose finding study of dibutyryl cyclic AMP ointment in skin ulcers: a double‐blind randomized clinical trial. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicine) 1990;6(8):1577‐98.
Niimura 1991 {published data only}
-
- Niimura M, Ishibashi Y, Imamura S, Hori Y, Nishikawa T, Ogawa H, et al. Clinical study of dibutyryl cyclic AMP ointment (DT‐5621) in chronic skin ulcers: well‐controlled comparative study with lysozyme ointment. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicine) 1991;7(3):677‐92.
Nixon 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bridel‐Nixon J, McElvenny D, Brown J, Mason S. A randomized controlled trial using a double‐triangular sequential design: methodology and management issues. Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 1997 April 27‐29; Milan, Italy. 1997:65‐6.
-
- Bridel‐Nixon J, McElvenny D, Brown J, Mason S. Findings from a double‐triangular sequential‐design randomized clinical trial of a dry polymer gel pad. Conference of the European Wound Management Association; 1997 April 27‐29; Milan, Italy. 1997:20‐1.
-
- Nixon J, McElvenny D, Mason S, Brown J, Bond S. A sequential randomised controlled trial comparing a dry visco‐elastic polymer pad and standard operating table mattress in the prevention of post‐operative pressure sores. International Journal of Nursing Studies 1998;35(4):193‐203. - PubMed
Ohura 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ohura T, Sanada H, Mino Y. Clinical activity‐based cost effectiveness of traditional versus modern wound management in patients with pressure ulcers. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:18.
Olivar 1999 {published data only}
-
- Olivar AE, Martinez PG, Lobato BE, Isaza MS, Jativa ED, Rios LA. Efficiency of a protocol for the treatment of cutaneous wounds in an elderly care centre in Madrid. Eighth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1998 April 26‐28; Madrid, Spain. 1999:61‐3.
Ovington 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ovington L. Dressings and ajunctive therapies: AHCPR Guidelines revisited. Ostomy/Wound management 1999;45(1A):94S‐108S. - PubMed
Ozdemir 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ozdemir F, Kasapoglu MK, Oymak F, Murat S. Efficiency of magnetic field treatment on pressure sores in bedridden patients. Balkan Medical Journal 2011;28(3):274‐8.
Panahi 2015 {published data only}
-
- Panahi Y, Izadi M, Sayyadi N, Rezaee R, Jonaidi‐Jafari N, Beiraghdar F, et al. Comparative trial of Aloe vera/olive oil combination cream versus phenytoin cream in the treatment of chronic wounds. Journal of Wound Care 2015;24(10):459‐60. - PubMed
Payne 2001 {published data only}
-
- Payne WG, Ochs DE, Meltzer DD, Hill DP, Mannari RJ, Robson LE, et al. Long‐term outcome study of growth factor‐treated pressure ulcers. American Journal of Surgery 2001;181(1):81‐6. - PubMed
Perez 2000 {published data only}
-
- Perez RC, Aguilar VC, Colome AM, Garcia AG, Torra i Bou JE. A comparison of the effectiveness and cost of moist environment dressings treatment as compared to traditional dressings treatment. Revista de Enfermeria 2000;23(1):17‐24. - PubMed
-
- Torra i Bou JE, Perez RC, Aguilar VC, Colome AM, Garcia AG. Comparison of the cost of traditional treatment methods versus moist wound healing in the treatment of chronic wounds. Eighth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1998 April 26‐28; Madrid, Spain. 1999:14.
Peschardt 1997 {published data only}
-
- Peschardt A, Alsbjorn B, Gottrup F. A comparative randomized study on performance characteristics of a new hydrogel versus saline gauze for the treatment of pressure sores. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1995 November 21‐24; Harrogate, UK. 1997:283.
Picard 2015 {published data only}
-
- Picard F, Hersant B, Bosc R, Meningaud J‐P. Should we use platelet‐rich plasma as an adjunct therapy to treat 'acute wounds', 'burns', and 'laser therapies'? A review and a proposal of a quality criteria checklist for further studies. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2015;23(2):163‐70. - PubMed
Pierce 1994 {published data only}
Pullen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pullen R, Popp R, Volkers P, Fusgen I. Prospective randomized double‐blind study of the wound‐debriding effects of collagenase and fibrinolysin/deoxyribonuclease in pressure ulcers. Age and Ageing 2002;31(2):126‐30. - PubMed
Quelard 1985 {published data only}
-
- Quelard B, Cordier ME, Regent MC, Tenette M. Comparative study to determine the relative efficiency of two types of treatment of decubitus ulcers of sacro and ischial tuberosities: topical ozone treatment versus the traditional methods. Annales médicales de Nancy et de l'Est 1985;24:329‐34.
Ramsay 1979 {published data only}
-
- Ramsay BM. Pressure sores in para‐ and tetraplegic patients. Nursing Times 1979;75(9):361‐4. - PubMed
Rhodes 1979 {published data only}
-
- Rhodes B, Daltrey D, Chattwood JG. The treatment of pressure sores in geriatric patients: a trial of sterculia powder. Nursing Times 1979;75(9):365‐8. - PubMed
Rhodes 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rhodes RS, Heyneman CA, Culbertson VL, Wilson SE, Phatak HM. Topical phenytoin treatment of stage II decubitus ulcers in the elderly. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2001;35(6):675‐81. - PubMed
Roberts 1959 {published data only}
-
- Roberts GW. Silicone emulsion for bedsores. Lancet 1959;273(7084):1207‐8.
Robson 1992a {published data only}
Robson 1992b {published data only}
-
- Robson MC, Phillips LG, Thomason A, Altrock BW, Pence PC, Heggers JP, et al. Recombinant human platelet‐derived growth factor‐BB for the treatment of chronic pressure ulcers. Annals of Plastic Surgery 1992;29(3):193‐201. - PubMed
Robson 1992c {published data only}
-
- Robson MC, Phillips LG, Thomason A, Robson LE, Pierce GF. Platelet‐derived growth factor BB for the treatment of chronic pressure ulcers. Lancet 1992;339(8784):23‐5. - PubMed
Robson 1994 {published data only}
-
- Robson MC, Abdullah A, Burns BF, Phillips LG, Garrison L, Cowan W, et al. Safety and effect of topical recombinant human interleukin‐1B in the management of pressure sores. Wound Repair and Regeneration 1994;2(3):177‐81. - PubMed
Romanelli 2008 {published data only}
-
- Romanelli M, Dimi V, Bertone MS, Mazzatenta C, Martini P. Efficacy and tolerability of 'Fitostimoline antibiotico' soaked gauzes in the topical treatment of cutaneous sores, ulcers and burns, complicated with bacterial contamination: an open‐label, controlled, randomised, multicentre, parallel group. Gazzetta Medica Italiana 2008;167(6):251‐60.
Romanelli 2009 {published data only}
-
- Palao i Domenech R, Romanelli M, Tsiftsis DD, Slonkova V, Jortikka A, Johannesen N, et al. Effect of an ibuprofen‐releasing foam dressing on wound pain: a real‐life RCT. Journal of Wound Care 2008;17(8):342, 344‐8. - PubMed
-
- Romanelli M, Dini V, Polignano R, Bonadeo P, Maggio G. Ibuprofen slow‐release foam dressing reduces wound pain in painful exuding wounds: preliminary findings from an international real‐life study. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2009;20(1):19‐26. - PubMed
Rooman 1991 {published data only}
-
- Rooman RP, Janssen H. Ketanserin promotes wound healing: clinical and preclinical results. Progress in Clinical and Biological Research 1991;365:115‐28. - PubMed
Routkovsky‐Norval 1996 {published data only}
-
- Routkovsky‐Norval C, Meaume S, Goldfarb JM, Provost C, Preauchat A. Randomized comparative study of two hydrocolloid dressings in the treatment of decubitus ulcers. Revue de Gériatrie 1996;21(3):213‐8.
Saha 2012 {published data only}
Saidkhani 2016 {published data only}
Sayag 1996 {published data only}
-
- Sayag J, Meaume S, Bohbot S. Healing properties of calcium alginate dressings. Journal of Wound Care 1996;5(8):357‐62. - PubMed
Saydak 1990 {published data only}
-
- Saydak SJ. A pilot test of two methods for the treatment of pressure ulcers. Journal of Enterostomal Therapy 1990;17(3):140‐2. - PubMed
Scevola 2010 {published data only}
Scott 1999 {published data only}
-
- Scott D, Sholler KA, Beck K, Weaver MC. The use of a papain‐urea debriding ointment in combination with surgical/sharp debridement. 31st Annual Wound, Ostomy and Continence Conference; 1999 June 19‐23; Minneapolis (MN) 1999.
Seaman 2000 {published data only}
-
- Seaman S, Herbster S, Muglia J, Murray M, Rick C. Simplifying modern wound management for nonprofessional caregivers. Ostomy/Wound Management 2000;46(8):18‐27. - PubMed
Sebern 1989 {published data only}
-
- Sebern MD. Cost and efficacy of pressure ulcer management in a metropolitan visiting nurse association. Decubitus 1989;2(3):58‐9. - PubMed
Serra 2005 {published data only}
-
- Serra N, Torres OG, Romo MI, Llovera JM, Vigil Escalera LJ, Soto MA, et al. Hydro‐colloidal dressings which release hydro‐active silver. Revista de Enfermeria 2005;28(2):13‐8. - PubMed
Settel 1969 {published data only}
-
- Settel E. Decubitus ulcer. A double blind study of an old problem and a new treatment. Medical Times 1969;97(4):220‐30. - PubMed
Shamimi Nouri 2008 {published data only}
-
- Shamimi Nouri K, Karimian R, Nasli E, Kamali K, Chaman R, Farhadi M, et al. Topical application of Semelil (ANGIPARS™) in treatment of pressure ulcers: a randomized clinical trial. Daru 2008;16(Suppl 1):54‐7.
Shannon 1988 {published data only}
-
- Shannon ML, Miller BM. Pressure sore treatment: a case in point. Geriatric Nursing 1988;9(3):154‐7. - PubMed
Sherman 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sherman RA. Maggot debridement therapy for treating non‐healing wounds. Wound Healing Society Educational Symposium; 2000 June 4‐6; Toronto, Canada. 2000:84.
Shirakawa 2005 {published data only}
-
- Shirakawa M, Isseroff RR. Topical negative pressure devices: use for enhancement of healing chronic wounds. Archives of Dermatology 2005;141(11):1449‐53. - PubMed
Shojaei 2008 {published data only}
-
- Shojaei H, Sokhangoei Y, Soroush MR. Low level laser therapy in the treatment of pressure ulcers in spinal cord handicapped veterans living in Tehran. Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences 2008;33:44‐8.
Shrivastava 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shrivastava R. Clinical evidence to demonstrate that simultaneous growth of epithelial and fibroblast cells is essential for deep wound healing. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2011;92(1):92‐9. - PubMed
Sibbald 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sibbald RG, Coutts P, Woo KY. Reduction of bacterial burden and pain in chronic wounds using a new polyhexamethylene biguanide antimicrobial foam dressing‐clinical trial results. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2011;24 (2 ):78‐84. - PubMed
Small 2002 {published data only}
-
- Small N, Mulder M, Mackenzie MJ, Nel M. A comparative analysis of pressure sore treatment modalities in community settings. Curationis 2002;25(1):74‐82. - PubMed
Smietanka 1981 {published data only}
-
- Smietanka MA, Opit LJ. A trial of a transparent adhesive dressing ('Op Site') in the treatment of decubitus ulcer. Australian Nurses' Journal 1981;10(8):40‐2. - PubMed
Souliotis 2016 {published data only}
-
- Souliotis K, Kalemikerakis I, Saridi M, Papageorgiou M, Kalokerinou A. A cost and clinical effectiveness analysis among moist wound healing dressings versus traditional methods in home care patients with pressure ulcers. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2016;24(3):596‐601. - PubMed
Stepan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Stepan J, Ehrlichova J, Hladikova M. Efficacy and safety of symphytum herb extract cream in the treatment of pressure ulcers. Zeitschrift für Gerontologie und Geriatrie 2014;47(3):228‐35. - PubMed
Stephen 2016 {published data only}
-
- Stephen S, Agnihotri M, Kaur S. A randomized, controlled trial to assess the effect of topical insulin versus normal saline in pressure ulcer healing. Ostomy/Wound Management 2016;62(6):16‐23. - PubMed
Stoker 1990 {published data only}
-
- Stoker F. A major contributor. Evaluation of Comfeel pressure relieving dressing. Professional Nurse 1990;5(12):644‐53. - PubMed
Strong 1985 {published data only}
-
- Strong V, Mermel VM. A comparative study of the effectiveness of a nonpetroleum and a petroleum moisturizing agent on healing of stage I and stage II skin lesions. Journal of Enterostomal Therapy 1985;12(6):195‐202. - PubMed
Subbanna 2007 {published data only}
-
- Subbanna PK, Shanti MF, George J, Tharion G, Neelakantan N, Durai S, et al. Topical phenytoin solution for treating pressure ulcers: a prospective, randomized, double‐blind clinical trial. Spinal Cord 2007;45(11):739‐43. - PubMed
Takahashi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Takahashi J, Yokota O, Fujisawa Y, Sasaki K, Ishizu H, Aoki T, et al. An evaluation of polyvinylidene film dressing for treatment of pressure ulcers in older people. Journal of Wound Care 2006;15(10):449‐50, 452‐4. - PubMed
Teot 1997 {published data only}
-
- Teot L. A multi‐centre randomized comparative study of Aquacel versus a traditional dressing regimen for the management of pressure sores. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1996 October 1‐4; Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1997:283.
Teot 2008 {published data only}
-
- Teot L, Trial C, Lavigne JP. Results of RCT on the antimicrobial effectiveness of a new silver alginate wound dressing. EWMA Journal 2008;8(Suppl 2):54. [Abstract 69] - PubMed
Tewes 1993 {published data only}
-
- Tewes M. Prevention and treatment of pressure sores: a neglected research subject? An overview of clinically controlled studies in the period 1987‐91. Vard i Norden 1993;13(2):4‐7. - PubMed
Thomas 1993 {published data only}
-
- Thomas S, Fear M. Comparing two dressings for wound debridement. Journal of Wound Care 1993;2(5):272‐4. - PubMed
Thomas 1997b {published data only}
-
- Thomas S, Banks V, Fear M, Hagelstein S, Bale S, Harding KG. A study to compare two film dressings used as secondary dressings. Journal of Wound Care 1997;6(7):333‐6. - PubMed
Toba 1997 {published data only}
-
- Toba K, Sudoh N, Nagano K, Eto M, Mizuno Y, Nakagawa H, et al. Randomized prospective trial of gentian violet with dibutyryl cAMP and povidone‐iodine with sugar as treatment for pressure sores infected with methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus in elderly patients. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi (Japanese Journal of Geriatrics) 1997;34(7):577‐82. - PubMed
Tolentino 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tolentino AC, Takemoto ML, Fernandes RA, Takemoto MM, Santos PM. Cost‐effectiveness analysis of three wound dressings for the treatment of pressure ulcers from the public hospital perspective. Value in Health 2011;14(3):A83. [Abstract PMD22]
Toriyabe 2004 {published data only}
-
- Toriyabe S. A film‐dressing therapy for pressure ulcers at NPUAP stages lll/lV. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:154.
Torra i Bou 1999 {published data only}
-
- Torra i Bou JE. Randomized, comparative clinical trial on the debriding effect of Purilon gel versus Intrasite gel on pressure ulcers. Ninth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1999 November 9‐11; Harrogate, UK. 1999:23.
Trial 2010 {published data only}
-
- Trial C, Darbas H, Lavigne JP, Sotto A, Simoneau G, Tillet Y, et al. Assessment of the antimicrobial effectiveness of a new silver alginate wound dressing: a RCT. Journal of Wound Care 2010;19(1):20‐6. - PubMed
Tricco 2015 {published data only}
-
- Tricco AC, Antony J, Vafaei A, Khan PA, Harrington A, Cogo E, et al. Seeking effective interventions to treat complex wounds: an overview of systematic reviews. BMC Medicine 2015;13(89):Available from bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916‐015‐0288‐5. - PMC - PubMed
Unglaub 2004 {published data only}
-
- Unglaub F, Ulrich D, Pallua N. Effect of promogran matrix on healing rate and elastase and plasmin activity in patients with pressure sores. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:55.
Valentini 2015 {published data only}
-
- Valentini SR, Nogueira AC, Fenelon VC, Sato F, Medina AN, Santana RG, et al. Insulin complexation with hydroxypropyl‐beta‐cyclodextrin: spectroscopic evaluation of molecular inclusion and use of the complex in gel for healing of pressure ulcers. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2015;490(1‐2):229‐39. - PubMed
Van Leen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Leen MW. A prospective randomized study in recalcitrant pressure sores with poly hydrated ionogens is feasible. Second World Union of Wound Healing Societies Meeting; 2004 July 8‐13; Paris, France. 2004:poster.
Varma 1973 {published data only}
-
- Varma AO, Bugatch E, German FM. Debridement of dermal ulcers with collagenase. Surgery, Gynecology and Obstetrics 1973;136(2):281‐2. - PubMed
Vernassiere 2005 {published data only}
-
- Vernassiere C, Cornet C, Trechot P, Alla F, Truchetet F, Cuny JF, et al. Study to determine the efficacy of topical morphine on painful chronic skin ulcers. Journal of Wound Care 2005;14(6):289‐93. - PubMed
Wagstaff 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wagstaff MJ, Driver S, Coghlan P, Greenwood JE. A randomized, controlled trial of negative pressure wound therapy of pressure ulcers via a novel polyurethane foam. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2014;22(2):205‐11. - PubMed
Wallace 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wallace M. Review: evidence on the effectiveness of honey for healing wounds is limited. Evidence‐Based Nursing 2009;12(2):53. - PubMed
Wang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wang C, Huang S, Zhu T, Sun X, Zou Y, Wang Y. Efficacy of photodynamic antimicrobial therapy for wound flora and wound healing of pressure sore with pathogen infection. National Medical Journal of China 2014;94(31):2455‐9. - PubMed
Wanner 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wanner MB, Schwarzl F, Strub B, Zaech GA, Pierer G. Vacuum‐assisted wound closure for cheaper and more comfortable healing of pressure sores: a prospective study. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery 2003;37(1):28‐33. - PubMed
Watts 1994 {published data only}
-
- Watts C, Lee S. Comparison of Allevyn cavity wound dressing to saline‐moistened gauze. Third European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1993 October 19‐22; Harrogate, UK. 1994:159.
Waycaster 2011 {published data only}
-
- Waycaster C. Cost‐effectiveness of collagenase versus hydrogel dressings for chronic‐wound debridement in a long‐term care setting. Value in Health 2011;14(3):A54. [Abstract PSS9]
Waycaster 2013 {published data only}
-
- Waycaster C, Milne C. Economic and clinical benefit of collagenase ointment compared to a hydrogel dressing for pressure ulcer debridement in a long‐term care setting. Wounds 2013;25(6):141‐7. - PubMed
Weheida 1991 {published data only}
-
- Weheida SM, Nagubib HH, El‐Banna HM, Marzouk S. Comparing the effects of two dressing techniques on healing of low grade pressure ulcers. Journal of the Medical Research Institute 1991;12(2):259‐78.
Weststrate 1999 {published data only}
-
- Weststrate JT, Bruining HA. Use of a hydrocolloid dressing to save nursing time. Eighth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1998 April 26‐28; Madrid, Spain. 1999:57.
Whitney 1999 {published data only}
-
- Whitney J, Higa L, Savadalena G, Mich M. Effect of radiant heat treatment on pressure ulcer healing: preliminary findings. 31st Annual Wound, Ostomy and Continence Conference; 1999 June 19‐23; Minneapolis (MN). 1999:478.
Whitney 2001 {published data only}
-
- Whitney JD, Salvadalena G, Higa L, Mich M. Treatment of pressure ulcers with noncontact normothermic wound therapy: healing and warming effects. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing 2001;28(5):244‐52. - PubMed
Wild 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wild T, Bruckner M, Payrich M, Schwarz C, Eberlein T. Prospective randomized study for eradication of MRSA with polyhexanid containing cellulose dressing compare with polyhexanid wound solution. old.ewma.org/fileadmin/user_upload/EWMA/pdf/conference_abstracts/2009/Po... (accessed 13 March 2017).
Wild 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wild T, Bruckner M, Payrich M, Schwarz C, Eberlein T, Andriessen A. Eradication of methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pressure ulcers comparing a polyhexanide‐containing cellulose dressing with polyhexanide swabs in a prospective randomized study. Advances in Skin and Wound Care 2012;25(1):17‐22. - PubMed
Winter 1990 {published data only}
-
- Winter A, Hewitt H. Testing a hydrocolloid. Nursing Times 1990;86(50):59‐62. - PubMed
Woo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Woo KY, Sibbald RG. Topical treatment of pain in pressure ulcers: a systematic review. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing 2009;36(3 (Suppl)):S58.
Worsley 1991 {published data only}
-
- Worsley M. Comparing efficacies: hydrocolloid dressing (Comfeel ulcer dressing) vs non‐adherent dressing (Betadine + melonin dressing). Nursing Standard 1991;5(25):5‐6.
Yastrub 2004 {published data only}
-
- Yastrub DJ. Relationship between type of treatment and degree of wound healing among institutionalized geriatric patients with stage II pressure ulcers. Care Management Journals 2004;5(4):213‐8. - PubMed
Yastrub 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yastrub DJ. Relationship between type of treatment and degree of wound healing among institutionalized geriatric patients with stage II pressure ulcers. Clinical Excellence for Nurse Practitioners 2005;9(2):89‐94. - PubMed
Young 1973 {published data only}
-
- Young CG, Oden PW. Treatment of decubitus ulcers in paraplegic patients: a comparison of three topical agents: absorbable [sic] gelatin sponge, gelatin powder, and enzyme ointment. Southern Medical Journal 1973;66(12):1375‐8. - PubMed
Young 1997 {published data only}
-
- Young T, Williams C, Benboz M, Collier M, Banks V, Jones H. A study of two hydrogels used in the management of pressure sores. Sixth European Conference on Advances in Wound Management; 1996 October 1‐4; Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1997:103‐6.
Yura 1984 {published data only}
-
- Yura J, Ando M, Ishikawa S, Ohashi M, Ishigaki M, Ueda H, et al. Clinical evaluation of silver sulfadiazine in the treatment of decubitus ulcer or chronic dermal ulcers: double‐blind study comparing to placebo. Chemotherapy 1984;32(4):208‐22.
Zhou 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zhou DP, Lu LQ, Mao XL. Insulin and hyperosmotic glucose solution external used for treating pressure sore. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao (Bulletin of Hunan Medical University) 2001;26(5):475‐6. - PubMed
Zuloff‐Shani 2010 {published data only}
-
- Zuloff‐Shani A, Adunsky A, Even‐Zahav A, Semo H, Orenstein A, Tamir J, et al. Hard to heal pressure ulcers (stage III‐IV): efficacy of injected activated macrophage suspension (AMS) as compared with standard of care (SOC) treatment controlled trial. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2010;51(3):268‐72. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ChiCTR‐TRC‐13003959 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR‐TRC‐13003959. Moxibustion for the promotion of wound healing of pressure ulcers: randomized controlled pilot study. www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=5608 (first received 7 December 2013).
ISRCTN57842461 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN57842461. To compare the polyurethane foam dressing (hydrocellular) and the hydrocolloid dressing in patients with pressure ulcers (stage II) in primary care. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN57842461 (first received 19 June 2012).
Additional references
AHRQ 2013
-
- Saha S, Smith ME, Totten A, Fu R, Wasson N, Rahman B, et al. US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Pressure ulcer treatment strategies: comparative effectiveness review 90. May 2013. effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/ehc/products/308/1492/Pressure‐ulcer‐treatm... (accessed 21 December 2016). - PubMed
Allman 1999
-
- Allman RM, Goode PS, Burst N, Bartolucci AA, Thomas DR. Pressure ulcers, hospital complications, and disease severity: impact on hospital costs and length of stay. Advances in Wound Care 1999;12:22‐30. - PubMed
Balshem 2011
-
- Balshem H, Helfand M, Schunemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:401‐6. - PubMed
Bennett 2004
-
- Bennett G, Dealey C, Posnett J. The cost of pressure ulcers in the UK. Age and Ageing 2004;33(3):230‐5. - PubMed
BNF 2016
-
- British Medical Association, British Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. British National Formulary (BNF). www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/bnf/current/ (accessed 21 December 2016).
Bradley 1999
-
- Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson EA, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D. Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(17 (part 2)):1‐35. - PubMed
Brandeis 1994
-
- Brandeis GH, Ooi WL, Hossain M, Morris JN, Lipsitz LA. A longitudinal study of risk factors associated with the formation of pressure ulcers in nursing homes. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 1994;42:388‐93. - PubMed
Caldwell 2005
Caldwell 2014
Cardinal 2009
-
- Cardinal M, Eisenbud DE, Armstrong DG, Zelen C, Driver V, Attinger C, et al. Serial surgical debridement: a retrospective study on clinical outcomes in chronic lower extremity wounds. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2009;17(3):306‐11. - PubMed
Chaimani 2013a
-
- Chaimani A, Salanti G. Background document: stream 2 (statistical issues in NMA). methods.cochrane.org/sites/methods.cochrane.org.cmi/files/public/uploads... (accessed 19 December 2016).
Chaimani 2013b
Chaimani 2015
-
- Chaimani A, Salanti G. Visualizing assumptions and results in network meta‐analysis: the network graphs package. Stata Journal 2015;15(4):905‐50.
Cipriani 2013
-
- Cipriani A, Higgins JP, Geddes JR, Salanti G. Conceptual and technical challenges in network meta‐analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;159:130‐7. - PubMed
Coleman 2013
-
- Coleman S, Gorecki C, Nelson EA, Closs SJ, Defloor T Halfens R. Patient risk factors for pressure ulcer development: Systematic review. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2013;50:974–1003. - PubMed
Cullum 2016
-
- Cullum N, Buckley H, Dumville J, Hall J, Lamb K, Madden M, et al. Wounds research for patient benefit: a 5‐year programme of research. Programme Grants for Applied Research 2016;4:1‐299. - PubMed
Dealey 2012
-
- Dealey C, Posnett J, Walker A. The cost of pressure ulcers in the United Kingdom. Journal of Wound Care 2012;21:261‐2, 264, 266. - PubMed
Dias 2010
-
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Caldwell DM, Ades AE. Checking consistency in mixed treatment comparison meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2010;29(7‐8):932‐44. - PubMed
Dias 2013
Dias 2016
-
- Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Ades AE. NICE DSU technical support document 2: a generalised linear modelling framework for pairwise and network meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. Last updated September 2016. www.nicedsu.org.uk/TSD2%20General%20meta%20analysis%20corrected%202Sep20... (accessed 21 December 2016). - PubMed
Dumville 2012
Dumville 2015a
Dumville 2015b
EPUAP‐NPUAP‐PPPIA 2014
-
- European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (EPUAP) National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP), Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance (PPPIA). Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers: Quick Reference Guide. October 2014. www.npuap.org/wp‐content/uploads/2014/08/Updated‐10‐16‐14‐Quick‐Referenc... (accessed 21 December 2016).
Essex 2009
-
- Essex HN, Clark M, Sims J, Warriner A, Cullum N. Health‐related quality of life in hospital inpatients with pressure ulceration: assessment using generic health‐related quality of life measures. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2009;17:797‐805. - PubMed
Gasparrini 2015
-
- Gasparrini 2015. Multivariate and univariate meta‐analysis and meta‐regression. cran.r‐project.org/web/packages/mvmeta/mvmeta.pdf (accessed 15 December 2016).
Gillespie 2012
-
- Gillespie BM, Chaboyer W, Niuewenhoven P, Rickard CM. Drivers and barriers of surgical wound management in a large healthcare organisation: results of an environmental scan. Wound Practice and Research 2012;20(2):90‐102.
Grant 2013
-
- Grant ES, Calderbank‐Batista T. Network meta‐analysis for complex social interventions: problems and potential. Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research 2013;4(4):406‐20.
Graves 2005
-
- Graves N, Birrell F, Whitby M. Modelling the economic losses from pressure ulcers among hospitalized patients in Australia. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2005;13:462‐7. - PubMed
Guyatt 2011a
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 4. rating the quality of evidence ‐ study limitations (risk of bias). Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:407‐15. - PubMed
Guyatt 2011b
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines: 6. rating the quality of evidence ‐ imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283‐93. - PubMed
Hall 2014
Higgins 1996
-
- Higgins JP, Whitehead A. Borrowing strength from external trials in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 1996;15:2733–49. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA, editor(s). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2012
Hutchinson 1991
-
- Hutchinson JJ, Lawrence JC. Wound infections under occlusive dressings. Journal of Hospital Infection 1991;17(2):83‐94. - PubMed
Jansen 2013
Kelly 2015
-
- Kelly J, Clifton E, Fearns N, Harbour J, Heller‐Murphy S, Herbert P, et al. Antimicrobial wound dressings (AWDs) for chronic wounds. Healthcare Improvement Scotland. Health Technology Assessment. December 2015. www.healthcareimprovementscotland.org/our_work/technologies_and_medicine... (accessed 21 December 2016).
Keogh 2013
-
- Keogh SJ, Nelson EA, Webster J, Jolly J, Ullman AJ, Chaboyer WP. Hydrocolloid dressings for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010364] - DOI
Kibret 2014
Krahn 2013
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Liberati 2009
Lu 2004
-
- Lu G, Ades AE. Combination of direct and indirect evidence in mixed treatment comparisons. Statistics in Medicine 2004;23(20):3105–24. - PubMed
Lunn 2000
-
- Lunn DJ, Thomas A, Best N, Spiegelhalter D. WinBUGS ‐ a Bayesian modelling framework: concepts, structure, and extensibility. Statistics and Computing 2000;10:325‐37.
Lunn 2009
-
- Lunn D, Spiegelhalter D, Thomas A, Best N. The BUGS project: evolution, critique and future directions. Statistics in Medicine 2009;28:3049–67. - PubMed
McInnes 2011
NHS Quality Observatory 2015
-
- NHS Quality Observatory. National Safety Thermometer Data 2015. www.safetythermometer.nhs.uk/index.php?option=com_dashboards&view=cl... (accessed 22 January 2015).
NICE 2014
-
- National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Pressure ulcers: prevention and management. Clinical guideline [CG179]. April 2014. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg179 (accessed 1 April 2015).
NPUAP 2016
-
- National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP). Change in terminology from pressure ulcer to pressure injury. April 2016. www.npuap.org/national‐pressure‐ulcer‐advisory‐panel‐npuap‐announces‐a‐c... (accessed 18 May 2017).
Peters 2008
-
- Peters J, Sutton A, Jones D, Abrams K, Rushton L. Contour‐enhanced meta‐analysis funnel plots help distinguish publication bias from other causes of asymmetry. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(10):991‐6. - PubMed
Power 2012
Reddy 2008
-
- Reddy M, Gill SS, Kalkar SR, Wu W, Anderson PJ, Rochon PA. Treatment of pressure ulcers: a systematic review. JAMA 2008;300:2647‐62. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Russo 2008
-
- Russo A, Steiner C, Spector W, US Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. Hospitalizations related to pressure ulcers among adults 18 years and older, 2006. www.hcup‐us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb64.jsp (accessed 21 December 2016). - PubMed
Salanti 2008
-
- Salanti G, Higgins JP, Ades AE, Ioannidis JP. Evaluation of networks of randomized trials. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 2008;17:279–301. - PubMed
Salanti 2011
-
- Salanti G, Ades A, Ioannidis J. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple‐treatment meta‐analysis: an overview and tutorial. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:163‐71. - PubMed
Salanti 2014
Saramago 2014
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
SIGN 2017
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Search filters. www.sign.ac.uk/methodology/filters.html (accessed 13 June 2017).
Smith 2013
-
- Smith ME, Totten A, Hickam DH, Fu R, Wasson N, Rahman B, et al. Pressure ulcer treatment strategies: a systematic comparative effectiveness review. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;159:39‐50. - PubMed
Soares 2014
-
- Soares MO, Dumville JC, Ades AE, Welton NJ. Treatment comparisons for decision making: facing the problems of sparse and few data. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series A 2014;177(1):259–79.
Spiegelhalter 2003
-
- Spiegelhalter D, Abrams K, Myles J. Bayesian Approaches to Clinical Trials and Health‐care Evaluation. Chichester: Wiley, 2003.
STATA 2013 [Computer program]
-
- StataCorp LLC. Stata data analysis and statistical software. Version 13. College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC, 2013.
Thorlund 2012
Tierney 2007
Tu 2012
-
- Tu Y‐K, Faggion CM. A primer on network meta‐analysis for dental research. International Scholarly Research Notices Dentistry 2012, issue Article ID 276520:available from www.hindawi.com/journals/isrn/2012/276520/. [DOI: 10.5402/2012/276520] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Turner 2012
Vanderwee 2007
-
- Vanderwee K, Clark M, Dealey C, Gunningberg L, Defloor T. Pressure ulcer prevalence in Europe: a pilot study. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 2007;13(2):227‐35. - PubMed
VanGilder 2009
-
- VanGilder C, Amlung S, Harrison P, Meyer S. Results of the 2008‐2009 International Pressure Ulcer Prevalence Survey and a 3‐year, acute care, unit‐specific analysis. Ostomy Wound Management 2009;55(11):39‐45. - PubMed
Veroniki 2013
Walker 2014
White 2012
WinBUGS 2015 [Computer program]
-
- Medical Research Council Biostatistics Unit. WinBUGS. Version 1.4.3. Cambridge, UK: Medical Research Council Biostatistics Unit, 2015.
Winter 1962
-
- Winter GD. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelization of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. Nature 1962;193:293‐4. - PubMed
Winter 1963a
-
- Winter GD, Scales JT. Effect of air drying and dressings on the surface of a wound. Nature 1963;197:91‐2. - PubMed
Winter 1963b
-
- Winter GD. Effect of air exposure and occlusion on experimental human skin wounds. Nature 1963;200:378‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

