Brief Report: Recovery of Bone Mineral Density After Discontinuation of Tenofovir-Based HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis
- PMID: 28639995
- PMCID: PMC5597476
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001475
Brief Report: Recovery of Bone Mineral Density After Discontinuation of Tenofovir-Based HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis
Abstract
Background: Oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) for HIV prevention and treatment is associated with decreases in bone mineral density (BMD). Previous reports suggest that these changes may be reversible after discontinuation of TDF.
Setting: A metabolic substudy of 498 participants in a randomized, placebo-controlled HIV prevention trial of oral coformulated TDF with emtricitabine (TDF/FTC, Truvada) for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) enrolling a global sample of men who have sex with men and trans women.
Methods: Participants underwent dual X-ray absorptiometry to quantify bone mineral density (BMD) in the hip and spine during PrEP and at 2 visits after stopping (median of 23 and 79 weeks post-PrEP, respectively). Results are stratified by pharmacologic measure of TDF/FTC adherence.
Results: There was no significant difference in change in hip/spine BMD at any time point between placebo and those with low adherence. Adherent participants had a mean (standard error) BMD change at TDF/FTC discontinuation of -1.02% (0.24) in the hip and -1.84% (0.36) in the spine. After stop, annualized BMD increases of 1.13% per year (0.27) in hip and 1.81% per year (0.36) in spine BMD were observed in adherent participants compared with 0.19% (0.16) and 0.74% (0.21) in the placebo group, respectively (P = 0.003, both comparisons). On average, BMD returned to baseline levels by 1 year after PrEP stop. Recovery was consistent across age, baseline BMD z-score, and treatment duration.
Conclusions: Mean BMD returns to baseline levels within 12-18 months after TDF-based PrEP discontinuation in both hip and spine with consistency across participant subgroups.
Clinical trials registration: clinicaltrials.gov NCT00458393.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

All Participants – Available Scans
All Participants – Results of Multiple Imputation
Participants Aged < 25 years at iPrEx Entry
Participants Aged ≥ 25 years at iPrEx Entry
Baseline Hip Z-score < −1 at iPrEx Entry
Baseline Hip Z-score ≥ 1 at iPrEx Entry
Duration Randomized Treatment ≥ 1 Year
Duration Randomized Treatment < 1 Year
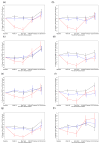
All Participants – Available Scans
All Participants – Results of Multiple Imputation
Participants Aged < 25 years at iPrEx Entry
Participants Aged ≥ 25 years at iPrEx Entry
Baseline Spine Z-score < −1 at iPrEx Entry
Baseline Spine Z-score ≥ 1 at iPrEx Entry
Duration Randomized Treatment ≥ 1 Year
Duration Randomized Treatment < 1 Year
References
-
- Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:423–434. - PubMed
-
- Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2083–2090. - PubMed
-
- Molina JM, Capitant C, Spire B, et al. On-demand preexposure prophylaxis in men at high risk for HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;37:2237–2246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

