PHLDA1 (pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1) knockdown promotes migration and invasion of MCF10A breast epithelial cells
- PMID: 28640659
- PMCID: PMC5810790
- DOI: 10.1080/19336918.2017.1313382
PHLDA1 (pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1) knockdown promotes migration and invasion of MCF10A breast epithelial cells
Abstract
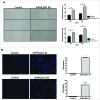
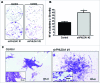
PHLDA1 (pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1) is a multifunctional protein that plays distinct roles in several biological processes including cell death and therefore its altered expression has been identified in different types of cancer. Progressively loss of PHLDA1 was found in primary and metastatic melanoma while its overexpression was reported in intestinal and pancreatic tumors. Previous work from our group showed that negative expression of PHLDA1 protein was a strong predictor of poor prognosis for breast cancer disease. However, the function of PHLDA1 in mammary epithelial cells and the tumorigenic process of the breast is unclear. To dissect PHLDA1 role in human breast epithelial cells, we generated a clone of MCF10A cells with stable knockdown of PHLDA1 and performed functional studies. To achieve reduced PHLDA1 expression we used shRNA plasmid transfection and then changes in cell morphology and biological behavior were assessed. We found that PHLDA1 downregulation induced marked morphological alterations in MCF10A cells, such as changes in cell-to-cell adhesion pattern and cytoskeleton reorganization. Regarding cell behavior, MCF10A cells with reduced expression of PHLDA1 showed higher proliferative rate and migration ability in comparison with control cells. We also found that MCF10A cells with PHLDA1 knockdown acquired invasive properties, as evaluated by transwell Matrigel invasion assay and showed enhanced colony-forming ability and irregular growth in low attachment condition. Altogether, our results indicate that PHLDA1 downregulation in MCF10A cells leads to morphological changes and a more aggressive behavior.
Keywords: MCF10A; PHLDA1; aggressive phenotype; breast cancer; invasion; mammary epithelial cells; migration.
Figures



References
-
- Oberst MD, Beberman SJ, Zhao L, Yin JJ, Ward Y, Kelly K. TDAG51 is an ERK signaling target that opposes ERK-mediated HME16C mammary epithelial cell transformation. BMC Cancer 2008; 8:189; PMID:18597688; https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-8-189 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johnson EO, Chang KH, de Pablo Y, Ghosh S, Mehta R, Badve S, Shah K. PHLDA1 is a crucial negative regulator and effector of Aurora A kinase in breast cancer. J Cell Sci 2011; 124(Pt 16):2711-22; PMID:21807936; https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.084970 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moad AI, Muhammad TS, Oon CE, Tan ML. Rapamycin induces apoptosis when autophagy is inhibited in T-47D mammary cells and both processes are regulated by Phlda1. Cell Biochem Biophys 2013; 66(3):567-87; PMID:23300026; https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9504-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li G, Wang X, Hibshoosh H, Jin C, Halmos B. Modulation of ErbB2 blockade in ErbB2-positive cancers: the role of ErbB2 Mutations and PHLDA1. PLoS One 2014; 9(9):e106349; PMID:25238247; https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106349 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
