Glucose dysregulation and response to common anti-diabetic agents in the FATZO/Pco mouse
- PMID: 28640857
- PMCID: PMC5480999
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179856
Glucose dysregulation and response to common anti-diabetic agents in the FATZO/Pco mouse
Abstract
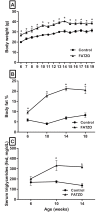
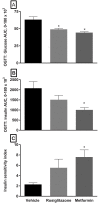
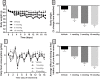
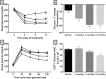
The FATZO/Pco mouse is the result of a cross of the C57BL/6J and AKR/J strains. The crossing of these two strains and the selective inbreeding for obesity, insulin resistance and hyperglycemia has resulted in an inbred strain exhibiting obesity in the presumed presence of an intact leptin pathway. Routinely used rodent models for obesity and diabetes research have a monogenic defect in leptin signaling that initiates obesity. Given that obesity and its sequelae in humans are polygenic in nature and not associated with leptin signaling defects, the FATZO mouse may represent a more translatable rodent model for study of obesity and its associated metabolic disturbances. The FATZO mouse develops obesity spontaneously when fed a normal chow diet. Glucose intolerance with increased insulin levels are apparent in FATZO mice as young as 6 weeks of age. These progress to hyperglycemia/pre-diabetes and frank diabetes with decreasing insulin levels as they age. The disease in these mice is multi-faceted, similar to the metabolic syndrome apparent in obese individuals, and thus provides a long pre-diabetic state for determining the preventive value of new interventions. We have assessed the utility of this new model for the pre-clinical screening of agents to stop or slow progression of the metabolic syndrome to severe diabetes. Our assessment included: 1) characterization of the spontaneous development of disease, 2) comparison of metabolic disturbances of FATZO mice to control mice and 3) validation of the model with regard to the effectiveness of current and emerging anti-diabetic agents; rosiglitazone, metformin and semaglutide.
Conclusion: Male FATZO mice spontaneously develop significant metabolic disease when compared to normal controls while maintaining hyperglycemia in the presence of high leptin levels and hyperinsulinemia. The disease condition responds to commonly used antidiabetic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Reaven GM (1988) Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37: 1595–1607. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM (2003) The insulin resistance syndrome. Curr Atheroscler Rep 5: 364–371. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM (2009) Is diagnosing metabolic syndrome a uniquely simple way to predict incident type 2 diabetes mellitus? CMAJ 180: 601–602. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.090092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ervin RB (2009) Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among adults 20 years of age and over, by sex, age, race and ethnicity, and body mass index: United States, 2003–2006. Natl Health Stat Report 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Wildman RP, Muntner P, Reynolds K, McGinn AP, Rajpathak S, Wylie-Rosett J, et al. (2008) The obese without cardiometabolic risk factor clustering and the normal weight with cardiometabolic risk factor clustering: prevalence and correlates of 2 phenotypes among the US population (NHANES 1999–2004). Arch Intern Med 168: 1617–1624. doi: 10.1001/archinte.168.15.1617 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

