Oroxylin A promotes retinal ganglion cell survival in a rat optic nerve crush model
- PMID: 28640893
- PMCID: PMC5480866
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178584
Oroxylin A promotes retinal ganglion cell survival in a rat optic nerve crush model
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effect of oroxylin A on the survival of retinal ganglion cells (RGC) and the activation of microglial cells in a rat optic nerve (ON) crush model.
Methods: Oroxylin A (15mg/Kg in 0.2ml phosphate-buffered saline) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS control) was immediately administered after ON crush once by subcutaneous injection. Rats were euthanized at 2 weeks after the crush injury. The density of RGC was counted by retrograde labeling with FluoroGold and immunostaining of retina flat mounts for Brn3a. Electrophysiological visual function was assessed by flash visual evoked potentials (FVEP). TUNEL assay, immunoblotting analysis of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in the retinas, and immunohistochemistry of GFAP in the retinas and ED1 in the ON were evaluated.
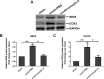
Results: Two weeks after the insult, the oroxylin A-treated group had significantly higher FG labeled cells and Brn3a+ cells suggesting preserved RGC density in the central and mid-peripheral retinas compared with those of the PBS-treated group. FVEP measurements showed a significantly better preserved latency of the P1 wave in the ON-crushed, oroxylin A-treated rats than the ON-crushed, PBS treated rats. TUNEL assays showed fewer TUNEL positive cells in the ON-crushed, oroxylin A-treated rats. The number of ED1 positive cells was reduced at the lesion site of the optic nerve in the ON-crushed, oroxylin A-treated group. Increased GFAP expression in the retina was reduced greatly in ON-crushed, oroxylin A-treated group. Furthermore, administration of oroxylin A significantly attenuated ON crush insult-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression in the retinas.
Conclusions: These results demonstrated that oroxylin A hasss neuroprotective effects on RGC survival with preserved visual function and a decrease in microglial infiltration in the ONs after ON crush injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effect of 4-(Phenylsulfanyl)butan-2-one on optic nerve crush model in rats.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Feb;143:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.10.004. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26472213
-
Neuroprotective effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in neurodegeneration after optic nerve crush in rats.Exp Eye Res. 2008 Sep;87(3):242-50. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.06.004. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Exp Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18602391
-
Lack of protective effect of local administration of triamcinolone or systemic treatment with methylprednisolone against damages caused by optic nerve crush in rats.Exp Eye Res. 2011 Feb;92(2):112-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.12.008. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Exp Eye Res. 2011. PMID: 21185832
-
Mitochondrial targeted therapy with elamipretide (MTP-131) as an adjunct to tumor necrosis factor inhibition for traumatic optic neuropathy in the acute setting.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Oct;199:108178. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108178. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32758490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods to Identify Rat and Mouse Retinal Ganglion Cells in Retinal Flat-Mounts.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2708:175-194. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3409-7_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37558971 Review.
Cited by
-
AAV2-mediated GRP78 Transfer Alleviates Retinal Neuronal Injury by Downregulating ER Stress and Tau Oligomer Formation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Sep 4;59(11):4670-4682. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24427. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30267089 Free PMC article.
-
CD200Fc Attenuates Retinal Glial Responses and RGCs Apoptosis After Optic Nerve Crush by Modulating CD200/CD200R1 Interaction.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Feb;64(2):200-210. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-1020-z. Epub 2017 Dec 26. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29280053
-
Anticancer potential of oroxylin A: from mechanistic insight to synergistic perspectives.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Feb;396(2):191-212. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02298-0. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36214865 Review.
-
Oroxylin A: A Promising Flavonoid for Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 26;12(9):1185. doi: 10.3390/biom12091185. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Oroxylin A on Retinal Ganglion Cells in Experimental Model of Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 3;10(6):902. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060902. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinsapir KD. Traumatic optic neuropathy. Current opinion in ophthalmology. 1999;10(5):340–2. Epub 2000/01/06. . - PubMed
-
- Quigley HA. Ganglion cell death in glaucoma: pathology recapitulates ontogeny. Australian and New Zealand journal of ophthalmology. 1995;23(2):85–91. Epub 1995/05/01. . - PubMed
-
- Levin LA, Louhab A. Apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Archives of ophthalmology. 1996;114(4):488–91. Epub 1996/04/01. . - PubMed
-
- Solomon AS, Lavie V, Hauben U, Monsonego A, Yoles E, Schwartz M. Complete transection of rat optic nerve while sparing the meninges and the vasculature: an experimental model for optic nerve neuropathy and trauma. Journal of neuroscience methods. 1996;70(1):21–5. Epub 1996/12/01. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0270(96)00098-2 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

