Regulation of glycolysis in brown adipocytes by HIF-1α
- PMID: 28642579
- PMCID: PMC5481455
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04246-y
Regulation of glycolysis in brown adipocytes by HIF-1α
Abstract
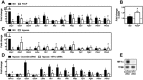
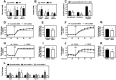
Brown adipose tissue takes up large amounts of glucose during cold exposure in mice and humans. Here we report an induction of glucose transporter 1 expression and increased expression of several glycolytic enzymes in brown adipose tissue from cold-exposed mice. Accordingly, these genes were also induced after β-adrenergic activation of cultured brown adipocytes, concomitant with accumulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein levels. HIF-1α accumulation was dependent on uncoupling protein 1 and generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Expression of key glycolytic enzymes was reduced after knockdown of HIF-1α in mature brown adipocytes. Glucose consumption, lactate export and glycolytic capacity were reduced in brown adipocytes depleted of Hif-1α. Finally, we observed a decreased β-adrenergically induced oxygen consumption in Hif-1α knockdown adipocytes cultured in medium with glucose as the only exogenously added fuel. These data suggest that HIF-1α-dependent regulation of glycolysis is necessary for maximum glucose metabolism in brown adipocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

