Host Factors in Coronavirus Replication
- PMID: 28643204
- PMCID: PMC7119980
- DOI: 10.1007/82_2017_25
Host Factors in Coronavirus Replication
Abstract
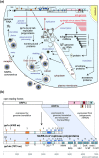
Coronaviruses are pathogens with a serious impact on human and animal health. They mostly cause enteric or respiratory disease, which can be severe and life threatening, e.g., in the case of the zoonotic coronaviruses causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in humans. Despite the economic and societal impact of such coronavirus infections, and the likelihood of future outbreaks of additional pathogenic coronaviruses, our options to prevent or treat coronavirus infections remain very limited. This highlights the importance of advancing our knowledge on the replication of these viruses and their interactions with the host. Compared to other +RNA viruses, coronaviruses have an exceptionally large genome and employ a complex genome expression strategy. Next to a role in basic virus replication or virus assembly, many of the coronavirus proteins expressed in the infected cell contribute to the coronavirus-host interplay. For example, by interacting with the host cell to create an optimal environment for coronavirus replication, by altering host gene expression or by counteracting the host's antiviral defenses. These coronavirus-host interactions are key to viral pathogenesis and will ultimately determine the outcome of infection. Due to the complexity of the coronavirus proteome and replication cycle, our knowledge of host factors involved in coronavirus replication is still in an early stage compared to what is known for some other +RNA viruses. This review summarizes our current understanding of coronavirus-host interactions at the level of the infected cell, with special attention for the assembly and function of the viral RNA-synthesising machinery and the evasion of cellular innate immune responses.
Figures
References
-
- Baas T, Taubenberger JK, Chong PY, Chui P, Katze MG. SARS-CoV virus-host interactions and comparative etiologies of acute respiratory distress syndrome as determined by transcriptional and cytokine profiling of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. J Interferon Cytokine Res: The Official Journal of The International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research. 2006;26:309–317. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailey-Elkin BA, Knaap RC, Johnson GG, Dalebout TJ, Ninaber DK, van Kasteren PB, Bredenbeek PJ, Snijder EJ, Kikkert M, Mark BL. Crystal structure of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) papain-like protease bound to ubiquitin facilitates targeted disruption of deubiquitinating activity to demonstrate its role in innate immune suppression. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:34667–34682. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

