Structure and Function of the Human Insula
- PMID: 28644199
- PMCID: PMC6032992
- DOI: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000377
Structure and Function of the Human Insula
Abstract
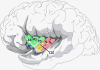
The insular cortex, or "Island of Reil," is hidden deep within the lateral sulcus of the brain. Subdivisions within the insula have been identified on the basis of cytoarchitectonics, sulcal landmarks, and connectivity. Depending on the parcellation technique used, the insula can be divided into anywhere between 2 and 13 distinct subdivisions. The insula subserves a wide variety of functions in humans ranging from sensory and affective processing to high-level cognition. Here, we provide a concise summary of known structural and functional features of the human insular cortex with a focus on lesion case studies and recent neuroimaging evidence for considerable functional heterogeneity of this brain region.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural Connections of Functionally Defined Human Insular Subdivisions.Cereb Cortex. 2018 Oct 1;28(10):3445-3456. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx211. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 28968768 Free PMC article.
-
Altered functional organization within the insular cortex in adult males with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder: evidence from connectivity-based parcellation.Mol Autism. 2016 Oct 5;7:41. doi: 10.1186/s13229-016-0106-8. eCollection 2016. Mol Autism. 2016. PMID: 27713815 Free PMC article.
-
The insular cortex.Curr Biol. 2017 Jun 19;27(12):R580-R586. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.05.010. Curr Biol. 2017. PMID: 28633023
-
The insula (Island of Reil) and its role in auditory processing. Literature review.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2003 May;42(2):143-54. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(03)00172-3. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2003. PMID: 12738055 Review.
-
Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1996 Oct;22(3):229-44. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(96)00011-2. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1996. PMID: 8957561 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered cerebellar-cortical resting-state functional connectivity in cannabis users.J Psychopharmacol. 2021 Jul;35(7):823-832. doi: 10.1177/02698811211019291. Epub 2021 May 25. J Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34034553 Free PMC article.
-
Neural mechanisms of brand love relationship dynamics: Is the development of brand love relationships the same as that of interpersonal romantic love relationships?Front Neurosci. 2022 Nov 10;16:984647. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.984647. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36440289 Free PMC article.
-
Individual Deviation-Based Functional Hypergraph for Identifying Subtypes of Autism Spectrum Disorder.Brain Sci. 2024 Jul 24;14(8):738. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14080738. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39199433 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of the Involvement of the Insular Cortex in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 5;22(5):2648. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052648. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphologic alterations of the fear circuitry: the role of sex hormones and oral contraceptives.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 7;14:1228504. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1228504. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38027091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustine JR. Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res Rev. 1996;22:229–244. - PubMed
-
- Mavridis IN. Insula: Neuroanatomy, Functions and Clinical Disorders. Nova Science Publishers; New York, NY: 2014. Gross, functional and neurosurgical anatomy of the human insula: From basic science to clinical practice.
-
- Brodmann K. Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde (in German) Leipzig: Johann Ambrosius Barth; 1909.
-
- Economo C, Koskinas GN. Die Cytoarchitektonik der Hirnrinde des erwachsenen Menschen (in German) Wien & Berlin: Springer; 1925.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

