Testing an Integrative Model of Affect Regulation and Avoidance in Non-Suicidal Self-Injury and Disordered Eating
- PMID: 28644927
- PMCID: PMC5917567
- DOI: 10.1080/13811118.2017.1340854
Testing an Integrative Model of Affect Regulation and Avoidance in Non-Suicidal Self-Injury and Disordered Eating
Abstract
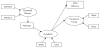
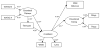
This research tested a model that integrates risk factors among non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) and eating disorder (ED) behaviors with the aim of elucidating possible shared and unique mechanisms underlying both behaviors. Emotional distress, limited access to emotion regulation (ER) strategies, experiential avoidance, and NSSI/ED frequency were examined in a sample of 230 female undergraduates. Structural equation modeling indicated that limited access to ER strategies and avoidance mediated relationship between emotional distress and avoidance, which in turn was associated with NSSI and ED behaviors. Results suggest NSSI and ED behaviors may serve similar emotion regulation functions, and specifically highlight the role of experiential avoidance in these behaviors.
Keywords: eating disorders; emotion regulation; experiential avoidance; non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI).
Figures
References
-
- Boelen PA, Reijntjes A. Measuring experiential avoidance: Reliability and validity of the Dutch 9-item acceptance and action questionnaire (AAQ) Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment. 2008;30(4):241–251. doi: 10.1007/s10862-008-9082-4. - DOI
-
- Bond FW, Hayes SC, Baer RA, Carpenter KM, Guenole N, Orcutt HK, … Zettle RD. Preliminary psychometric properties of the acceptance and action Questionnaire–II: A revised measure of psychological inflexibility and experiential avoidance. Behavior Therapy. 2011;42(4):676–688. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2011.03.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
