Identification of major routes of HIV transmission throughout Mesoamerica
- PMID: 28645708
- PMCID: PMC5610625
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.06.021
Identification of major routes of HIV transmission throughout Mesoamerica
Abstract
Background: Migration and travel are major drivers of the spread of infectious diseases. Geographic proximity and a common language facilitate travel and migration in Mesoamerica, which in turn could affect the spread of HIV in the region.
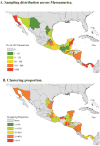
Methods: 6092 HIV-1 subtype B partial pol sequences sampled from unique antiretroviral treatment-naïve individuals from Mexico (40.7%), Guatemala (24.4%), Honduras (19%), Panama (8.2%), Nicaragua (5.5%), Belize (1.4%), and El Salvador (0.7%) between 2011 and 2016 were included. Phylogenetic and genetic network analyses were performed to infer putative relationships between HIV sequences. The demographic and geographic associations with clustering were analyzed and viral migration patterns were inferred using the Slatkin-Maddison approach on 100 iterations of random subsets of equal number of sequences per location.
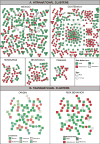
Results: A total of 1685/6088 (27.7%) of sequences linked with at least one other sequence, forming 603 putative transmission clusters (range: 2-89 individuals). Clustering individuals were significantly more likely to be younger (median age 29 vs 33years, p<0.01) and men-who-have-sex-with-men (40.4% vs 30.3%, p<0.01). Of the 603 clusters, 30 (5%) included sequences from multiple countries with commonly observed linkages between Mexican and Honduran sequences. Eight of the 603 clusters included >10 individuals, including two comprised exclusively of Guatemalans (52 and 89 individuals). Phylogenetic and migration analyses suggested that the Central and Southern regions of Mexico along with Belize were major sources of HIV throughout the region (p<0.01) with genetic flow southward from Mexico to the other nations of Mesoamerica. We also found evidence of significant viral migration within Mexico.
Conclusion: International clusters were infrequent, suggesting moderate migration between HIV epidemics of the different Mesoamerican countries. Nevertheless, we observed important sources of transnational HIV spread in the region, including Southern and Central Mexico and Belize.
Keywords: Clusters; HIV; Mesoamerica; Migration; Network.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Antoine Chaillon, Santiago Avila-Ríos, Ann Dennis, Claudia García-Morales, Daniela Tapia-Trejo, Juan M. Pascale, Guillermo Porras-Cortés, Carlos J. Quant-Durán C, Ivette Lorenzana, Rita I. Meza, Elsa Y. Palou, Marvin Manzanero, Rolando A. Cedillos, Gustavo Reyes-Terán, Sanjay R. Mehta do not have any commercial or other associations that might pose a conflict of interest. Carlos R Mejia Villatoro has received supports from Merck, Gilead, Roche and Joel O. Wertheim has received grant support from Gilead Science Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Faria NR, Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Baele G, Bedford T, Ward MJ, Tatem AJ, Sousa JD, Arinaminpathy N, Pépin J, Posada D, Peeters M, Pybus OG, Lemey P. HIV epidemiology. The early spread and epidemic ignition of HIV-1 in human populations. Science. 2014;346(6205):56–61. doi: 10.1126/science.1256739. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hawkes S, Hart GJ, Johnson AM, Shergold C, Ross E, Herbert KM, Mortimer P, Parry JV, Mabey D. Risk behaviour and HIV prevalence in international travellers. Aids. 1994;8(2):247–52. Epub 1994/02/01. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

