Combined BTK and PI3Kδ Inhibition with Acalabrutinib and ACP-319 Improves Survival and Tumor Control in CLL Mouse Model
- PMID: 28645939
- PMCID: PMC5626587
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0650
Combined BTK and PI3Kδ Inhibition with Acalabrutinib and ACP-319 Improves Survival and Tumor Control in CLL Mouse Model
Abstract
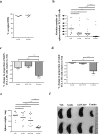
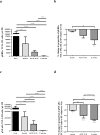
Purpose: Targeting the B-cell receptor (BCR) pathway with inhibitors of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) and PI3Kδ is highly effective for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). However, deep remissions are uncommon, and drug resistance with single-agent therapy can occur. In vitro studies support the effectiveness of combing PI3Kδ and BTK inhibitors.Experimental Design: As CLL proliferation and survival depends on the microenvironment, we used murine models to assess the efficacy of the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib combined with the PI3Kδ inhibitor ACP-319 in vivo We compared single-agent with combination therapy in TCL1-192 cell-injected mice, a model of aggressive CLL.Results: We found significantly larger reductions in tumor burden in the peripheral blood and spleen of combination-treated mice. Although single-agent therapy improved survival compared with control mice by a few days, combination therapy extended survival by over 2 weeks compared with either single agent. The combination reduced tumor proliferation, NF-κB signaling, and expression of BCL-xL and MCL-1 more potently than single-agent therapy.Conclusions: The combination of acalabrutinib and ACP-319 was superior to single-agent treatment in a murine CLL model, warranting further investigation of this combination in clinical studies. Clin Cancer Res; 23(19); 5814-23. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
FK, TC, RI are employees and equity holders of Acerta Pharma. RU is an equity holder and member of the board of directors of Acerta Pharma. BL is a former employee of Acerta and entitled to milestone payments. AW received research funding from Pharmacylics and Acerta Pharma. NC has received research funding from Pharmacylics. CN received funding from the Danish Cancer Society and the Novo Nordisk Foundation, and has received grants/consultancy fees from Abbvie, Janssen, Gilead, Roche and Novartis outside of this study. HMJ, SSC, and SH declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- NCI. Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results. [website] 2012 [cited 2013 10–17]; Available from:
-
- Brown JR, Hallek MJ, Pagel JM. Chemoimmunotherapy Versus Targeted Treatment in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: When, How Long, How Much, and in Which Combination? American Society of Clinical Oncology educational book/ASCO American Society of Clinical Oncology Meeting. 2016;35:e387–98. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

