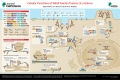
Cellular functions of WASP family proteins at a glance
- PMID: 28646090
- PMCID: PMC5536917
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.199570
Cellular functions of WASP family proteins at a glance
Abstract
Proteins of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family function as nucleation-promoting factors for the ubiquitously expressed Arp2/3 complex, which drives the generation of branched actin filaments. Arp2/3-generated actin regulates diverse cellular processes, including the formation of lamellipodia and filopodia, endocytosis and/or phagocytosis at the plasma membrane, and the generation of cargo-laden vesicles from organelles including the Golgi, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the endo-lysosomal network. Recent studies have also identified roles for WASP family members in promoting actin dynamics at the centrosome, influencing nuclear shape and membrane remodeling events leading to the generation of autophagosomes. Interestingly, several WASP family members have also been observed in the nucleus where they directly influence gene expression by serving as molecular platforms for the assembly of epigenetic and transcriptional machinery. In this Cell Science at a Glance article and accompanying poster, we provide an update on the subcellular roles of WHAMM, JMY and WASH (also known as WASHC1), as well as their mechanisms of regulation and emerging functions within the cell.
Keywords: Actin; Arp2/3; JMY; N-WASP; WASH; WASP; WAVE; WHAMM; WHAMY.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
References
-
- Bartuzi P., Billadeau D. D., Favier R., Rong S., Dekker D., Fedoseienko A., Fieten H., Wijers M., Levels J. H., Huijkman N. et al. (2016). CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL. Nat. Commun. 7, 10961 10.1038/ncomms10961 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources