Staphylococcus aureus Strain Newman Photoinactivation and Cellular Response to Sunlight Exposure
- PMID: 28646114
- PMCID: PMC5561283
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01052-17
Staphylococcus aureus Strain Newman Photoinactivation and Cellular Response to Sunlight Exposure
Abstract
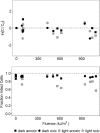
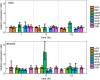
Sunlight influences microbial water quality of surface waters. Previous studies have investigated photoinactivation mechanisms and cellular photostress responses of fecal indicator bacteria (FIB), including Escherichia coli and enterococci, but further work is needed to characterize photostress responses of bacterial pathogens. Here we investigate the photoinactivation of Staphylococcus aureus (strain Newman), a pigmented, waterborne pathogen of emerging concern. We measured photodecay using standard culture-based assays and cellular membrane integrity and investigated photostress response by measuring the relative number of mRNA transcripts of select oxidative stress, DNA repair, and metabolism genes. Photoinactivation experiments were performed in both oxic and anoxic systems to further investigate the role of oxygen-mediated and non-oxygen-mediated photoinactivation mechanisms. S. aureus lost culturability much faster in oxic systems than in anoxic systems, indicating an important role for oxygen in photodecay mechanisms. S. aureus cell membranes were damaged by sunlight exposure in anoxic systems but not in oxic systems, as measured by cell membrane permeability to propidium iodide. After sunlight exposure, S. aureus increased expression of a gene coding for methionine sulfoxide reductase after 12 h of sunlight exposure in the oxic system and after 6 h of sunlight exposure in the anoxic system, suggesting that methionine sulfoxide reductase is an important enzyme for defense against both oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent photostresses. This research highlights the importance of oxygen in bacterial photoinactivation in environmentally relevant systems and the complexity of the bacterial photostress response with respect to cell structure and transcriptional regulation.IMPORTANCEStaphylococcus aureus is a pathogenic bacterium that causes gastrointestinal, respiratory, and skin infections. In severe cases, S. aureus infection can lead to life-threatening diseases, including pneumonia and sepsis. Cases of community-acquired S. aureus infection have been increasing in recent years, pointing to the importance of considering S. aureus transmission pathways outside the hospital environment. Associations have been observed between recreational water contact and staphylococcal skin infections, suggesting that recreational waters may be an important environmental transmission pathway for S. aureus However, prediction of human health risk in recreational waters is hindered by incomplete knowledge of pathogen sources, fate, and transport in this environment. This study is an in-depth investigation of the inactivation of a representative strain of S. aureus by sunlight exposure, one of the most important factors controlling the fate of microbial contaminants in clear waters, which will improve our ability to predict water quality changes and human health risk in recreational waters.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; coastal waters; enterococci; fecal indicator bacteria; photoinactivation.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptional Response of Staphylococcus aureus to Sunlight in Oxic and Anoxic Conditions.Front Microbiol. 2018 Feb 23;9:249. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00249. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29599752 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for photoinactivation of Enterococcus faecalis in seawater.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Nov;78(21):7776-85. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02375-12. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22941072 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of four methionine sulfoxide reductases in Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0117594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117594. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25680075 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic approaches to study Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis.J Proteomics. 2010 Feb 10;73(4):701-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Oct 29. J Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 19879388 Review.
-
The thioredoxin antioxidant system.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 23899494 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional Response of Staphylococcus aureus to Sunlight in Oxic and Anoxic Conditions.Front Microbiol. 2018 Feb 23;9:249. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00249. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29599752 Free PMC article.
-
Sunlight-mediated inactivation of health-relevant microorganisms in water: a review of mechanisms and modeling approaches.Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2018 Aug 16;20(8):1089-1122. doi: 10.1039/c8em00047f. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2018. PMID: 30047962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases in Oxidative Stress Tolerance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus and Other Bacteria.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;7(10):128. doi: 10.3390/antiox7100128. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative proteomic investigation of multiple methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains generated through adaptive laboratory evolution.iScience. 2021 Aug 6;24(9):102950. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102950. eCollection 2021 Sep 24. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34458699 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

