CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing via postnatal administration of AAV vector cures haemophilia B mice
- PMID: 28646206
- PMCID: PMC5482879
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04625-5
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing via postnatal administration of AAV vector cures haemophilia B mice
Abstract
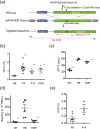
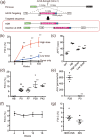
Haemophilia B, a congenital haemorrhagic disease caused by mutations in coagulation factor IX gene (F9), is considered an appropriate target for genome editing technology. Here, we describe treatment strategies for haemophilia B mice using the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/Cas9 system. Administration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) 8 vector harbouring Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 (SaCas9) and single guide RNA (sgRNA) to wild-type adult mice induced a double-strand break (DSB) at the target site of F9 in hepatocytes, sufficiently developing haemophilia B. Mutation-specific gene editing by simultaneous induction of homology-directed repair (HDR) sufficiently increased FIX levels to correct the disease phenotype. Insertion of F9 cDNA into the intron more efficiently restored haemostasis via both processes of non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) and HDR following DSB. Notably, these therapies also cured neonate mice with haemophilia, which cannot be achieved with conventional gene therapy with AAV vector. Ongoing haemophilia therapy targeting the antithrombin gene with antisense oligonucleotide could be replaced by SaCas9/sgRNA-expressing AAV8 vector. Our results suggest that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing using an AAV8 vector provides a flexible approach to induce DSB at target genes in hepatocytes and could be a good strategy for haemophilia gene therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
T.O. received research funding from Bayer AG. S.M. owns equity in a gene therapy company (Gene Therapy Research Institution) that commercializes the use of AAV vectors for gene therapy applications. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Young G. New challenges in hemophilia: long-term outcomes and complications. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:362–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

