Steroidal Saponins from the Genus Smilax and Their Biological Activities
- PMID: 28646341
- PMCID: PMC5507813
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-017-0139-5
Steroidal Saponins from the Genus Smilax and Their Biological Activities
Abstract
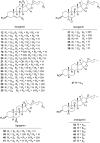
The Smilax species, widely distributed in tropical region of the world and the warm areas of East Asia and North America, are extensively used as folk medicine to treat inflammatory disorders. Chemical investigation on Smilax species showed they are rich sources of steroidal saponins with diversified structure types, including spirostane, isospirostane, furostane, pregnane, and cholestane. This review mainly summarizes the steroidal saponins (1-104) reported from the genus Smilax between 1967 and 2016, and their biological activities. The relationship between structures of steroidal saponins and related biological activities were briefly discussed.
Keywords: Biological activities; Smilax; Steroidal saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Editorial Committee of the flora of the Chinese Aacdemy of Sciences, ‘Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae’, Beijing House of Science Press (1978)
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission . Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2015.
-
- Compilation Group of Chinese Hebral Medicine . The Assembly of Chinese Herbal Medicine. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 1975.
-
- Ma H, Wang W, Dong F. Zhongguo Yaofang. 2009;20:1191–1193.
-
- Yi Y, Liu Y, Peng Y, Xie Y, Wang S. Zhongguo Yaofang. 2011;25:1430–1432.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

