Endothelial cell apoptosis in angiogenesis and vessel regression
- PMID: 28646366
- PMCID: PMC11107683
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-017-2577-y
Endothelial cell apoptosis in angiogenesis and vessel regression
Abstract
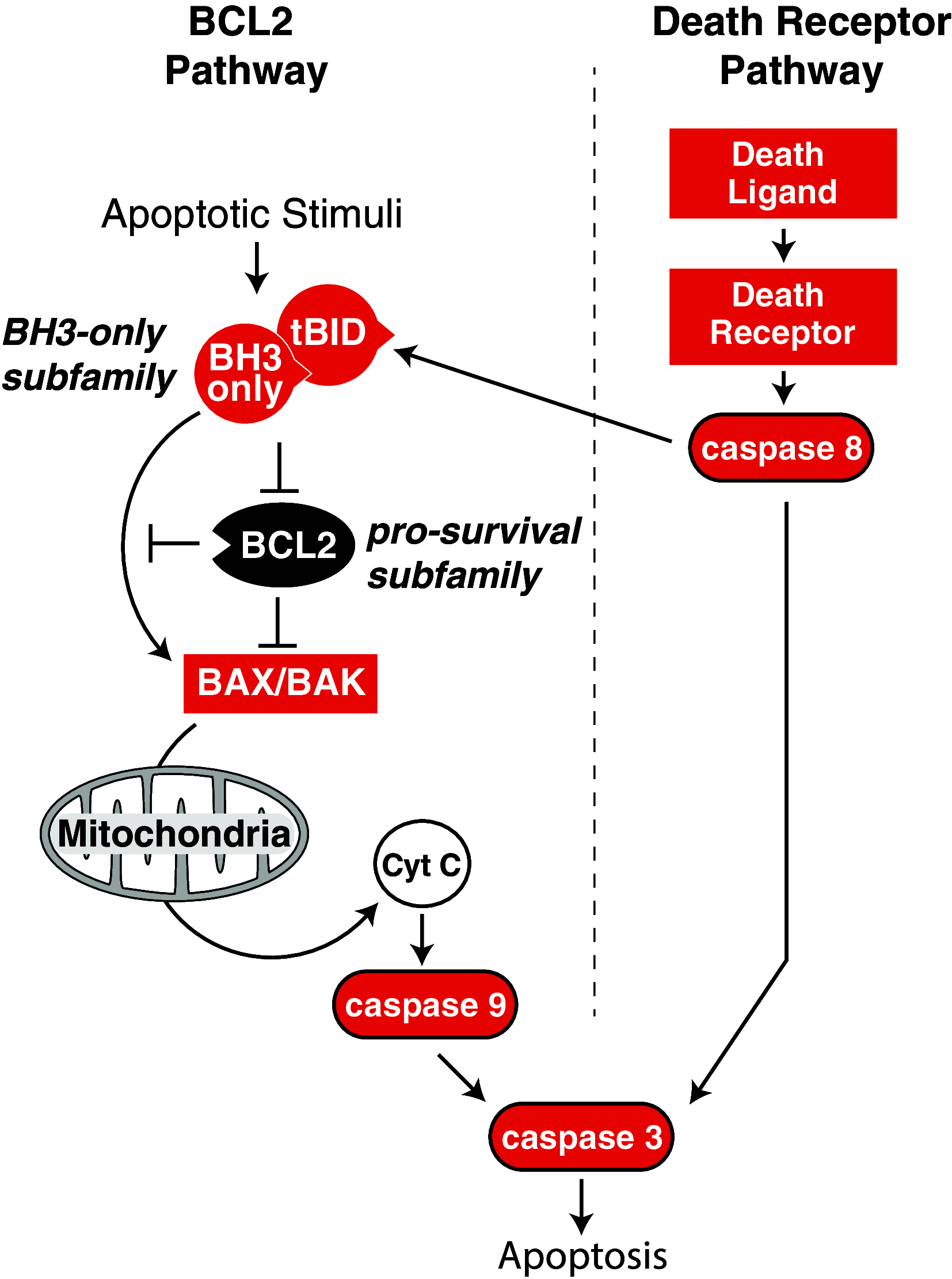
Blood vessel regression is an essential process for ensuring blood vessel networks function at optimal efficiency and for matching blood supply to the metabolic needs of tissues as they change over time. Angiogenesis is the major mechanism by which new blood vessels are produced, but the vessel growth associated with angiogenesis must be complemented by remodeling and maturation events including the removal of redundant vessel segments and cells to fashion the newly forming vasculature into an efficient, hierarchical network. This review will summarize recent findings on the role that endothelial cell apoptosis plays in vascular remodeling during angiogenesis and in vessel regression more generally.
Keywords: BCL2; Death receptors; Diabetes; Diabetic retinopathy; Vessel pruning.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

