IFNγ-producing CD4+ T lymphocytes: the double-edged swords in tuberculosis
- PMID: 28646367
- PMCID: PMC5482791
- DOI: 10.1186/s40169-017-0151-8
IFNγ-producing CD4+ T lymphocytes: the double-edged swords in tuberculosis
Abstract
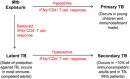
IFNγ-producing CD4+ T cells (IFNγ+CD4+ T cells) are the key orchestrators of protective immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Primarily, these cells act by enabling Mtb-infected macrophages to enforce phagosome-lysosome fusion, produce reactive nitrogen intermediates (RNIs), and activate autophagy pathways. However, TB is a heterogeneous disease and a host of clinical and experimental findings has also implicated IFNγ+CD4+ T cells in TB pathogenesis. High frequency of IFNγ+CD4+ T cells is the most invariable feature of the active disease. Active TB patients mount a heightened IFNγ+CD4+ T cell response to mycobacterial antigens and demonstrate an IFNγ-inducible transcriptomic signature. IFNγ+CD4+ T cells have also been shown to mediate TB-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB-IRIS) observed in a subset of antiretroviral therapy (ART)-treated HIV- and Mtb-coinfected people. The pathological face of IFNγ+CD4+ T cells during mycobacterial infection is further uncovered by studies in the animal model of TB-IRIS and in Mtb-infected PD-1-/- mice. This manuscript encompasses the evidence supporting the dual role of IFNγ+CD4+ T cells during Mtb infection and sheds light on immune mechanisms involved in protection versus pathogenesis.
Keywords: CD4+ T cell; Granuloma; IFN-gamma; Macrophage; Matrix metalloproteinase; Necrosis; Neutrophil; Pathogenesis; Protection; TB–IRIS; Tuberculosis.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2016. 2016
-
- Mahnke YD, Greenwald JH, DerSimonian R, Roby G, Antonelli LR, Sher A, et al. Selective expansion of polyfunctional pathogen-specific CD4+ T cells in HIV-1–infected patients with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Blood. 2012;119(13):3105–3112. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-380840. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
