Lipophilicity Influences Drug Binding to α1-Acid Glycoprotein F1/S Variants But Not to the A Variant
- PMID: 28646384
- PMCID: PMC5629133
- DOI: 10.1007/s40268-017-0193-9
Lipophilicity Influences Drug Binding to α1-Acid Glycoprotein F1/S Variants But Not to the A Variant
Abstract
Objective: Human α1-acid glycoprotein has genetic variants, the F1, S, and A variants, which can be separated isoelectrophoretically. These variants show differences in their affinity of binding to several drugs. In this study, we investigated the factors determining drug binding to these α1-acid glycoprotein genetic variants using disopyramide, warfarin, and tamsulosin as marker compounds.
Methods: Binding of the marker drugs to human α1-acid glycoprotein was determined by ultra-filtration in the presence or absence of various other drugs. For screening of the α1-acid glycoprotein variants to which the marker drugs became bound, the effects of various other drugs on their binding were studied. The binding data were analyzed using a competitive inhibition model and the relationship between the estimated dissociation constants and physicochemical properties, such as log P, was also analyzed.
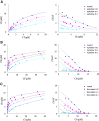
Results: The binding of tamsulosin was significantly decreased by aprindine, carvedilol, erythromycin, thioridazine, and warfarin, but not by disopyramide. The dissociation constants of drugs bound to F1/S variants were significantly correlated with their lipophilicity, but those for the A variant were not.
Conclusions: We were able to develop a simple screening method for determining individual α1-acid glycoprotein variants to which drugs would bind. The binding of drugs to F1/S variants may be determined mainly by drug lipophilicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
No funding was received for the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Kazuhiko Hanada has no conflict of interest directly relevant to the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selective binding of tamsulosin to genetic variants of human alpha1-acid glycoprotein.Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Aug;30(8):1593-5. doi: 10.1248/bpb.30.1593. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007. PMID: 17666829
-
Binding of disopyramide, methadone, dipyridamole, chlorpromazine, lignocaine and progesterone to the two main genetic variants of human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: evidence for drug-binding differences between the variants and for the presence of two separate drug-binding sites on alpha 1-acid glycoprotein.Pharmacogenetics. 1996 Oct;6(5):403-15. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199610000-00004. Pharmacogenetics. 1996. PMID: 8946472
-
Differential binding of disopyramide and warfarin enantiomers to human alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein variants.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Dec;56(6):664-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01909.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14616427 Free PMC article.
-
[Drug binding analysis of human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein using capillary electrophoresis].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003 Sep;123(9):781-8. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.123.781. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14513769 Review. Japanese.
-
Ethnic differences in reactions to drugs and xenobiotics. Other protein variants with pharmacogenetic consequences: albumin and orosomucoid.Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;214:345-55. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986. PMID: 3523512 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
An overview of albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein main characteristics: highlighting the roles of amino acids in binding kinetics and molecular interactions.Heliyon. 2019 Nov 21;5(11):e02879. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02879. eCollection 2019 Nov. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31844752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Canine orosomucoid (alpha-1 acid glycoprotein) variants and their influence on drug plasma protein binding.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jan;44(1):116-125. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12899. Epub 2020 Aug 3. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32744755 Free PMC article.
-
Into the Labyrinth of the Lipocalin α1-Acid Glycoprotein.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 8;12:686251. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.686251. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34168570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Daemen MARC, Heemskerk VH, vant’s eer C, Denecker G, Wolfs TGAM, Vandenabeele P, Buurman WA. Functional protection by acute phase proteins alpha1-acid glycoprotein and alpha1-antitrypsin against ischemia/reperfusion injury by preventing apoptosis and inflammation. Circulation. 2000;102:1420–1426. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.12.1420. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

