Conformational regulation of CRISPR-associated nucleases
- PMID: 28646675
- PMCID: PMC5687066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.05.010
Conformational regulation of CRISPR-associated nucleases
Abstract
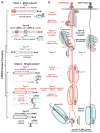
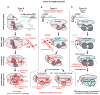
Adaptive immune systems in bacteria and archaea rely on small CRISPR-derived RNAs (crRNAs) to guide specialized nucleases to foreign nucleic acids. The activation of these nucleases is controlled by a series of molecular checkpoints that ensure precise cleavage of nucleic acid targets, while minimizing toxic off-target cleavage events. In this review, we highlight recent advances in understanding regulatory mechanisms responsible for controlling the activation of these nucleases and identify emerging regulatory themes conserved across diverse CRISPR systems.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Mohanraju P, Makarova KS, Zetsche B, Zhang F, Koonin EV, van der Oost J. Diverse evolutionary roots and mechanistic variations of the CRISPR-Cas systems. Science. 2016;353:aad5147. - PubMed
-
- Wright AV, Nuñez JK, Doudna JA. Biology and Applications of CRISPR Systems: Harnessing Nature’s Toolbox for Genome Engineering. Cell. 2016;164:29–44. - PubMed
-
- Sternberg SH, Doudna JA. Expanding the Biologist’s Toolkit with CRISPR-Cas9. Mol Cell. 2015;58:568–574. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, Marraffini LA. CRISPR-Cas: New Tools for Genetic Manipulations from Bacterial Immunity Systems. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015;69:209–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

