Common Molecular Subtypes Among Asian Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 28648284
- PMCID: PMC5524207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.05.009
Common Molecular Subtypes Among Asian Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
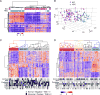
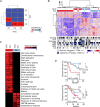
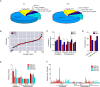
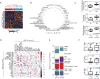
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are clinically disparate primary liver cancers with etiological and biological heterogeneity. We identified common molecular subtypes linked to similar prognosis among 199 Thai ICC and HCC patients through systems integration of genomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics. While ICC and HCC share recurrently mutated genes, including TP53, ARID1A, and ARID2, mitotic checkpoint anomalies distinguish the C1 subtype with key drivers PLK1 and ECT2, whereas the C2 subtype is linked to obesity, T cell infiltration, and bile acid metabolism. These molecular subtypes are found in 582 Asian, but less so in 265 Caucasian patients. Thus, Asian ICC and HCC, while clinically treated as separate entities, share common molecular subtypes with similar actionable drivers to improve precision therapy.
Keywords: TIGER-LC; cancer driver; cancer genomics; hepatocellular carcinoma; integrated genomics; intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; liver cancer; metabolomics; molecular subtypes; transcriptomics.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Banales JM, Cardinale V, Carpino G, Marzioni M, Andersen JB, Invernizzi P, Lind GE, Folseraas T, Forbes SJ, Fouassier L, et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA) Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2016;13:261–280. - PubMed
-
- Bridgewater J, Galle PR, Khan SA, Llovet JM, Park JW, Patel T, Pawlik TM, Gores GJ. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Journal of hepatology. 2014;60:1268–1289. - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. NEnglJ Med. 2003;348:1625–1638. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

