HOTAIR: a key regulator in gynecologic cancers
- PMID: 28649178
- PMCID: PMC5480152
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-017-0434-6
HOTAIR: a key regulator in gynecologic cancers
Abstract
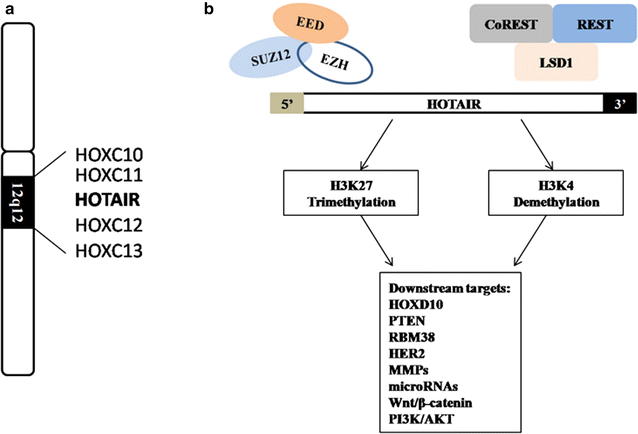
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play critical roles in the initiation and progression of human cancers. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) is an lncRNA localized to the mammalian HOXC gene cluster; it can interact with polycomb repressive complex 2 and the lysine-specific histone demethylase/CoREST/REST complex, and it manipulates the expression of various genes. HOTAIR promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by silencing tumor suppressors, and activating oncogenes and signaling pathways. HOTAIR is deregulated in many human cancers; despite its critical roles in health and disease, the underlying mechanisms governing HOTAIR function are unknown. In this review, we summarize the recent findings on the roles of HOTAIR in gynecologic cancers.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Chemoresistance; HOTAIR; Invasion; Metastasis; Radioresistance; lncRNAs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2017 Aug;14(2):1233-1239. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6312. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28789338 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA in genome regulation: prospects and mechanisms.RNA Biol. 2010 Sep-Oct;7(5):582-5. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.5.13216. Epub 2010 Sep 1. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 20930520 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in carcinogenesis and metastasis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014 Jan;46(1):1-5. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmt117. Epub 2013 Oct 27. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014. PMID: 24165275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR, a driver of malignancy, predicts negative prognosis and exhibits oncogenic activity in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2013 Oct 15;109(8):2266-78. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.548. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24022190 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of HOTAIR Long Non-coding RNA in Gliomas and Other CNS Disorders.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Feb 16;44(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01455-8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38366205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR in Central Nervous System Disorders: New Insights in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Potential.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jun 23;15:949095. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.949095. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35813070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic impacts on thermostability of onco-lncRNA HOTAIR during the development and progression of endometriosis.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 5;16(3):e0248168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248168. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33667269 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Transcriptome Patterns in Endometrial Cancers from Obese and Lean Women.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11471. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911471. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232772 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinopathological and Prognostic Significance of SPOCK1 in Gynecological Cancers: A Bioinformatics Based Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2025 Feb 16;14(2):209. doi: 10.3390/biology14020209. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001977 Free PMC article.
-
Biological roles of SLC16A1-AS1 lncRNA and its clinical impacts in tumors.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Mar 30;24(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03285-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38555465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen LL, Carmichael GG. Long noncoding RNAs in mammalian cells: what, where, and why? Wiley Interdiscipl Rev RNA. 2010;1(1):2–21. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources