GLYX-13, a NMDA Receptor Glycine-Site Functional Partial Agonist, Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia Injury In Vivo and Vitro by Differential Modulations of NMDA Receptors Subunit Components at Different Post-Ischemia Stage in Mice
- PMID: 28649199
- PMCID: PMC5465280
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00186
GLYX-13, a NMDA Receptor Glycine-Site Functional Partial Agonist, Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia Injury In Vivo and Vitro by Differential Modulations of NMDA Receptors Subunit Components at Different Post-Ischemia Stage in Mice
Abstract
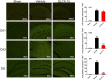
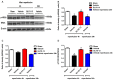
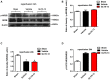
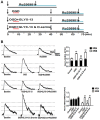
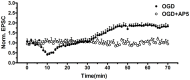
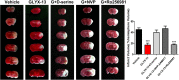
Excessive activation of NMDA receptors (NMDARs) is implicated in pathological synaptic plasticity also known as post-ischemic long-term potentiation (i-LTP) which was produced by glutamate mediated excitotoxicity after stroke. In the past decades, many NMDARs inhibitors failed in clinical investigations due to severe psychotomimetic side effects. GLYX-13 is a NMDAR modulator with glycine site partial agonist properties and has potential protective effects on ischemic neuronal death. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of GLYX-13 attenuating the ischemic neuronal damage remains elusive. Our study was conducted to examine the molecular, cellular and behavioral actions of GLYX-13 in stroke, and further characterize the mechanism underlying the neuroprotective actions via modulation of the NMDAR subunit composition. In present study we found that in vitro oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) stroke model, GLYX-13 blocked i-LTP and restored the ratio of NR2A/NR2B subunit composition. The glycine site of NMDARs full coagonist D-serine completely blocked the effects of GLYX-13 on i-LTP. Besides, in vivo middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model, GLYX-13 decreased the cerebral infarct volume and reduced injury of hippocampus. Western analysis showed that GLYX-13 down-regulated the expression of phosphorylated NR2B (Tyr1472) and up-regulated phosphorylated NR2A (Tyr1325). Furthermore, GLYX-13 treatment along with NR2B specific antagonist (Ro256981) failed to exhibit any additional neuro-protective effects, whereas the application of NR2A antagonist (NVP-AAM007) abolished the neuroprotective effects of GLYX-13, which suggested that the protective action of GLYX-13 should be by its regulation of NMDAR subunit components. Our study provides important insights on the potential protective mechanism of GLYX-13 in ischemia and proposes the glycine site of NMDARs as a novel target for developing therapeutic strategies to store synaptic function in stroke.
Keywords: GLYX-13; ischemia; oxygen-glucose deprivation; pathological synaptic plasticity; transient middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A NMDA receptor glycine site partial agonist, GLYX-13, simultaneously enhances LTP and reduces LTD at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in hippocampus.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Dec;55(7):1238-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.018. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18796308 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection by a novel NMDAR functional glycine site partial agonist, GLYX-13.Neuroreport. 2009 Aug 26;20(13):1193-7. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32832f5130. Neuroreport. 2009. PMID: 19623090
-
GLYX-13, a NMDA receptor glycine-site functional partial agonist, induces antidepressant-like effects without ketamine-like side effects.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Apr;38(5):729-42. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.246. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23303054 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
-
GLYX-13, an NMDA receptor glycine site functional partial agonist enhances cognition and produces antidepressant effects without the psychotomimetic side effects of NMDA receptor antagonists.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Feb;23(2):243-54. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.852536. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24251380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Levodopa Improves Cognitive Function and the Deficits of Structural Synaptic Plasticity in Hippocampus Induced by Global Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats.Front Neurosci. 2020 Nov 30;14:586321. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.586321. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33328857 Free PMC article.
-
ERK/mTOR signaling may underlying the antidepressant actions of rapastinel in mice.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 22;12(1):522. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02290-5. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36550125 Free PMC article.
-
An enriched environment promotes synaptic plasticity and cognitive recovery after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Mar;14(3):462-469. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.245470. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30539814 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine-induced NMDA receptor internalization provides neuroprotection and preserves vasculature following ischemic stroke.iScience. 2021 Dec 3;25(1):103539. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103539. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34977503 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo biloba extracts inhibit post-ischemic LTP through attenuating EPSCs in rat hippocampus.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Dec;36(8):2299-2311. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00830-4. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 34463942
References
-
- Burgdorf J., Zhang X. L., Nicholson K. L., Balster R. L., Leander J. D., Stanton P. K., et al. . (2013). GLYX-13, a NMDA receptor glycine-site functional partial agonist, induces antidepressant-like effects without ketamine-like side effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 38, 729–742. 10.1038/npp.2012.246 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burgdorf J., Zhang X. L., Weiss C., Gross A., Boikess S. R., Kroes R. A., et al. . (2015). The long-lasting antidepressant effects of rapastinel (GLYX-13) are associated with a metaplasticity process in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 308, 202–211. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cooper M. D., Rosenblat J. D., Cha D. S., Lee Y., Kakar R., McIntyre R. S. (2016). Strategies to mitigate dissociative and psychotomimetic effects of ketamine in the treatment of major depressive episodes: a narrative review. World J. Biol. Psychiatry [Epub ahead of print]. 10.3109/15622975.2016.1139747 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

