Addictive neurons
Abstract
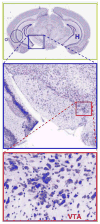
Since the reward center is considered to be the area tegmentalis ventralis of the hypothalamus, logically its neurons could mainly be responsible for addiction. However, the literature asserts that almost any neurons of CNS can respond to one or another addictive compound. Obviously not only addictive nicotine, but also alcohol, amphetamine, cannabis, cocaine, heroin and morphine may influence dopaminergic cells alone in VTA. Moreover, paradoxically some of these drugs ameliorate symptoms, counterbalance syndromes, cure diseases and improve health, not only those related to the CNS and in adults, but also almost all other organs and in children, e.g. epilepsy.
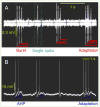
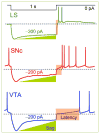
Keywords: ADP; AHP; LTD; LTP; amygdala; lateral septum; medial prefrontal cortex; paired pulse facilitation; rebound action potential; spike.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicting interests The author has declared that no conflict of interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cocaine Promotes Coincidence Detection and Lowers Induction Threshold during Hebbian Associative Synaptic Potentiation in Prefrontal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2017 Jan 25;37(4):986-997. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2257-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28123030 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical control of VTA function and influence on nicotine reward.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;86(8):1173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23933294 Review.
-
Loss of mGluR1-LTD following cocaine exposure accumulates Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors and facilitates synaptic potentiation in the prefrontal cortex.J Neurogenet. 2021 Sep-Dec;35(4):358-369. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2021.1931180. Epub 2021 Jun 7. J Neurogenet. 2021. PMID: 34092163 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies.Behav Brain Res. 1999 Jun;101(2):129-52. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00022-4. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10372570 Review.
-
D-amphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization: effect of lesioning dopaminergic terminals in the medial prefrontal cortex, the amygdala and the entorhinal cortex.Neuroscience. 2002;109(3):499-516. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00508-5. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 11823062
Cited by
-
Adam, amigo, brain, and K channel.Biophys Rev. 2023 Nov 6;15(5):1393-1424. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01163-5. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 37975011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kodirov SA. Targets of addictive nicotine in CNS and interactions with alcohol. In: Preedy VP, editor. The neuropathology of drug addictions and substance misuse. Elsevier; London: 2016. pp. 168–178.
-
- Bogomolets VI. Electrophysiological properties of neurons and neuronal organization of the crayfish somatogastric ganglion. Neurophysiology. 1970;2:233–237.
-
- Chaves C, Zuardi AW, Hallak JE. Minocycline as a potential treatment in the early stages of schizophrenia: a translational approach. Ther Targets Neurol Dis. 2015;2:e580.
-
- Stowie AC, Prosser RA, Glass JD. Cocaine modulation of the mammalian circadian clock: potential therapeutic targets. Ther Targets Neurol Dis. 2015;2:e607.
-
- Briun EA, Gekht AB, Polunina AG, Davydov DM, Gusev EI. Neuropsychological deficit in chronic heroin abusers. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2001;101:10–19. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
