Somatostatin binds to the human amyloid β peptide and favors the formation of distinct oligomers
- PMID: 28650319
- PMCID: PMC5505701
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.28401
Somatostatin binds to the human amyloid β peptide and favors the formation of distinct oligomers
Abstract
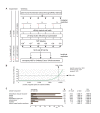
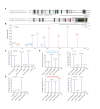
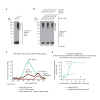
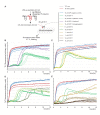
The amyloid β peptide (Aβ) is a key player in the etiology of Alzheimer disease (AD), yet a systematic investigation of its molecular interactions has not been reported. Here we identified by quantitative mass spectrometry proteins in human brain extract that bind to oligomeric Aβ1-42 (oAβ1-42) and/or monomeric Aβ1-42 (mAβ1-42) baits. Remarkably, the cyclic neuroendocrine peptide somatostatin-14 (SST14) was observed to be the most selectively enriched oAβ1-42 binder. The binding interface comprises a central tryptophan within SST14 and the N-terminus of Aβ1-42. The presence of SST14 inhibited Aβ aggregation and masked the ability of several antibodies to detect Aβ. Notably, Aβ1-42, but not Aβ1-40, formed in the presence of SST14 oligomeric assemblies of 50 to 60 kDa that were visualized by gel electrophoresis, nanoparticle tracking analysis and electron microscopy. These findings may be relevant for Aβ-directed diagnostics and may signify a role of SST14 in the etiology of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; abeta; biochemistry; human; interactome; mass spectrometry; mouse; neuroscience; oligomer; somatostatin.
Conflict of interest statement
HWa: Holds provisionary US patent on amyloid-beta binding polypeptides based on the results of this study (filing number 62/451,309).
GS-U: Holds provisionary US patent on amyloid-beta binding polypeptides based on the results of this study (filing number 62/451,309).
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Somatostatin in Alzheimer's disease: A new Role for an Old Player.Prion. 2018 Jan 2;12(1):1-8. doi: 10.1080/19336896.2017.1405207. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Prion. 2018. PMID: 29192843 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin, an In Vivo Binder to Aβ Oligomers, Binds to βPFOAβ(1-42) Tetramers.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Oct 21;11(20):3358-3365. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00470. Epub 2020 Oct 1. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32915532
-
Aggregation of Aβ40/42 chains in the presence of cyclic neuropeptides investigated by molecular dynamics simulations.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Mar 12;17(3):e1008771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008771. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33711010 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Alzheimer's β-amyloid peptides with cholesterol: mechanistic insights into amyloid pore formation.Biochemistry. 2014 Jul 22;53(28):4489-502. doi: 10.1021/bi500373k. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25000142 Review.
-
Functional Amyloids and their Possible Influence on Alzheimer Disease.Discoveries (Craiova). 2017 Oct 16;5(4):e79. doi: 10.15190/d.2017.9. Discoveries (Craiova). 2017. PMID: 32309597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular origin of somatostatin-positive neuron vulnerability.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Apr;27(4):2304-2314. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01463-4. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35145229 Free PMC article.
-
An endogenous PI3K interactome promoting astrocyte-mediated neuroprotection identifies a novel association with RNA-binding protein ZC3H14.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100118. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015389. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33234594 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin: Linking Cognition and Alzheimer Disease to Therapeutic Targeting.Pharmacol Rev. 2024 Oct 16;76(6):1291-1325. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.124.001117. Pharmacol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39013601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-species comparative hippocampal transcriptomics in Alzheimer's disease.iScience. 2023 Dec 7;27(1):108671. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108671. eCollection 2024 Jan 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38292167 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Cardiac Glycoside Exhibiting Favorable Brain Bioavailability and Potency for Reducing Levels of the Cellular Prion Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 26;23(23):14823. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314823. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anoop A, Ranganathan S, Das Dhaked B, Jha NN, Pratihar S, Ghosh S, Sahay S, Kumar S, Das S, Kombrabail M, Agarwal K, Jacob RS, Singru P, Bhaumik P, Padinhateeri R, Kumar A, Maji SK. Elucidating the role of disulfide bond on amyloid formation and fibril reversibility of somatostatin-14: relevance to its storage and secretion. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2014;289:16884–16903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548354. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai Y, Markham K, Chen F, Weerasekera R, Watts J, Horne P, Wakutani Y, Bagshaw R, Mathews PM, Fraser PE, Westaway D, St George-Hyslop P, Schmitt-Ulms G. The in vivo brain interactome of the amyloid precursor protein. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2008;7:15–34. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M700077-MCP200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barghorn S, Nimmrich V, Striebinger A, Krantz C, Keller P, Janson B, Bahr M, Schmidt M, Bitner RS, Harlan J, Barlow E, Ebert U, Hillen H. Globular amyloid beta-peptide oligomer - a homogenous and stable neuropathological protein in Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neurochemistry. 2005;95:834–847. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03407.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

