Subversion of RAB5-regulated autophagy by the intracellular pathogen Ehrlichia chaffeensis
- PMID: 28650718
- PMCID: PMC6748376
- DOI: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1332506
Subversion of RAB5-regulated autophagy by the intracellular pathogen Ehrlichia chaffeensis
Abstract
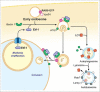
Intracellular pathogens often exploit RAB functions to establish a safe haven in which to survive and proliferate. Ehrlichia chaffeensis, an obligatory intracellular bacterium, resides in specialized membrane-bound inclusions that have early endosome-like characteristics, e.g., resident RAB5 GTPase and RAB5 effectors, including VPS34 (the catalytic subunit of class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase), but the inclusions lack late endosomal or lysosomal markers. Within inclusions, Ehrlichia obtains host-derived nutrients by inducing RAB5-regulated autophagy using Ehrlichia translocated factor-1 deployed by its type IV secretion system. This manipulation of RAB5 by a bacterial molecule offers a simple strategy for Ehrlichia to avoid destruction in lysosomes and obtain nutrients, membrane components, and a homeostatic intra-host-cell environment in which to grow.
Keywords: BECN1; Etf-1; RAB5; autophagy; class III PtdIns3K; endosome; infection; obligatory intracellular; type IV secretion.
Figures
References
-
- Pfeffer SR. Rab GTPases: Master regulators that establish the secretory and endocytic pathways. Mol Biol Cell 2017; 28:712-5; PMID:28292916; https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-10-0737 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhen Y, Stenmark H. Cellular functions of Rab GTPases at a glance. J Cell Sci 2015; 128:3171-6; PMID:26272922; https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.166074 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fratti RA, Chua J, Vergne I, Deretic V. Mycobacterium tuberculosis glycosylated phosphatidylinositol causes phagosome maturation arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003; 100:5437-42; PMID:12702770; https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0737613100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Puri RV, Reddy PV, Tyagi AK. Secreted acid phosphatase (SapM) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is indispensable for arresting phagosomal maturation and growth of the pathogen in guinea pig tissues. PloS One 2013; 8:e70514; PMID:23923000; https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070514 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Dominguez C, Madrazo-Toca F, Fernandez-Prieto L, Vandekerckhove J, Pareja E, Tobes R, Gomez-Lopez MT, Del Cerro-Vadillo E, Fresno M, Leyva-Cobián F, et al.. Characterization of a Listeria monocytogenes protein interfering with Rab5a. Traffic 2008; 9:325-37; PMID:18088303; https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00683.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
