A human endogenous retrovirus-derived gene that can contribute to oncogenesis by activating the ERK pathway and inducing migration and invasion
- PMID: 28651004
- PMCID: PMC5501692
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006451
A human endogenous retrovirus-derived gene that can contribute to oncogenesis by activating the ERK pathway and inducing migration and invasion
Abstract
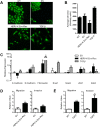
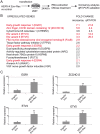
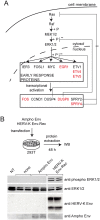
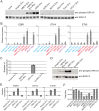
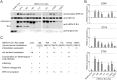
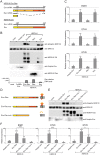
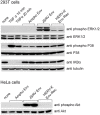
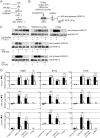
Endogenous retroviruses are cellular genes of retroviral origin captured by their host during the course of evolution and represent around 8% of the human genome. Although most are defective and transcriptionally silenced, some are still able to generate retroviral-like particles and proteins. Among these, the HERV-K(HML2) family is remarkable since its members have amplified relatively recently and many of them still have full length coding genes. Furthermore, they are induced in cancers, especially in melanoma, breast cancer and germ cell tumours, where viral particles, as well as the envelope protein (Env), can be detected. Here we show that HERV-K(HML2) Env per se has oncogenic properties. Its expression in a non-tumourigenic human breast epithelial cell line induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), often associated with tumour aggressiveness and metastasis. In our model, this is typified by key modifications in a set of molecular markers, changes in cell morphology and enhanced cell motility. Remarkably, microarrays performed in 293T cells reveal that HERV-K(HML2) Env is a strong inducer of several transcription factors, namely ETV4, ETV5 and EGR1, which are downstream effectors of the MAPK ERK1/2 and are associated with cellular transformation. We demonstrate that HERV-K(HML2) Env effectively activates the ERK1/2 pathway in our experimental setting and that this activation depends on the Env cytoplasmic tail. In addition, this phenomenon is very specific, being absent with every other retroviral Env tested, except for Jaagsiekte Sheep Retrovirus (JSRV) Env, which is already known to have transforming properties in vivo. Though HERV-K Env is not directly transforming by itself, the newly discovered properties of this protein may contribute to oncogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hofacre A, Fan H. Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus biology and oncogenesis. Viruses. 2010. December;2(12):2618–48. doi: 10.3390/v2122618 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caporale M, Cousens C, Centorame P, Pinoni C, De las Heras M, Palmarini M. Expression of the jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus envelope glycoprotein is sufficient to induce lung tumors in sheep. Journal of virology. 2006;80:8030–7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00474-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maeda N, Palmarini M, Murgia C, Fan H. Direct transformation of rodent fibroblasts by jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(8):4449–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.071547598 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen TE, Sherrill KJ, Crispell SM, Perrott MR, Carlson JO, DeMartini JC. The Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus envelope gene induces transformation of the avian fibroblast cell line DF-1 but does not require a conserved SH2 binding domain. J Gen Virol. 2002;83(Pt 11):2733–42. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-83-11-2733 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Duh FM, Kuzmin I, Angeloni D, Liu SL, Miller AD, et al. Hyaluronidase 2 negatively regulates RON receptor tyrosine kinase and mediates transformation of epithelial cells by Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(8):4580–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0837136100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

