Optimization of a murine and human tissue model to recapitulate dermal and pulmonary features of systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 28651005
- PMCID: PMC5484495
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179917
Optimization of a murine and human tissue model to recapitulate dermal and pulmonary features of systemic sclerosis
Abstract
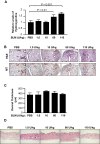
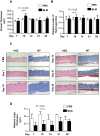
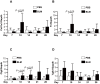
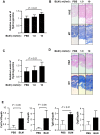
The murine bleomycin (BLM)-induced fibrosis model is the most widely used in systemic sclerosis (SSc) studies. It has been reported that systemic delivery of BLM via continuous diffusion from subcutaneously implanted osmotic minipumps can cause fibrosis of the skin, lungs, and other internal organs. However, the mouse strain, dosage of BLM, administration period, and additional important features differ from one report to the next. In this study, by employing the pump model in C57BL/6J mice, we show a dose-dependent increase in lung fibrosis by day 28 and a transient increase in dermal thickness. Dermal thickness and the level of collagen in skin treated with high-dose BLM was significantly higher than in skin treated with low dose BLM or vehicle. A reduction in the thickness of the adipose layer was noted in both high and low dose groups at earlier time points suggesting that the loss of the fat layer precedes the onset of fibrosis. High-dose BLM also induced dermal fibrosis and increased expression of fibrosis-associated genes ex vivo in human skin, thus confirming and extending the in vivo findings, and demonstrating that a human organ culture model can be used to assess the effect of BLM on skin. In summary, our findings suggest that the BLM pump model is an attractive model to analyze the underlying mechanisms of fibrosis and test the efficacy of potential therapies. However, the choice of mouse strain, duration of BLM administration and dose must be carefully considered when using this model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Almeida I, Faria R, Vita P, Vasconcelos C. Systemic sclerosis refractory disease: from the skin to the heart. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10(11):693–701. Epub 2011/05/07. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2011.04.025 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang IV, Schwartz DA. Epigenetics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Transl Res. 2015;165(1):48–60. Epub 2014/03/31. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.03.011 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4182166. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wynn TA. Common and unique mechanisms regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(3):524–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI31487 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC1804380. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kalluri R, Sukhatme VP. Fibrosis and angiogenesis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2000;9(4):413–8. . - PubMed
-
- Steen VD, Medsger TA. Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972–2002. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(7):940–4. Epub 2007/02/28. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.066068 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC1955114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

