Clinicopathological characteristics of extremely young Korean multiple myeloma patients: therapeutic implications
- PMID: 28651310
- PMCID: PMC5511945
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2016.256
Clinicopathological characteristics of extremely young Korean multiple myeloma patients: therapeutic implications
Abstract
Background/aims: Although multiple myeloma (MM) is typically a disease of the elderly, a certain subset of extremely young patients exists. It is necessary to establish clinicopathological characteristics for this population.
Methods: We reviewed the medical records of MM patients whose age was 40 years or younger at diagnosis.
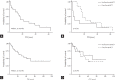
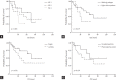
Results: A total of 32 patients were analyzed (male to female ratio 19:13, median age 37 years). According to International Staging System, 29%, 48%, and 16% were in stage I, II, and III, respectively. Light chain myeloma accounted for 30%. Clinically significant anemia, hypercalcemia, azotemia, and hypoalbuminemia were present in 29%, 28%, 13%, and 28%, respectively. Three or more lytic bone lesions were detected in 45% of the patients, whereas 13% had no lytic bone lesions. Regarding treatment, 79% of patients received autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. After a median follow-up duration of 64 months, the 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were 84%, 62%, and 54%, respectively. The median OS was 61 months for the entire cohort.
Conclusions: In our study, MM patients aged 40 years or younger at diagnosis showed no superior survival compared to those of the moderately elderly patients based on historical data.
Keywords: Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Multiple myeloma; Treatment outcome; Young adult.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical features and survival outcomes in patients with multiple myeloma: analysis of web-based data from the Korean Myeloma Registry.Acta Haematol. 2009;122(4):200-10. doi: 10.1159/000253027. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Acta Haematol. 2009. PMID: 19887776
-
Factors affecting outcome of patients with multiple myeloma.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2014 Jul-Sep;26(3):376-9. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2014. PMID: 25671952
-
Prolonged survival with a longer duration of maintenance lenalidomide after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma.Cancer. 2016 Dec 15;122(24):3831-3837. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30366. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27680710 Free PMC article.
-
The role of high-dose chemotherapy in the treatment of multiple myeloma: a controversy.Ann Oncol. 2000;11 Suppl 1:55-8. Ann Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10707780 Review.
-
Treatment of multiple myeloma.Haematologica. 1999 Jan;84(1):36-58. Haematologica. 1999. PMID: 10091392 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple myeloma in the young: insights on prognosis, clinical features and treatment outcome derived from nationwide German registry data and a nested multicenter sample.Haematologica. 2024 Nov 1;109(11):3795-3799. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285630. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 39021220 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multiple Myeloma in Young Adults: A Single Centre Real World Experience.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2021 Oct;37(4):679-683. doi: 10.1007/s12288-021-01410-3. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2021. PMID: 34690457 Free PMC article.
-
Young age and autologous stem cell transplantation are associated with improved survival in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2021 Jul-Sep;43(3):295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.htct.2020.06.014. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2021. PMID: 32912838 Free PMC article.
-
Young Myeloma Patients: A Systematic Review of Manifestations and Outcomes.Curr Oncol. 2023 May 23;30(6):5214-5226. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30060396. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37366879 Free PMC article.
-
Disease Characteristics and Outcomes of 493 Young Myeloma Patients Treated With Modern Therapies: A Canadian Myeloma Research Group Database Study.Cancer Med. 2024 Nov;13(21):e70332. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70332. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39499045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergsagel D. The incidence and epidemiology of plasma cell neoplasms. Stem Cells. 1995;13 Suppl 2:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Corso A, Klersy C, Lazzarino M, Bernasconi C. Multiple myeloma in younger patients: the role of age as prognostic factor. Ann Hematol. 1998;76:67–72. - PubMed
-
- Blade J, Kyle RA. Multiple myeloma in young patients: clinical presentation and treatment approach. Leuk Lymphoma. 1998;30:493–501. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Pouli A, Anagnostopoulos A, et al. Macrofocal multiple myeloma in young patients: a distinct entity with favorable prognosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006;47:1553–1556. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
