Uterine responses to early pre-attachment embryos in the domestic dog and comparisons with other domestic animal species
- PMID: 28651344
- PMCID: PMC5803782
- DOI: 10.1093/biolre/iox063
Uterine responses to early pre-attachment embryos in the domestic dog and comparisons with other domestic animal species
Abstract
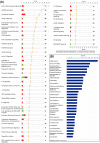
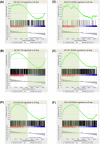
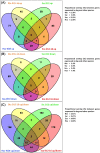
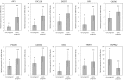
In the dog, there is no luteolysis in the absence of pregnancy. Thus, this species lacks any anti-luteolytic endocrine signal as found in other species that modulate uterine function during the critical period of pregnancy establishment. Nevertheless, in the dog an embryo-maternal communication must occur in order to prevent rejection of embryos. Based on this hypothesis, we performed microarray analysis of canine uterine samples collected during pre-attachment phase (days 10-12) and in corresponding non-pregnant controls, in order to elucidate the embryo attachment signal. An additional goal was to identify differences in uterine responses to pre-attachment embryos between dogs and other mammalian species exhibiting different reproductive patterns with regard to luteolysis, implantation, and preparation for placentation. Therefore, the canine microarray data were compared with gene sets from pigs, cattle, horses, and humans. We found 412 genes differentially regulated between the two experimental groups. The functional terms most strongly enriched in response to pre-attachment embryos related to extracellular matrix function and remodeling, and to immune and inflammatory responses. Several candidate genes were validated by semi-quantitative PCR. When compared with other species, best matches were found with human and equine counterparts. Especially for the pig, the majority of overlapping genes showed opposite expression patterns. Interestingly, 1926 genes did not pair with any of the other gene sets. Using a microarray approach, we report the uterine changes in the dog driven by the presence of embryos and compare these results with datasets from other mammalian species, finding common-, contrary-, and exclusively canine-regulated genes.
Keywords: dog (Canis lupus familiaris); early pregnancy; embryo-maternal communication.
© The Authors 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for the Study of Reproduction.
Figures


References
-
- Paria BC, Reese J, Das SK, Dey SK. Deciphering the cross-talk of implantation: advances and challenges. Science 2002; 296:2185–2188. - PubMed
-
- Bazer FW. History of maternal recognition of pregnancy. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 2015; 216:5–25. - PubMed
-
- Niswender GD, Juengel JL, Silva PJ, Rollyson MK, McIntush EW. Mechanisms controlling the function and life span of the corpus luteum. Physiol Rev 2000; 80:1–29. - PubMed
-
- Short RV. Implantation and the maternal recognition of pregnancy. In: O’Connor M, Wolstenholme GEW (eds.), Ciba Foundation Symposium - Foetal Autonomy. Churchill, London: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; 1969:2–31.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

